A healthy dog is what every owner wants. When an animal is sick, the first thing every owner notices is changes in the skin. Such changes can be caused by various diseases, both infectious and non-infectious etiologies. Changes in the skin can be independent or expressed as a symptom of a disease. One of these independent diseases is pyoderma. In this article we will figure out what it is, why it develops and how to prevent it.
Pyoderma in dogs
Skin is a very important organ of any living creature.
It protects it from mechanical damage and is responsible for preventing fluid loss. In addition, its extreme elasticity allows the owner to move easily. Clean and healthy skin does not allow fungi and bacteria to develop on its surface. The slightest erosion, boils or persistent itching may be signs that unwanted disturbances are occurring in the dog’s body. That is why you should pay increased attention to the condition of your pet’s skin and hair. You should immediately seek advice from a veterinary dermatologist before pyoderma or other serious disease develops into a deep form
Symptoms of pyoderma in dogs
Very often, the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria is facilitated by serious disorders of the immune system. There are superficial and deep pyoderma in dogs. In the first case, the epidermis and hair follicles are affected. In the second - even fat cells located under the layers of skin. This disease is caused by dangerous bacteria from the staphylococcus family.
Here are the main symptoms of pyoderma:
- rash;
- itching;
- redness of the skin;
- the appearance of ulcers;
- inflammation;
- unpleasant smell.
Causes of pyoderma in dogs
Acute weeping dermatitis quite often begins in humid and hot weather. The favorite habitat of staphylococci is the groin area, near the tail, near the loop of bitches, on the neck, dewlap. Interdigital pyoderma in dogs can be caused by splinters, thorns, tangles, damage to the skin while walking on sharp gravel, and chemical burns. This type of disease is also caused by fungal diseases or various parasites.
The fact is that long hair, injuries, allergies and poor dog care are the factors that contribute to the development of many skin diseases. A special feature of the structure of the coat of some dog breeds is numerous folds. These depressions are poorly ventilated, and saliva or urine accumulates on them, which also contributes to irritation and the appearance of staphylococci in this area. In animals with a short muzzle (Pekingese, bulldogs), in many cases the forehead and cheeks are affected, in some other breeds - near the upper lip. Quite often, staphylococci can be found on the skin of completely healthy animals. The fact is that good immune protection does not allow them to multiply here and harm the dog’s body. That is why during the treatment of pyoderma, the doctor always prescribes immunity-stimulating drugs and supplements to improve the condition of the hair.
Treatment of pyoderma in dogs
Around the lesions of the animal, the hair is cut off so that the pustules can be reached. These areas are treated with antiseptics - iodized alcohol, brilliant green, solutions of chlorhexidine bigluconate or potassium permanganate. Depending on the severity of the disease, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, ointments, vitamins, and immunostimulants.
Quite often, pet owners pay little attention to minor damage to the skin, frivolously believing that a slight itching or rash will go away without outside intervention. All this leads to the fact that a deep form of pyoderma occurs and it is no longer possible to do without the use of antibiotics
Treatment lasts several weeks or even months
It is important to continue it until complete recovery occurs. In no case should you stop taking medications ahead of time, especially if the dog has already developed a chronic form of pyoderma
The neglected process often even leads to death.
Degree of disease
During the course of the disease, there are 2 degrees of severity.
It is important to prevent the infection from developing and developing into a complicated disease.
Superficial pyoderma
The condition is characterized by the appearance of red spots on the animal’s body, itching, and peeling. The skin becomes inflamed and soon thickens and darkens. The infection does not penetrate beyond the stratum corneum. Superficial pyoderma often appears in dogs under one year of age. The puppy develops red blisters filled with exudate on his stomach. They can open on their own.
Deep
At this stage of the disease, the infection penetrates into the deep layers of the skin, causing the appearance of fistulas, weeping wounds, and an unpleasant odor.
Deep pyoderma requires immediate medical intervention.
Treatment of pyoderma in dogs
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the disease. If the infection penetrates very deeply, then it is quite difficult to cope with the pathology.
Most often, large animals are prescribed antibiotics.
. Your veterinarian may also prescribe immunotherapy.
The dog should be treated with antibiotics.
First aid
The skin is treated:
- Antibacterial ointment.
- Epicide.
- Potassium permanganate solution.
- Zelenka.
- Yodez.
First aid for a dog can be provided with Zelenka.
It is allowed to bathe your pet using antibacterial shampoo.
