Sometimes dog breeders encounter problems with their pets such as coughing. Dogs, like people, cough for a variety of reasons. A dog’s cough can be foamy, dry or wet, whistling or occurring when lying down, in a certain season, and so on. It is important to understand why a dog coughs and vomits white foam , and for this you need to become familiar with the types of coughs and their origins. Remember that it is important to contact a veterinarian without delaying the visit.
Etiology of the phenomenon
The most common reasons:
- Entry of a foreign object;
- Neck injuries (for example, when using a collar that is too narrow);
- Heart diseases.
If a dog swallows a toy or chokes on leftover food, these objects clog the airways. As a result, this leads to the development of an inflammatory process, which is often accompanied by the appearance of sputum.
Some animals have an abnormal structure of the respiratory system from birth. The most striking example is the collapse of the trachea experienced by owners of small breeds. In pathology, the cough is grunting, resulting from the accumulation of air and fluid in the pleural cavity.
Take the Attention Test! Find 10 differences! (click right here!)
Find the answer Are you bothered by some problem or question? Enter “Breed” or “Name of the problem” into the form, press Enter and you will find out everything about the issue that interests you.
A dangerous cause of coughing and vomiting will be pneumonia or adenovirus, the latter disease is transmitted by airborne droplets from an infected individual. Cough is caused by viral diseases, for example, tracheobronchitis (“enclosure” cough). A banal infection of the body with worms causes coughing in dogs.
More often, the dog copes with illnesses on its own, but with a weakened immune system, it will not be possible to recover on its own. If shortness of breath, loss of appetite, or lethargy occurs, contact a veterinarian.
Types of cough in dogs
First, let's figure out what a cough is and why it occurs.
Coughing is a protective reflex with the help of which foreign substances/objects are removed from the respiratory system.
If we consider this reflex at the microscopic level, then this is the movement of the villi of the ciliated epithelium. The villi continuously move mucus towards the larynx, and when a foreign substance enters with inhaled air, severe irritation occurs, which causes a protective reflex.
Cough in animals is divided according to the same principle as in humans. By the presence of sputum, the nature of the course, the severity of the manifestation and its frequency. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Presence/absence of sputum
- wet (accompanied by mucus);
- dry (no mucus is produced).
Character of the current
- acute course (appears suddenly, pronounced);
- subacute course (develops gradually, clinical signs are more pronounced);
- chronic course (lasts a long time, more than 1 month).
Severity of manifestation
- minor (does not cause significant discomfort, manifests itself under heavy loads);
- strong (appears regularly, regardless of physical activity);
- paroxysmal (manifested by attacks).
Cough frequency
- rare;
- frequent.
An important condition for preventing diseases that cause coughing is good maintenance and proper balanced feeding.
Causes of mucus, foam or drool
Coughing in dogs is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms - the appearance of foam and mucus, which may indicate congenital anomalies or the development of viral or bacterial diseases.
Kennel cough
A cough is usually accompanied by the appearance of foam, which the dog regurgitates. It develops as a result of a viral infection, in difficult situations it is supplemented by a bacterial complication.
The first sign is the pet's heavy breathing, accompanied by a dry, prolonged cough. In the absence of therapy, vomiting appears, resembling white foam.
Pet owners of any age encounter this disease, but it usually affects young dogs under 2 years of age. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, so you can become infected anywhere through contact with a sick dog. The dog owner himself becomes the causative agent, bringing infectious agents from the street on clothes or shoes.
Therapy for this disease is complex and lengthy. This is due to the fact that viruses are constantly changing and mutating.
Pathology is usually caused by groups of viruses - reovirus and adenovirus. Often the disease is complicated by the addition of bacteria. Only a doctor can prescribe treatment based on test results and diagnosis. Self-medication is dangerous - the owner’s wrong actions will harm the pet.
In puppies, pregnant and lactating
Most diseases occur in dogs with weakened immune systems. Puppies, pregnant bitches or dogs nursing offspring are at risk.
Proper care of your pet, proper nutrition, and the use of immunomodulators (medicines can only be prescribed by a veterinarian) will help avoid this problem.
