Many people know about ixodid ticks that carry piroplasmosis, but only a few know about their closest relatives (microscopic Demodex canis). These tiny parasites, whose length does not exceed 0.3 mm, cause demodicosis in dogs - a dangerous pathology, often complicated by secondary infection. A sick pet may die from exhaustion or sepsis, so it is very important not to lose sight of the first alarming symptoms.
What kind of disease is demodicosis in dogs?
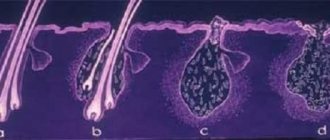
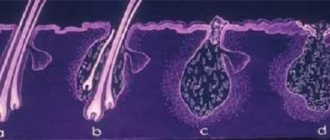
A parasite called Demodex canis lives in dogs' bodies on a permanent basis. It can be found in hair follicles, as well as the sebaceous and sweat glands located next to the hairs.
This endoparasite feeds on keratin, and its larvae feed on dead particles of the epidermis. After destroying the reserves inside one hair, the adult gnaws its way to another, that is, it is constantly in motion.
Despite such a strange cohabitation, discomfort in a four-legged pet appears only when demodex actively multiplies. Due to a sharp drop in immunity, the number of eggs laid and the number of parasites are rapidly increasing. The depth of the tunnels increases as ticks have to look for new food sources. Not only the skin, but also the internal organs are affected.
The vital activity of parasites provokes severe itching and intoxication. As a result of numerous scratches, the likelihood of a secondary infection increases.
Types of ticks
Any owner shudders at the thought of fleas or ticks crawling on their pet. Regular prevention protects dogs, but does not guarantee that the parasite will not live on your pet for some time.
] preventive agents [/anchor] openly say that ticks on a treated dog die within 48 hours. If the treatment was carried out more than a month ago or the parasite is resistant to the drug, prevention may not be effective. Recently, cases have become more frequent when live ticks and fleas resistant to fepronil are found on a treated dog.
The conclusion is obvious: even if you adhere to the rules of regular prevention, you need to know the types of ticks that can be found on a dog. You should not ignore daily inspections, especially during the period when parasites are active, that is, in early spring and autumn.
Main causes of manifestation
Most of the time, ticks are dormant. Their awakening is associated with a number of unfavorable factors that differ depending on the age of the animal.
In puppies - juvenile
Demodicosis in a puppy is called juvenile. Most often it is transmitted from a sick mother and is accompanied by zonal baldness around the eyes. Activation of the parasite occurs when:
- infection with viruses or bacteria;
- change of baby teeth;
- docking of ears or tail;
- introduction of the first vaccine.
All these situations complicate the independent fight against the pathogen, so children have to be treated with medications. All recovered animals must be sterilized to eliminate the possibility of transmitting the disease to future offspring.
In adults
Pets older than 1 year are more resistant to the pathogen, but they can also get sick. The sudden drop in their immunity is usually to blame for:
- helminthiases and infections (pyoderma, distemper);
- autoimmune disorders (lupus, pemphigus);
- oncology;
- allergies and dermatitis;
- hormonal imbalances (estrus, pregnancy, childbirth);
- surgery and long-term use of certain medications;
- mental disorders and stress;
- poor quality nutrition;
- hypothermia and unsuitable climatic conditions.
Those at risk include Afghan Hounds, Great Danes, Airedale Terriers, Shar-Peis, English Bulldogs, Alaskan Malamutes and Weimaraners. Representatives of these breeds require increased attention, since genetic predisposition has no prevention.
Contagiousness to animals and people
Demodex causes disease in both animals and humans. The only difference is the type of pathogen. Dog ticks are completely safe for humans, and human ticks are completely safe for dogs. Treatment of a sick pet can be carried out without special protective equipment.
If there are other four-legged animals in the house, be sure to isolate them from the infected person. Transmission of ticks is possible by touching parts of the body: paws, muzzles or ears. During treatment, it is recommended to regularly carry out wet cleaning with disinfectants and treat the sick dog’s personal belongings with acaricidal preparations.
Prevention
The basis of prevention is timely treatment and examination of the dog after each walk. For treatment against external parasites, the most effective modern means are tablets:
Nexgard
Bravecto
Simparica
Drops on the withers are also effective:
Advantix
Frontline
Collars are not very effective and can only be used in combination with other drugs.
Forms of pathology
Based on the area of damage, the pathology is divided into 2 forms:
- localized, characterized by the presence of no more than 4 lesions with a diameter of up to 2.5 cm;
- generalized, covering most of the body and often acting as a complication of the localized form.