After bathing, the dog's skin should be treated with Terramycin, Septogel or Chlorhexidine. The use of these drugs helps disinfect the epidermis.
Use of antibiotics
A dog suffering from pyoderma is prescribed the following antibiotic drugs:
- amoxicillin;
- cephalexin;
- gentamicin;
- sulfamethox.
Amoxicillin is a drug prescribed for pyoderma.
Antibiotic therapy is prescribed only for severe damage to the skin.
Amoxicillin has the most powerful effect
. It does not cause any side effects. In rare cases, nausea occurs.
Gentamicin is prescribed as an ointment or spray.
Antibiotic treatment usually lasts several weeks or months.
Features of immunotherapy
To get rid of painful symptoms, the doctor prescribes medications that help improve immunity. Helvet is considered the best medicine. It can be used simultaneously with Evinton.
The drug Gamavit helps restore the skin.
Express help
To provide quick assistance to an animal, the following means are used:
- Maxidin.
- Vedinol.
- Streptomycin ointment.
These products help to quickly improve the condition of the skin.
You can use Venidol balm to treat your dog.
Maxidin can be prescribed intravenously. Injections are often accompanied by pain. To relieve it, it is recommended to use 0.3 ml of Novocaine or Lidocaine.
If you stop taking the prescribed medications, the symptoms of the disease will worsen. This can lead to relapse of the pathology and even death of the animal.
In order to prevent a decrease in immunity, you need to feed your dog special food. You should not give your animal inexpensive, low-quality types of feed. The type of food depends on the dog’s breed, its age and the characteristics of its body.
You need to feed your dog high-quality food.
It is very important to walk your pet every day. Walks should be long, but not too exhausting
If you plan to go outdoors, you need to worry about protecting your dog’s paws in advance.
Wounds and cracks need to be treated with special solutions that promote rapid healing and have a powerful disinfectant effect.
What to do and how to avoid?
Some people believe that pyoderma is an incurable disease. As a result, the process is left to chance, treatment is not carried out, which leads to a worsening of the condition. In some cases, it is possible that the disease will lead to the death of the animal.
In addition, if dogs show signs of a skin disease, there is no need to treat pyoderma from the first days. You will not be able to determine on your own what caused the pathology. Every owner should know that similar skin symptoms can be caused by distemper, demodicosis, and all kinds of dermatomycosis. Therefore, if your dog is bothered by pustular rashes, the first thing you should do is see a veterinarian. Only he, after a complete examination and exclusion of other pathologies, will be able to make a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
The treatment of pyoderma itself consists of treating erosions. To do this, the crusts are removed and treated with brilliant green. In addition, you can use an alcohol solution of iodine. It should be especially recalled that this disease develops as a result of decreased immunity or as a result of another disease. Therefore, first of all, you need to get rid of the causative pathology, as well as increase immunity. In this regard, immunomodulators and vitamin complexes are prescribed.
In addition, the underlying disease should be treated. Antibiotics or antiviral drugs may be used for this. In the event that a parasitic infection occurs, it is necessary to select an effective remedy in this case.
If the animal has long hair, it should be cut off. In short-haired dogs, this procedure may not be carried out. If there is an inflammatory process in the folds of the skin, you should treat the eczema as often as possible and prevent dampness in them.
At the same time, everyone knows perfectly well that treatment will not be required if prevention is carried out in time. In the first place is good nutrition. The diet should include a sufficient amount of vitamins and microelements. In addition, make sure that the dog does not develop infectious processes, that is, beware of hypothermia, contact with suspicious animals, and so on.
Prevention of allergic reactions is of considerable importance, since it can also lead to pyoderma. To do this, select shampoo and care products together with your veterinarian. In addition, prevent your pet from coming into contact with household chemicals and other hazardous substances.
Do not forget to carry out deworming and vaccination on time. If your animal is prone to skin diseases, pay more attention to caring for the skin and folds.
Preventive actions
To prevent your dog from getting pyoderma, it is necessary to carry out some preventive actions, which include:
- eating only high-quality and balanced food for animals
- regular pet care
- maximum protection of the dog from the slightest injury
- carry out timely treatment of chronic diseases
- prevent a decrease in the immune system.
Also, an excellent way to prevent the disease is vaccination, which can also be carried out at our veterinary emergency center “YA-VET”. The vaccine against pyoderma will contribute to the resistance of the animal’s body and strengthen its effects.