Features of breeds
Every breed has breed-specific diseases. For example, the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel is prone to heart disease. Spitz, Pekingese, and Chihuahuas are often diagnosed with tracheal collapse. The main symptom of these pathologies is cough.
What to do during attacks
If the animal begins to choke, call a veterinarian immediately. While the specialist is on his way, they help their pet. First, the pharynx is examined for the presence of a foreign body. If a piece of food or a small toy is not stuck too deep, try to pull it out with tweezers, holding the pet tightly.
The animal’s pharynx is examined even in the presence of simple wheezing. This is one of the symptoms of a foreign object entering the respiratory tract.
If unpleasant signs are caused by other reasons, they do not take any measures on their own, do not give medication - this will only do harm, since treatment is prescribed by a doctor after an examination and study of the medical history.
Actions in case of suffocation
If the animal is choking and suffocating, the dog owner must use one of the special techniques. You also need to know the list of prohibited actions:
- Don't hit your dog on the back. This is an ineffective and dangerous method, due to which the choking object may fall deeper into the trachea, which will aggravate the situation. Animals of small breeds should not be hit on the back, because the thin spine is very easy to damage.
- Do not pour vegetable oil down your throat. It will not help the foreign object slip out, and the owner will lose valuable time saving the pet.
The main thing is not to panic, not to scream. This will worry the pet even more: it may not give in to help. You need to calm down, gently but firmly take your pet and take actions to help save his life:
- Use the gravity of the earth. The four-legged friend must be taken by the hind limbs and lifted slightly. Small rocks can even be lifted off the ground by holding them head down. To avoid damaging the spine, you should hold the dog by the neck. A large or medium-sized dog only needs to be lifted slightly. The foreign object should fall out of the throat on its own - if it does not sink deeply.
- The Heimlich maneuver, used for humans and animals. The pet is grabbed from the back at the waist. Then they find the place where the ribs end and the stomach is located. A folded fist is placed there, another hand is placed on top, then rhythmically squeezed upward. Due to the contraction of the esophagus and trachea, the object will pop out. Don't press too hard to avoid breaking the ribs. You need to be extremely careful with small breeds.
- Removing a foreign object manually. The dog's mouth is opened, it is firmly fixed and, illuminated with a flashlight, a foreign body is discovered. The next step is to remove it with tweezers or your fingers. The main task is not to injure the mucous membrane of the throat or palate.
If the dog has lost consciousness, resuscitation measures are carried out. They involve pressing on the chest in a certain rhythm: 15 rhythms per 1 breath. The rescued and calmed pet is taken to the veterinarian. Knowing first aid techniques can help save your pet's life.
After determining the cause
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the correct diagnosis. For each disease, its own therapeutic regimens have been developed:
- Viral disease. If present, the veterinarian will prescribe antitussives and expectorants, which are taken in parallel. It is recommended to purchase a humidifier to improve your pet's condition. During treatment, the sick dog is isolated from other animals, ensuring him peace. To prevent the development of viral diseases, they are vaccinated every year.
- Ingestion of a foreign object, in which coughing is accompanied by vomiting and convulsions. Most pets refuse food and behave lethargically. You can independently remove an object that has entered the respiratory tract if it is not too deep. In other cases, this work is entrusted to veterinarians - for the procedure, the dog is put under anesthesia, using special equipment to assist.
- Allergy. The cough is accompanied by sneezing and the appearance of a rash on the skin. Allergies often develop in spring and summer and may occur to foods. To prescribe treatment, tests are performed to identify the allergen, and antihistamines are prescribed.
- Helminths. Treatment medications are prescribed after the test results are deciphered. After completion of therapy, they are taken again to make sure there are no parasites.
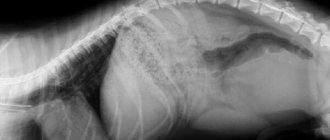
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. After examination and a CT scan and ultrasound of the heart, the dog will be prescribed medications, many of which need to be taken for a long time. Heart pathologies require regular check-ups with a veterinarian.
Treatment of diseases that are manifested by cough and vomiting with white foam
Treatment of a disease accompanied by coughing and “empty” vomiting is prescribed individually and only after the dog has been accurately diagnosed. Depending on what kind of disease is detected in the pet, one or another method of therapy is chosen.
