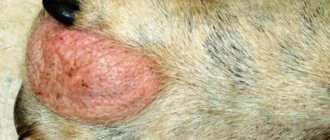
Bacterial pododermatitis or pyoderma in dogs is a deep microbial infection that affects the toes. This disease is otherwise called interdigital pyoderma.
It is worth noting that this pathology occurs secondary to various etiological factors. However, in some cases, primary development of pododermatitis is observed. The breed's tendency is typical for the English bulldog, Great Dane, English bull terrier, boxer, German shepherd, etc.
general information
The owner of a cheerful, cheerful and active pet suddenly notices that the dog has stopped loving to walk. During walks he limps heavily, and at home he constantly licks his paws. An external examination shows that the pads and interdigital spaces are inflamed, reddened, and the hair around them is moist. If this is the case, there is every reason to assume that the dog has pododermatitis.
Bulldogs, German shepherds, Pekingese, Shar Peis, Chow Chows, Labradors, Mastiffs, Boxers, and Bull Terriers are especially susceptible to the disease. Pododermatitis is especially difficult in overweight dogs.
Yersiniosis
Transmission routes
The natural reservoir of Yersinia are wild and domestic animals, mainly rodents (mice, rats), as well as pigs, less often dogs, cats, cows, etc. Infection mainly occurs through food products contaminated with animal excrement. Infection is possible when drinking water from open reservoirs. Due to the persistence of the pathogen in the external environment, contamination of products (milk, butter, vegetables, fruits, etc.) stored in refrigerators and vegetable stores is common.
Clinical signs
In the development of yersinia infection, several phases are distinguished: enteral, regional, generalized and the phase of secondary focal manifestations. The last two phases are associated with bacteremia, hematogenous foci of inflammation and septicemia.
There are intestinal, abdominal, septic, articular and icteric forms. In the septic form, multiple manifestations of septicemia are described: abscess pneumonia, purulent arthritis, osteomyelitis, etc. Arthritis develops during the period of a detailed clinical picture of the disease - from several days to 2 weeks or more from its onset. Most often, a few joints are affected (oligoarthritis).
Characterized by swelling of the joints, pain of varying intensity, skin hyperemia, limited function and other signs of inflammation. The lesions are often asymmetrical. The duration of arthritis symptoms ranges from several days to several weeks, and even months if the course is prolonged. Recovery, as a rule, occurs without residual effects, but relapses are possible.
Diagnostic features
Cytological examination. The synovial fluid is inflammatory in nature with high cytosis and a predominance of neutrophils.
Bacteriological culture of synovium and synovial membrane: The pathogen, as a rule, is not detected.
X-ray changes in the joints at the initial stage are not detected
The results of bacteriological analysis of feces, urine, and mucus from the throat for the presence of Yersinia during the first 2-3 weeks of the disease are decisive. The diagnosis is subsequently confirmed by the detection of yersinia antibodies in the blood serum in titers of 1:200 or higher and their decrease over time with repeated testing. The diagnosis of yersinia arthritis is based on the identification of yersiniosis in a patient.
Causes
The disease occurs against the background of a weakening of the body's protective functions. Low immunity is unable to cope with pathogenic microflora, which is always present in a certain amount on the animal’s skin, so it begins to actively multiply.
It is very important to diagnose the disease on time. Only in this case can you fight not the consequence, but the true cause of pododermatitis.
Main reasons:
- parasitic infections, the presence of mites or helminths (scabies, soil nematodes);
- fungal skin diseases;
- allergic contact dermatitis or general allergic reaction;
- autoimmune disorders (systemic lupus erythematosus, erythema, vasculitis);
- hormonal disorders, diseases of the endocrine system;
- oncological diseases.
In addition to illness, lameness and painful sensations in the paws can be caused by:
- injuries, cracks;
- sharp objects stuck into the skin while walking;
- irritation from prolonged contact with asphalt or other surfaces.