Symptoms of pyoderma
Pyoderma occurs in two forms:
- Superficial. It is accompanied by shallow lesions in the upper layers of the skin and slight loss of fur in the areas of infection.
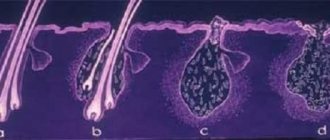
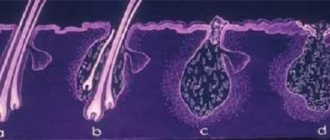
- Shallow pyoderma. All layers of the epidermis and hair follicles are damaged (pictured).
- Deep. In addition to the skin, the dog's muscle tissue and fat layer are damaged and may be accompanied by baldness.
General symptoms:
- lethargic state;
- loss of appetite;
- papules;
- itching;
- purulent discharge;
- dandruff;
- calluses;
- skin sensitivity.
Veterinarians distinguish two other types of pyoderma: acute dehydratic dermatitis (smelly small sores on the skin with discharge) and puppy pyoderma (pink blisters on the skin of puppies).
There are three clinical groups of pyoderma in dogs:
- diaper rash of the folds of the lips, vulva, tail, manifested by hot, weeping spots;
- superficial rash and follicle damage;
- deep pyoderma, accompanied by acne, damage to the interdigital gap.
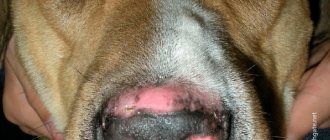
Diaper rash in dogs appears in the area of skin folds - on the sacrum, around the anus, on the muzzle, and on the ears. Such spots have a regular defined shape with erythematous or ulcerative inflammation. The affected area is hairless and covered with exudate or crusts.
Superficial pyoderma can develop throughout the body. Signs of deep purulent skin lesions are found on the back of the nose, chin, and paws.
Pyoderma, which is a sign of endocrine pathology, is accompanied by increased thirst, increased urination, general lethargy, and exhaustion. After eliminating the damage to the metabolic organs, the itching goes away along with the pustules
Itching and other signs of skin damage can indicate a variety of diseases, so it is important to conduct additional research:
- skin scraping is done to exclude scabies mites, demodicosis, microsporia;
- if these tests are unsuccessful, a bacterial culture is done to determine the bacterial infection and its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- allergic diagnostics are carried out - sensitivity is identified, various types of food are gradually excluded;
- laboratory diagnosis of immune and metabolic problems.
The disease can be suspected if a pustular rash forms on the dog’s thighs and abdomen. As a rule, it soon disappears if it is not a sign of a viral illness.
Pyoderma in dogs, the symptoms of which should certainly alert the pet owner, is a serious disease. You should always remember this.
The disease develops and the rash transforms into pyoderma, divided into two types:
- Staphylococcal - secondary - infection that aggravates all types of dermatitis.
A) Superficial form of pyoderma.
3-5 days after microbes enter the dog’s body, the animal begins to feel painful sensations and skin inflammation begins.
Blisters of various sizes, yellow and red, appear on the skin. If you pierce such a bubble, a liquid with an unpleasant odor will pour out of it.
The animal's fur begins to fall out.
B). Deep form of pyoderma.
As time passes, the blisters begin to expand, creating separate infected areas on the dog's body. They have the ability to explode at any point on the animal’s skin.
The body, head, and limbs are most often affected by manifestations of the disease, which, especially in short-haired breeds, are similar to urticaria.
Signs of deep pyoderma in dogs are:
- pain;
- skin redness;
- rash;
- the presence of an unpleasant odor;
- discharge on the skin consisting of blood and pus;
- edema;
- more noticeable hair loss than usual.
The area of the muzzle, chin, elbows, and interdigital areas is more prone to deep infections.
Interdigital dermatitis is characterized by redness of the skin.
Clinical signs that may indicate a problem:
- reddened skin between the toes and on the toes themselves, paw pads;
- thinning hair in affected areas;
- swelling of the limb and itching, which the dog tries to stop by licking;
- weeping wounds, fistulas and boils may appear between the fingers;
- Pain in the limbs when walking can result in limping.
Treatment and prevention of pyoderma in dogs
In this article I will talk about what pyoderma is in dogs. I will list the main causes of development and describe the symptoms of the disease. I’ll tell you how pyoderma in dogs is diagnosed and treated. I will give the rules of prevention.
Risk group, causes of development and routes of transmission
The term “pyoderma” refers to purulent lesions of the skin in dogs. Breeds with folded skin are more susceptible to this disease: Shar Pei, Pug, Bulldogs, Mastino Neapolitan, Bullmastiff, Chow Chow.