Important! Antitussive and antiemetic drugs should absolutely not be given to a dog without a prescription from a veterinarian.
The general principles are:
| A type of illness accompanied by coughing and vomiting | Prescribed drugs |
| Viral infection | There is no specific treatment, so symptomatic medications are used - expectorants, antispasmodics, immunomodulators, immunoglobulins |
| Bacterial infection | Antibiotics, antimicrobials |
| Helminth infection | Antihelminthics |
| Heart failure | Diuretics, cardiac glycosides, bronchodilators (expand the lumen in the bronchi), vasodilators (dilate blood vessels), drugs to improve cardiac function, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, drugs that lower blood pressure |
| Oncology | Antimetabolites, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, antitumor drugs |
| Allergy | Antihistamines, corticosteroids |
| Chemical poisoning | absorbents; drugs that coat the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus |
| Liver diseases | Hepatoprotectors |
| Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract | Antiemetics, analgesics, proton pump inhibitors, sometimes antibiotics and probiotics |
Prevention
There are no uniform measures to prevent cough - it depends on the main cause of this symptom. But there are general recommendations for strengthening the immune system, which will allow your pet to cope with the disease faster.
Recommendations:
- Proper care;
- Complete nutrition for your pet;
- Normal maintenance of the animal.
If you notice a cough, you should not immediately make an appointment at the veterinary clinic. It is worth observing the animal’s behavior for a couple of days. But if the pet’s condition does not improve, the temperature begins to rise, and other symptoms appear in addition to coughing, you should not hesitate, since these signs indicate serious problems with the dog’s health.
Care and feeding
To restore strength, the pet will need a temporary diet and care from the owner. Innovations in care are followed until recovery.
Gentle diet
After poisoning, it is recommended to avoid feeding for 1 day. This is necessary for complete cleansing of the body. The next day, you can give the dog his first complementary food of pureed chicken or turkey. Add some chopped zucchini or fresh herbs to the meat. In the first days, the diet should consist of puree and chicken broth. If you feel stable for more than two days, add slimy porridge with small pieces of well-cooked lean meat.
During treatment, exclude bones and dog treats. Stick to fractional meals. Reduce the usual portions and increase the number of feedings to 5-6 times a day. Use only freshly prepared food at room temperature.
More detailed recommendations depend on the diagnosis. In case of gastrointestinal diseases, the animal is transferred to veterinary food designed for animals with sensitive digestion and other features.
Drinking regime
With frequent vomiting attacks, the amount of fluid is limited. Drinking sweetened water through a syringe or licking ice cubes can help avoid dehydration. The liquid offered must be bottled, filtered or boiled. Change the bowl of water regularly to prevent bacteria from building up.
Conditions for recovery
The patient is prohibited from long walks outside and intense exercise. Walking time is reduced to 10 minutes. For small dogs, a home tray will be enough. If kept in an enclosure, temporarily move your pet home. To recover, he needs to be warm and comfortable. Prepare soft bedding for him in a quiet and comfortable place.
When the first improvements appear, do not stop taking your medications. The disappearance of symptoms does not guarantee a complete recovery, so follow your veterinarian's instructions.
Prepare before going to the vet
In the office, you may have to provide the veterinarian with all possible assistance (hold the animal while they take blood for analysis, give an injection, extinguish aggression, calm your voice, scratch its ears, stroke it). If you know that you are terrified of blood, IVs, or definitely cannot withstand the type of medical interventions, then perhaps you should ask a friend or relative for help.
Find a veterinary certificate, veterinary passport.
Take:
https://dog-care.ru/zdorove/bolezni/pochemu-kashlyaet-srygivaet.html
- Leash;
- Collar;
- Muzzle;
- Carrying;
- A pack of napkins;
- litter;
- Bowl, water (at the veterinarian's discretion)
Prepare answers to possible questions from the veterinarian:
- Are all vaccinations up to date on the animal?
- Pet’s behavior in recent days, appetite;
- His diet;
- What drugs and medicines did you give to the animal;
- Latest test data (if available).
It’s better to make an appointment in advance - you’ll save time and be able to calculate when you’ll have to take time off. This does not apply to life-threatening situations where you will have to take an animal to a veterinary clinic without an appointment.