Clinical picture and photographs of pododermatitis in dogs
The symptoms of the disease depend on what caused the inflammation. For example, if it is an infection, the pads will turn red and may become swollen. The temperature is locally elevated. Pustules and ulcers are noticeable, sometimes oozing pus is visible. If the disease is detected in a serious form, you may notice baldness of the dog's limbs.
With an allergic cause, the appearance of the skin is similar to the previous option, but the temperature does not increase. A significant difference is itching: the animal constantly licks and scratches its limbs. As a result of constant licking, the hair begins to fall out. The one that remains is constantly wet and sticky.
Important: If an allergy disease arises from contact with an allergen, only the pads will be inflamed, whereas in the case of a general allergy, pathology is observed on the face, ears, and body.
It’s bad if pododermatitis is caused by an autoimmune disease . In this case, ulcers and scabs appear throughout the body. The skin becomes dense, dark, and prone to allergies. This type of disease is not easy to detect because many complex tests are required.
If pododermatitis is caused by cancer, its manifestations depend on the type of tumor. Indurations, ulcers and neoplasms may occur. If you suspect a cancerous tumor, you should immediately consult a specialist. With every day of delay, the risk of death for the animal increases.
Characteristic symptoms
Pododermatitis in dogs can be caused by diseases of different nature. They determine the main symptoms of the disease.
An infectious or fungal disease can manifest itself as inflammation, redness of the pads and interdigital spaces, and the formation of pustular lesions and ulcers. Temperatures in this area are likely to rise slightly.
In case of a contact allergic reaction that occurs after walking on asphalt sprinkled with salt or a chemical reagent, severe itching is added to the inflammation and redness, which greatly worries the dog. The hair on the paws may fall out.
A general allergic reaction manifests itself with the same symptoms, but they affect not only the paws, but also other parts of the body (face, ears).
Autoimmune pododermatitis is the most difficult form of the disease to diagnose. To recognize it, you will need to conduct a lot of examinations. Symptoms are the same as for other forms of the disease. In addition, the skin on the paw pads may darken and thicken.
Swelling and redness of the skin in the interdigital spaces indicate hormonal and endocrine disorders.
Oncological pododermatitis is the most dangerous type. It is characterized by the appearance of compactions, neoplasms, and ulcers.
Clinical picture and photographs of pododermatitis in dogs
The symptoms of the disease depend on what caused the inflammation. For example, if it is an infection, the pads will turn red and may become swollen. The temperature is locally elevated. Pustules and ulcers are noticeable, sometimes oozing pus is visible. If the disease is detected in a serious form, you may notice baldness of the dog's limbs.
With an allergic cause, the appearance of the skin is similar to the previous option, but the temperature does not increase. A significant difference is itching: the animal constantly licks and scratches its limbs. As a result of constant licking, the hair begins to fall out. The one that remains is constantly wet and sticky.
If an allergy disease arises from contact with an allergen, only the pads will be inflamed, whereas in the case of a general allergy, pathology is observed on the face, ears, and body.
It’s bad if pododermatitis is caused by an autoimmune disease
. In this case, ulcers and scabs appear throughout the body. The skin becomes dense, dark, and prone to allergies. This type of disease is not easy to detect because many complex tests are required.
If pododermatitis is caused by cancer, its manifestations depend on the type of tumor. Indurations, ulcers and neoplasms may occur. If you suspect a cancerous tumor, you should immediately consult a specialist. With every day of delay, the risk of death for the animal increases.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, you must contact a veterinarian. While collecting anamnesis, he will ask the owner to answer the following questions:
- How long ago did the illness begin?
- Is it chronic or seasonal?
- Could it be related to changes in lifestyle or diet?
- Has there been contact with other animals?
- Have you tried to treat your dog at home?
The diagnosis is made based on the owner's responses and the results of a comprehensive examination. It should include cytological studies, biopsy, antibiotic sensitivity tests, allergy tests, blood and urine tests.
Possible postoperative complications
Veterinarians identify the following possible postoperative complications:
- Infection of a postoperative wound. It happens both in case of gross violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during the operation, and in case of failure to follow the veterinarian’s recommendations (wearing a surgical collar, changing bandages, etc.).