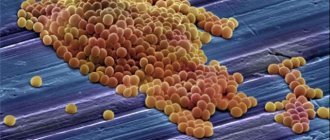
The main development factors are a sharp weakening of the immune system or skin trauma. The main cause of pyoderma is the active growth of staphylococci on the skin of the animal. The dog's immune system cannot cope with bacteria, and as a result, pustules, pustules, and ulcers form.
Symptoms of the disease
Veterinarians distinguish several types of pyoderma in dogs:
- Wet eczema. Weeping wounds appear on the animal's skin, which eventually become ulcers. This species is most often observed in furry pets during the warm season.
- Damage to skin folds. This look is typical for dogs whose skin is folded. The muzzle, cheeks, forehead, and paws are most often affected. In the folds, the skin becomes dry, inflamed, and smells unpleasant.
- Puppy pyoderma or impetigo. This type is observed in puppies aged 3-12 months. In this case, deeper skin layers are affected in areas of the body that are devoid of hair (usually on the stomach). A characteristic symptom is the formation of small blisters that burst and become covered with a yellow crust.
- Damage to the sebaceous glands. This type of pyoderma is also common in puppies. In this case, the lesion extends to the muzzle and chin. The disease goes away on its own after the pet reaches adulthood.
- Interdigital pyoderma. This type affects the skin between the dog's toes. The appearance of pustules can be caused by injury, a foreign body (thorn, splinter, etc.), tangles, or mites.
- Pyoderma calluses. This type is more often observed in large animals. Bacteria penetrate the calluses that form on the elbows or joints.
In the first case, all layers of the epidermis are affected; in severe cases, the subcutaneous fatty tissue is affected. With superficial pyoderma, the upper layer of skin and hair follicles are affected.
Common symptoms of pyoderma - damage to the dog's skin
Diagnosis and treatment of pyoderma in dogs
To make a diagnosis, the veterinarian examines the dog and its skin. Be sure to take smears from the affected areas and send them for cytological examination. The doctor also performs bacterial culture to determine the sensitivity of pathological bacteria to antibiotics.
Treatment of pyoderma is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Antibiotics. The drug is selected after bacterial culture. Most often, Amoxiclav, CeTilosin, Erythromycin, Lincomycin, Difloxacin, Clindamycin, etc. are prescribed for pyoderma. The course lasts at least 2 weeks; in advanced cases, treatment is extended to 6-12 weeks, but only under the supervision of a veterinarian. If there is no improvement, the drug must be changed.
- Bathing with medicated shampoo. An animal with pyoderma is washed 2-3 times a week with special shampoos containing chlorhexidine or benzoyl peroxide.
- Treatment for external parasites. This procedure is carried out even if ectoparasites have not been identified.
How to care for a sick dog
Treatment of pyoderma is a long process. Recovery may occur only several months after the start of therapy. The animal must be switched to a balanced diet.
Also, during treatment, increased stress is excluded, walks should be calm. All veterinarian instructions must be followed. Any deviation from the treatment regimen may lead to a worsening of the condition.
Only a veterinarian can treat the disease
Is pyoderma dangerous for people?
Everyone has staphylococci, which most often cause the development of the disease, but they begin to grow actively only when the immune system is sharply weakened.
Disease prevention
Prevention of pyoderma is as follows:
- Feeding the animal with balanced and complete food. It is better to choose ready-made industrial diets of high quality.
- Avoid contact of the animal with chemicals and toxic substances.
- Proper skin care (especially for pets with many folds).
- Avoiding hypothermia and skin injuries.
- Regularly treat your pet for external parasites.
Pyoderma is a non-contagious disease, the development of which is caused by staphylococci. It is treatable, but it needs to be started as early as possible. Following preventive measures will help reduce the risk of developing pyoderma in your dog.
Intertrigo
This is a type of pyoderma, a lesion of the dermis in the folds of the skin. Animals with overhanging skin that forms folds are susceptible to the disease. The infection worsens in hot weather and high humidity.
Which breeds are at risk?
All breeds of dogs that have loose skin with folds on the body: Shar-Pei, Mastino Neapolitan, Chihuahua, bulldog. Intertrigo occurs if the animal’s skin is not cared for regularly and basic rules of personal hygiene are not followed.