Be affectionate with your pet, play, talk to him. You can take his favorite toy with you so that while you wait for your turn at the reception, you can distract your friend from the new environment.
Furry, feathered or scaly ones also need to be prepared. No matter how much you want to treat your little one with something tasty, remember: you need an empty stomach. Feeding is prohibited!
You can wash your animal without using detergents. But it is important not to touch your pet if there is nasal discharge, watery eyes, salivation (salivation), dandruff, scratching, rashes, skin scabs, loss of hair/feathers/scales, wounds and other external manifestations of a potential disease.
If the veterinarian has instructed, collect the animal’s urine in a sterile container, and pick up the feces with a stick (no blades of grass, specks, or debris). Transfer the feces into a sterile container. Send to the biochemical laboratory within 6 hours. The feces are examined for eggs of roundworms, pinworms, tapeworms, liver flukes, echinoccus, alvecoccus, pork tapeworm, bovine tapeworm, and gastrointestinal bleeding is detected.
At the veterinary hospital, the animal’s blood will be analyzed for antibodies to allergens, viruses, bacteria, and parasites.
Symptoms of illness
Any disease has characteristic features, according to which the veterinarian makes an accurate diagnosis. Dangerous to the health of the animal is a severe, constant cough, which is combined with the secretion of foam, saliva and is expectorant in nature. The pet sticks out its tongue and makes movements as if expelling a foreign object from its throat.
Most often, such a cough is a signal of some kind of illness or injury. The accompanying signs confirming the pathology include the following options:
- The pet burps, and at the same time a copious discharge of mucus from the nose or foam from the mouth begins.
- The animal begins to rapidly lose weight. There is practically no appetite.
- Activity decreases to almost zero. The pet is depressed, tries to hide, does not want to go for a walk.
- The dog breathes unevenly even with slight physical exertion.
- The four-legged wheezes heavily and sneezes frequently.
- The gums bleed and sores appear on them.
- The temperature rises, chills and trembling appear.
If these symptoms occur, you should be seriously concerned: most likely, the dog is getting sick. He needs to be taken to a veterinary hospital and tested.
Choosing a veterinary clinic
We determine the veterinary clinic where you plan to go. A big PR company doesn't promise quality. The price is explained by the huge amount of money invested in advertising and “signboarding” of the establishment.
It’s great if you can ask your friends about clinics where their pets were treated “humanely.” If you travel far from them, it may be worth sacrificing time for the health of your pet.
A few more tips on how to spot an unverified veterinary clinic:
- Refusal to provide certificates and licenses for veterinary activities.
- Strange and suspicious behavior of the veterinarian (inconsistency, flattery, attempts to intimidate, shouting).
- Prices are too low (compared to other organizations).
- Refusal to freely visit the veterinary clinic.
“We have a sanitary day”
Beware of scammers!
When you contact the veterinary clinic, you are informed: “we cannot accept you at this address, sanitary day/repair/inspection.” How much intelligence does a dispatcher have? The client is persuaded to have a veterinarian come to his home. The price does not change.
A veterinary clinic can exist purely nominally. And the invited “Aibolit” will not bear responsibility. There is a high probability of running into a person without a veterinary diploma or simply an unprofessional.
It is better to find time to visit the veterinary clinic on your own. This is safer for the animal.
Games on feelings
In real veterinary clinics there will be elements of “divorce”.
Veterinarians say that this is often determined by the client’s wallet. The greater the opportunity to pay for services and the more the owner worries about his pet, the more likely the animal will be prescribed additional immunostimulants, dietary supplements, water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins, and special food. There are cases when this is really necessary (pedigreed, show animals, weakened after a serious illness). But it will be good if you ask your veterinarian in detail about the need for each appointment. Find out in detail about the results of the examination and analysis of your pet’s condition. Be persistent. Do not give in to attempts to intimidate you, be consistent in your questions. Consult a specialist who does not work at this veterinary clinic. If it turns out that half of the prescriptions are prescribed to enrich the veterinarian’s pocket, and not for the health of the animal, feel free to leave. And do not forget to leave a negative review about the organization - other owners may also suffer.