- A frequent complication of surgery to remove a malignant tumor is the formation of metastases. It is most often impossible to predict and prevent this. However, it is precisely because of the risk of metastasis in these cases that the animal is prescribed intensive chemotherapy.
Treatment options
There is no general scheme for treating pododermatitis in dogs. In each case, an individual approach is important.
Treatment tactics depend on the diagnostic results. The goal is to combat the causative agent of the underlying disease.
Based on the examination results, the following treatment may be prescribed:
- treatment of affected areas with antiseptic agents;
- antibacterial therapy;
- surgical intervention;
- antifungal therapy;
- antihistamines;
- dietary nutrition;
- lifelong maintenance therapy.
The choice of treatment method depends on what type of pododermatitis (type of inflammation) you are experiencing.
Aseptic pododermatitis
It manifests itself as a persistent inflammatory process and pain syndrome. There is no purulent tissue damage. The main treatment is thorough treatment with antiseptic drugs. It is carried out by the owner himself.
Purulent pododermatitis
A disease complicated by purulent tissue infection. This species has pronounced symptoms: the dog groans in pain and the body temperature rises. Antimicrobial therapy is indicated for the treatment of purulent pododermatitis. And in severe cases, surgery may be required. The doctor opens the abscesses and rinses the cavities with an antiseptic and antibiotics.
Surgical removal of the tumor
In many cases, surgical removal of the tumor is more effective. If the “bump” is benign, the operation is extremely simple. It is simply cut out and the wound is sutured. If cancer is suspected, the tumor is excised with as much tissue as possible (to minimize the risk of metastases). When a bone is damaged, it is often necessary to resort to amputation of the affected limb. In the latter case, treatment must be combined with chemotherapy.
If the swelling is a consequence of a broken claw, the remainder is excised and the remaining wound is cleaned. In advanced cases, amputation of the entire finger is recommended.
Prevention measures
The best prevention is careful adherence to the rules of keeping the animal - paw hygiene, organization of a healthy lifestyle, regular visits to the veterinarian.
To comply with these rules you must:
- promptly shorten overgrown claws;
- trim the hair growing between the toes and around the pillows;
- regularly deworm and destroy skin parasites;
- keep the dog clean;
- wash paws after walks.
Be attentive to your pet. The sooner you notice symptoms and take action, the sooner recovery will occur.
Preventive measures
You need to keep an eye on your pet. After a walk, the paws should be washed and disinfected, and the hair between the toes should be trimmed.
- You need to watch what your dog eats. Nutrition should be complete and balanced.
- If your four-legged animal is kept in a kennel, you should clean it regularly.
- It is important to pay attention to any changes in behavior and, if necessary, take your pet to the clinic.
- If the cause of the disease is an allergen, it should be eliminated.
The therapy must be correct. Medicines are prescribed by a doctor, but dosages should not be exceeded. If your pet has an allergy, you should inform your veterinarian.
- Seven Signs and Remedies for Getting Rid of Fleas in Dogs
- Thyroid dysfunction in dogs (hypothyroidism)
- The American Cocker Spaniel is an adroit hunter and loyal friend.
- How to recognize signs of dog poisoning from rat poisons
Fungal diseases leading to rotting of the paws of a pet
The most common problem that dog owners come to the veterinary clinic with is dermatophyses or fungus , and a dog of any age and living in any living conditions can become infected with the fungus. It is practically impossible to completely protect your pet from the appearance of fungus, but it is possible to use effective treatment methods thanks to a large number of modern drugs.
The fungus can appear in a dog’s body when interacting with already infected individuals, or simply by walking on the grass on which the pathogen is located. Even the owner himself can bring fungus on the sole of his own shoes. One of the reasons that will serve as a catalyst for the development of fungus is the dog’s low level of immunity, which requires constant monitoring of the condition of your pet and the introduction of a sufficient amount of vitamins into the diet.