Development factors
If a dog has clumps of fur (tangles) or folds, then in wet weather or after an active walk the skin under them begins to swell. In warm and humid environments, staphylococci develop, which leads to infection.
If the animal's skin inside the folds is not regularly wiped and treated, this will also lead to the development of pyoderma.
What is pyoderma in dogs?
Pyoderma is a purulent lesion of the dog's skin.
Most often in veterinary practice, pyoderma occurs in dogs of the following breeds:
- bulldog;
- bullmastiff;
- Dalmatian;
- Doberman Pinscher;
- pug;
- Neapolitan Mastiff;li>
- German boxer;li>
- dachshund;
- Shar Pei.
This dislocation of pustules is the most dangerous. After all, at an early stage they may simply not be noticed.
Types of disease
There are two types of pyoderma disease - deep and superficial:
- with superficial pyoderma, purulent foci form on the outer layers of the skin;
- with a deep course, the focus of the purulent lesion gradually shifts under the thickness of the skin, penetrating into the muscle tissue.
Manifestation of the disease
At the very beginning, superficial pyoderma in dogs makes itself felt:
- the appearance of itching;
- redness of the skin;
- the formation of yellowish blisters filled with liquid.
A little later, these signs are supplemented by bald patches and an unpleasant odor that appears when the pet scratches the pustular formations.
If the disease is not treated, it will progress, and the areas of purulent lesions will expand. From superficial type pyoderma, the disease can transform into deep type pyoderma.
Depending on the lesion, pyoderma manifests itself as:
- hidradenitis (the source of inflammation is in the sweat glands);
- carbuncle (the infection is localized in the skin tissue, combining several hair follicles);
- folliculitis (inflammation affects the hair follicle);
- boil (purulent lesion of the hair follicle and adjacent tissues).
Regardless of the location of purulent lesions, pyoderma is always accompanied by:
- swelling;
- itching;
- pain;
- increased blood supply to tissues adjacent to the lesion;
- elevated temperature.
Such a manifestation of pyoderma as hidradenitis is accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Causes
The causative agent of the disease is opportunistic staphylococcus bacteria. These dangerous microorganisms can remain in the body of a healthy dog with strong immunity throughout the animal’s life, without harming it in any way.
But against the backdrop of unfavorable circumstances, staphylococci begin to act, affecting the tissues and organs of the dog with such ailments as bronchitis, osteomyelitis, and sepsis. Pyoderma is the most common skin disease caused by staphylococcus.
If we talk about infection mechanisms, there are several of them, among which the most likely are:
- contact and household;
- airborne;
- artificial (in the conditions of a veterinary clinic, in case of violation of sanitary and hygienic standards by staff);
- nutritional.
Through the alimentary (fecal-oral) route, a pet can become infected while walking, bumping into the excrement of other animals.
Staphylococci can also enter the pet’s body through contaminated equipment, dishes, water, food, and damaged areas of the skin or mucous membranes.
Often, while walking, a pet can injure its paw. Cracks and wounds become the target of attack by staphylococci (“our own” or from the external environment). If the body's resistance is low, microorganisms multiply, become more active and exhibit their pathogenic properties.
Inflammatory processes at the site of infection cause itching, which forces the dog to scratch the skin. At the same time, new cracks appear and the disease progresses.
Types of pathology
Pyoderma is distinguished by the area of its localization. The infection can occur in dogs of all breeds and ages.
Purulent, interdigital
The cause of the disease is often injuries, cuts, and sensitive skin. Foci of infection are localized between the toes, redness, itching, pain, suppuration appear, and wounds may bleed.
Mozolnaya
The cause of the disease is weakened immunity, damage to the upper layers of the skin, and disruption of the thyroid gland. The lesion manifests itself in the area of a large joint. The disease is typical for large dogs.
Superficial pruritic folliculitis
The cause of the pathology is seborrhea, high skin sensitivity.
The main symptom is debilitating itching, during which the animal itches all day long and the affected areas of the skin become bald. If your pet's immunity is strong, the disease may go away on its own.
Acute dyshidrotic dermatitis
The disease is characterized by the appearance of itchy, weeping wounds. The dog injures them by constantly scratching them. Treatment for this pathology is long and serious.
Diagnosis of pyoderma in dogs
To conduct a high-quality and complete diagnosis, the dog must be taken to a veterinary clinic for examination, since the diagnosis requires the use of special equipment. At the appointment, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts a full examination of the animal and the necessary instrumental and laboratory diagnostics. Taking an anamnesis is one of the most important steps to making a diagnosis: it is necessary to find out the conditions of keeping and feeding the dog that could trigger the occurrence of pyoderma.