How to find out the truth
Another possible way for veterinarians to make dishonest money is to conceal the diagnosis. Let's say a veterinarian discovers a malignant tumor in a cat. But if he says that the tumor is benign and treatable. A housewife who dotes on her pet will give money for already useless procedures, medications and surgical interventions.
The veterinarian may deliberately “downplay” the diagnosis in order to earn more money. If something doesn't add up, insist on clarification. There is no need to be intimidated by unfamiliar terms - take a short break and try to find information on the Internet.
You are free to leave (or threaten to do so) to another clinic at any time.
Make sure that the veterinary clinic is honest - get tested in an independent laboratory.
Justice
What to do if an animal was injured as a result of unprofessional actions of a veterinarian:
- Write an official complaint addressed to the head of the clinic.
- File a complaint with the city veterinary department.
- You can contact Rospotrebnadzor.
- Contact a lawyer for help
The Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” and Article 245 of the Criminal Code “Cruelty to Animals” are the grounds for considering claims regarding the work of veterinary clinics.
Saving
What to do if funds are limited and your pet needs medical care:
- Some procedures can be carried out independently. Giving a drug injection to a cat or dog is not difficult. Dressing uncomplicated wounds is also sufficient. Ask your veterinarian to teach you.
- How to properly give a pill to an animal: hide it in a lump of tightly rolled minced meat. If the animal bites through the decoy, you can crush the tablet and dissolve it in water, milk, liquid porridge, or food.
- If an animal has been prescribed a course of vitamins or some other non-medicinal but expensive drugs, it may be worth finding analogues at a lower price.
- There are various benefit programs in which you can participate. This could be, for example, sterilization, castration, or vaccination of an animal.
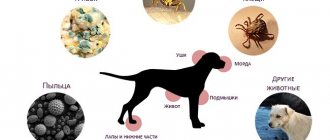
How dangerous is the condition and who is at risk?
Repeated vomiting attacks dehydrate and exhaust the body. If an animal refuses food and water, it may die from water-electrolyte imbalance. Small breeds and puppies are especially vulnerable.
Frequent drooling is typical for boxers and bulldogs, who are unable to retain drool inside the mouth due to the specific structure of the muzzle. Yorkies are also at risk. This breed has sensitive digestion, so their body often rejects new foods. The number of attacks can reach 1-2 times per week.
Spaniels, Great Danes, Labradors and Poodles are breeds prone to epileptic seizures. These animals require constant control from the owner.
Important points
- Refusal to vaccinate. This is dangerous for the animal and all those who will come into contact with it (people). Vaccination is a scientifically proven method of preventing many infectious diseases. Get your animal vaccinated by a trusted veterinarian (or with his approval yourself). It is important to get vaccinated against rabies - this is a fatal disease induced by the Rabies lyssavirus virus, which cannot be cured, but can be prevented.
- Anesthesia - inhalation, intravenous, anesthesia - epidural, conduction. They are necessary so that the animal does not suffer, to prevent painful shock. The veterinarian’s “hands on” are important here - both overdose and weak anesthesia lead to serious consequences (shock, poisoning, death) for the animal.
- Sterility, antiseptic. If you see that the veterinarian does not follow the rules of antiseptics (reuses disposable syringes, diapers, bandages, does not treat hands with antiseptic after contact with the previous animal), the best choice would be to contact another veterinarian.
- Important medicines:
- Antibiotics - amoxicillin, tilozil, trimethoprim, sulfadiazine, lincomycin, marbofloxacin;
- Antipyretics - paracetamol, salicylic acid preparations, antipyrine, butadione, amidopyrine;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - vedaprofen, choline salicylate cycloferon, aspirin;
- Anesthetics - novocaine, lidocaine, dicaine, trimecaine;
- Hemostatics - fibrinogen, thrombin, vikasol, phytomenadione, calcium chloride, etamsylate;
- Antiparasitic - praziquantel, aversectin, albendazole, ivermectin, fluralaner.
If you care what happens to your pet, you should not neglect appointments.
Don't let unverified veterinary clinics endanger your pet and profit from their owner's feelings! If you have time and desire, it is worth trying to achieve justice in case of violation of ethical or legal standards.