When conducting diagnostics, the doctor makes superficial and deep scrapings from the skin to exclude parasitic skin mites, and also takes fingerprint smears, stains them and conducts a cytological examination under a microscope. To exclude dermatophytosis, it is mandatory to carry out LUM diagnostics using a Wood's lamp, wool microscopy and, if necessary, taking material from the skin for additional diagnostics in the laboratory.
Often it is necessary to carry out a skin culture to determine the microflora (bacteria living on the skin) and select an antibiotic.
In some cases, a skin biopsy is necessary to make a diagnosis.
FAQ
Is pyoderma contagious to humans?
Pyoderma can affect not only animals, but also humans. But this disease is not an infection, so you cannot get it from an animal.
Is pyoderma contagious to other dogs?
Just like for humans, the disease is not transmitted from dog to dog.
Can I bathe a dog with pyoderma?
Can. In some cases this is a necessary measure.
General information about pyoderma, causes
Pyoderma (pyoderma or pyodermitis) is a purulent lesion of the skin of dogs, provoked by the activity of pathogenic bacteria such as:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- pneumococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
This disease affects absolutely all breeds and ages of dogs, but there is some increased predisposition in Shar-Peis, Chow Chows, English and French bulldogs, Boxers, Neapolitan Mastinos, Chihuahuas and Bullmastiffs.
The development of the disease is closely related to the state of the immune system, so any pathology can provoke the development of purulent inflammation of the skin due to a decrease in the body’s overall immune defense. Bacteria that cause pyoderma (for example, staphylococcus) are classified as opportunistic. This means that they are constantly on the dog’s skin, and begin their destructive activity in favorable conditions.
If left untreated or improperly treated, pyoderma can become chronic, lasting for years and slowly poisoning the dog’s body.
Pyoderma occurs due to:
- long stay of the dog in an uncomfortable warm and humid environment;
- unbalanced diet or sudden change in diet;
- helminthic infestations;
- lack of physical activity or its excess, leading to chronic fatigue;
- skin damage (scratches, microcracks, cuts, wounds);
- improper skin hygiene or its complete absence;
- allergies.
- the appearance and prolonged treatment of burns on the paw pads after walking on hot asphalt, gravel or sand (with interdigital pyoderma);
- splinters or thorns getting into the soft tissue of the paws.
Mechanisms of infection:
- airborne;
- nutritional (with food);
- artificial (infection in a veterinary institution that does not monitor the sanitary and hygienic condition of places for receiving animals);
- contact-household.
The course of the disease is greatly influenced by the presence of:
- diabetes mellitus;
- exhaustion;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract, and especially with the intestines;
- pathologies of the hematopoietic and circulatory system;
- the presence of cutaneous blood-sucking parasites (ticks, fleas).
Development of the pathological process:
- 3-5 days after injuries appear on the animal’s body, pathogenic bacteria develop, causing itching and inflammation. During the scratching process, microorganisms are spread to healthy skin far from the source of inflammation.
- The appearance on the surface of the skin of small papules (rash nodules) with purulent contents (most often on the abdomen, near the genitals, on the face, skin folds).
- The transformation of papules into erosions that are very itchy (the blisters burst, the liquid flows out onto the surrounding tissues, infecting the nearest healthy areas with bacteria).
- Spread of the inflammatory focus due to injury to the skin during scratching and the introduction of bacteria into microtraumas.
- If treatment is untimely or incorrectly provided, superficial pyoderma very quickly turns into deep pyoderma, affecting the skin with the appearance of deep bleeding ulcers.
- Weeping erosions develop in the skin folds, and an unpleasant putrid odor appears.
- A similar process develops in the interdigital spaces.
If the skin lesion covers large areas, this leads to a deterioration in the dog’s general health and well-being. The products of purulent activity of microorganisms enter the bloodstream, causing general intoxication, which, in turn, leads to disruption of the functions of many internal organs and systems. First of all, the kidneys and liver are affected - the organs that are the very first to be included in the detoxification process.
Symptoms
The pathology is quite serious, so its general symptoms are highlighted, corresponding to all types of this disease, when they appear, immediate action must be taken:
- the dog shows indifference and absolute weakness;
- refuses food;
- the affected areas are itchy and painful;
- vesicles with purulent fluid inside or it pours out, forming erosions;
- Infected areas give off an unpleasant odor due to open purulent wounds.
Such symptoms are a reason to take your pet to the veterinarian in order to detect the presence of bacterial enzymes using bacterial culture. The disease can last for years, and if help is not provided in a timely manner, purulent formations will slowly poison the dog.
Causes of the disease
Pathogenic microorganisms that cause the disease are conditionally pathogenic, since they are constantly present on the skin of the animal. Their impact begins when certain conditions arise.
In most cases, the disease develops in animals with weakened immune systems or as a result of the dog receiving skin injuries.
Minor wounds, scratches, splinters or burns cause the development of interdigital pyoderma.
The disease develops as a result of exposure to unfavorable external factors, such as high humidity, infection with skin parasites that accumulate in the neck, groin, tail or chest.
Dogs with long hair are prone to pyoderma, which, if not properly cared for, becomes matted and becomes a site for the reproduction and development of pathogenic bacteria.
A dog can become ill as a result of a change in diet or a lack of nutrients in the food.
Also, the causes of damage are infection with intestinal parasites, allergic reactions, insufficient physical activity or heavy physical exertion.
Interdigital pyoderma can result from long walks on hot sand or small stones.
Treatment of pyoderma in dogs
Before starting drug treatment, it is necessary to remove hair from the entire affected area, and then treat the skin with epacid, iodine, and brilliant green.
It is important to know that treatment is prescribed individually by a specialist. If the infection penetrates deep into the skin, it will be very difficult to cure your pet.
It is necessary not only to take into account the factors that provoked the disease, but also to regularly destroy parasites.
Treatment mainly consists of several stages:
- Fighting bacteria that cause pyoderma.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Getting rid of pus.
- Relief of itching and healing of wounds.
To effectively combat microorganisms, it is necessary to carry out bacterial culture. This method determines the microbe that caused the development of pathology and its sensitivity to antibiotics. The selection of material for this test causes discomfort to animals, and the results will only be available in a few days. Therefore, sometimes analysis is done only for advanced forms of pyoderma.
Experts use antibiotics to fight bacteria. Their choice depends on the specific microorganism and its sensitivity to drugs. When prescribing an antibiotic, the doctor must take into account the condition of the animal, the sensitivity of the microorganism, and other diseases.
Today, Baytril is very popular for the treatment of pyoderma. Take it in a dosage corresponding to the weight of the animal. It is necessary to continue the course exactly as many times and in the quantity as prescribed by the doctor. Even if all the symptoms have disappeared, it is necessary to complete the course, since its unauthorized cancellation causes a relapse of inflammation.
To increase immunity, it is necessary to reconsider the animal’s load and its diet. During the entire recovery period, it is necessary to reduce training, walks should be calm.
Drugs that enhance immunity are used a few days after adjusting the diet and exercise. Based on the advanced stage of the disease, drugs from human placenta, Catozal, Fosprenil for dogs, vitreous humor and others can be prescribed.
Removal of pus is carried out simultaneously with healing of the skin. Sometimes surgery is required.
When treating pyoderma, the affected skin is treated with antibacterial solutions and ointments.
Healing inflammation refers to the work of treating rashes and the areas around them. Most often, aluspray and its analogues are used, which neutralize microbes on the surface of various types of wounds. When treating deep forms of pyoderma, the use of absorbable agents is required. They contain iodine, chlorophyllipt, and other antimicrobials.
In case of severe skin damage, it is necessary to alleviate the general condition of the dog. For example, if there is a lot of pus, toxic substances enter the blood. To neutralize them and avoid liver damage, karsil may be prescribed. If it is necessary to remove poisons and support the heart, cocarboxylase and riboxin are administered to the animal through a dropper.
Experts' forecasts
After a full course of therapy for uncomplicated pyoderma, doctors give a favorable prognosis. The disease can be completely cured in the initial stages.
Complications
In advanced forms, pyoderma is difficult to treat. An incomplete course of antibiotic therapy will lead to relapses and the search for new effective drugs.
After treatment, scars, bald patches, and uncharacteristic skin color may remain on the animal’s body. If pyoderma enters the chronic stage, periodic exacerbation is possible.
Causes of pyoderma
Typically, this disease can occur due to a number of the following reasons:
1. Weakening of the dog’s immune system.
An animal’s immune system may weaken due to a sudden change in living conditions, changes in diet, and motor functions.
For example, an animal lived in the house all the time, and then the owners sent it outside. Or, on the contrary, after a long stay on the street, the animal is sent to live indoors. Regarding changes in diet, this may be due to a sharp transition from eating fresh meat to dry food or meat waste.
When a dog is switched to dry food, the state of its immune system is sharply suppressed. Switching the dog from dry food to natural food has the same effect on the dog’s body. Normalization of all processes is possible only after 2 months, and full recovery after 4 months.
It is also important not to forget that the more the dog moves, the more it needs to eat. Therefore, when training an animal’s skills, it is necessary to increase the amount of the daily diet by 15-20%, and if there is an exhausting training or participation in various competitions, then the daily portion must be increased by 40%
Lack of exercise is also a fairly common cause of decreased immunity in dogs. This state of affairs is due to the fact that in the absence of movement, dust, various keratinized parts of the skin, as well as various types of secretions begin to accumulate in the dog’s fur.
The animal's skin cannot cope with cleaning the fur on its own, resulting in a favorable environment for various microbes.
2. The occurrence of various injuries (cuts, scratches).
3. Presence of ticks, worms and fleas.
Consequences
Pyoderma is a serious dermatological disease that does not go away without consequences for pets. After illness, hairless areas, scars, and scars remain on the skin.
The disease leaves a significant mark on the immune system, significantly weakening it. Therefore, after an illness, the animal is very susceptible to any negative impact on the body.
Since scars remain, this spoils the aesthetic appearance of the animal. Because of this, the owner will not be able to perform with the dog at shows.
Veterinarians often observe relapses.
The effectiveness of treating pyoderma with folk remedies has not been proven, and can only harm the animal.
Treatment
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a veterinarian. The use of potent drugs is required; folk remedies are not effective in this case.
First of all, the affected area of skin is shaved. Ointments are applied only with gloves.
Treatment with antiseptics
The affected area is washed under running water and laundry soap. Afterwards they are treated with brilliant green, iodine, and chlorhexidine.
Antibacterial ointments
Antipruritic, local wound-healing preparations with an antibiotic are applied to the animal's skin. Fucicort, Lorinden, Celestoderm are often prescribed.
Allergy medications
To reduce the intensity of itching and alleviate the pet’s condition, he is given allergy pills.
The following drugs are suitable: Apoquel, Execan, Allergostop, Purisan Vet.
Treatment for ectoparasites
In parallel with treatment, the animal is treated for fleas, ticks, and lice. The following products are chosen: Bars, Practitioner, Inspector, Advantix.
Strengthening the immune system
Treatment is accompanied by taking immunomodulating drugs. The following medications are prescribed for dogs: Cycloferon, Gamavit, Pyrogenaz.
Danger of disease
At your first appointment, you need to find out from the veterinarian whether pyoderma is contagious to humans. The doctor will explain that you cannot contact a sick animal without protective equipment.
The purulent contents of the ulcers, getting on the human skin, infect it.
Contagious form
If streptococci, staphylococci and mites (Demodex) are detected in the animal after examination, treatment is carried out only with disposable gloves. Afterwards, wash your hands with soap and wipe with chlorhexidine solution.
The dog is given a separate bedding, which is washed and treated with antibacterial drugs. All places in the house where the dog was are also washed with chlorine.
Symptoms of pyoderma in dogs
Most often, dog owners come to the clinic with complaints of itching, an unpleasant odor from the pet’s skin, redness and inflammation of the skin, and the appearance of purulent discharge on the skin. At the same time, the dog becomes nervous, restless, cannot find a place for itself, chews itself, some of them whine, squeal, and the owners complain that the dog is interfering with their sleep. During an examination at an appointment, the doctor usually detects papules, pustules, and epidermal collars. The skin is hyperemic, thickened, compacted, or in some places, on the contrary, softened and loose. You can almost always notice signs of mechanical damage to the skin, marks from scratching, active licking and gnawing. The skin is covered with a wet film, pus, or a dry crust. The coat is absent or becomes much thinner, which occurs as a result of scratching, gnawing, and rubbing against objects.
Signs of the disease
Pyoderma begins with simple itching, and later an unpleasant odor appears. The animal constantly itches, even at night, whines, squeals, and becomes nervous.
Over time, the affected area becomes covered with a rash, turns red, and purulent papules appear. The abscesses open and seals form in their place.
Deep pyoderma is characterized by local skin damage, the development of ulcers, erosions, crusts, and fistulas. In advanced cases, sepsis, fever, and fever are possible.