The first form is curable in 90% of cases and very often goes away on its own. The second form is characterized by a more severe course with complications, so it is treated strictly with medication.
Notoedrosis
The disease is similar to sarcoptic mange and is caused by mites of the genus Notoedres.
Peculiarities
Notohedrosis mites parasitize the skin of dogs and form clusters (“nests”) inside the skin.
The causative agent of notohedrosis under a microscope. Photo: Babiy A.N. (Vetmedical)
Symptoms of notohedrosis
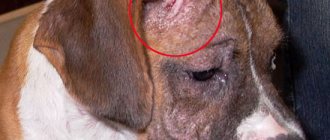
Characteristic nodules and blisters appear on the skin of a sick animal in affected areas (head, forehead, bridge of the nose, brow ridges and ears). The skin in these places becomes folded, and the hair may fall out. Then the ticks can spread to other parts of the body – the dog’s front (less often, back) paws. It is possible to develop purulent conjunctivitis and swelling of the eyelids and nasal passages. With notoedrosis, moderate itching is noted.
Symptoms of demodicosis in dogs with photos
Treatments for demodicosis in dogs depend on the symptoms. The photo clearly shows that the localized form can occur in different ways. It causes either severe dryness of the skin or ulceration.
Scaly
Accompanied by severe itching and redness of the skin. The most commonly affected areas are the ears, neck, eyelids, nose and interdigital spaces. Hairs deprived of keratin lose their strength and begin to fall out. The skin in these areas becomes rough and cracks.
Pustular
It develops independently or as a complication of scaly pathology. It is characterized by the appearance of dense nodules with purulent contents of black or red-brown color. Ripe abscesses burst, spraying foul-smelling exudate over neighboring areas. Spreading pus ulcerates healthy tissue and increases the affected area.
Generalized
Dried pus, mixed with blood and dead epidermis, turns into a scab. At this point, the disease becomes a generalized form, combining scaly and pustular symptoms. Due to the gradual damage to internal organs, the symptoms are complemented by a deterioration in appetite, weakness, vomiting, loss of coordination and convulsions.
Generalized pathology is very difficult to treat and has a poor prognosis. The chances of recovery decrease when a secondary infection occurs. In this case, the animal can be saved only in 50% of cases.
Sarcoptic mange (scabies)
The causative agent of sarcoptic mange, a mite of the genus Sarcoptes, is found both on the surface of the skin and in its thickness.
Peculiarities
Sarcoptic mange is highly contagious and is transmitted through direct contact with a sick animal or through care items (can also be transmitted to humans).
All dogs, without exception, are susceptible to the disease.
Symptoms of sarcoptic mange
In animals infected with sarcoptic mange, redness appears on the skin, scales and crusts form. Partial baldness is possible. Signs of the disease most often appear in the muzzle and elbow joints, but in case of severe damage they can spread throughout the body.
A dog with skin lesions due to sarcoptic mange. Photo: Judithsviews
The vital activity of sarcoptes causes severe itching, which may appear before other clinical signs.
Sarcoptic mange is also characterized by the so-called “ear-foot reflex” - touching the ear of a sick dog causes involuntary movements of the hind paw (an attempt to scratch the ear).
Severe infection of a dog with sarcoptic mange. Photo: Rosario Arredondo
In advanced cases, without timely provision of veterinary care to the dog, the entire skin is damaged, the animal is in a state of severe exhaustion, and a characteristic sour odor emanates from it.
Possible complications
The vital activity of parasites affects the functionality of the lymph nodes, kidneys, stomach, spleen and liver. Ticks block gaps in the capillaries, depriving internal organs of regular blood flow. Without timely treatment, this can be fatal.
Numerous tunnels gnawed by Demodex are filled with intercellular fluid. A moist and warm environment attracts bacteria, which easily make their way through wounds. Having avoided a collision with immune cells, a secondary infection aggravates the existing condition, provoking the transition of the disease to a generalized form.
Briefly about the main thing
- Ticks are dangerous pests that can carry diseases: piroplasmosis, borreliosis, ehrlichiosis and many others.
- At the first symptoms of illness after a bite, contact your veterinarian immediately. Even if it's just loss of appetite or depression.
- Inspect your pet yourself after each walk, especially the face, paws, belly and groin area.
- Follow the pest removal algorithm and don’t forget about your safety - wear gloves.
- You should not pour oil or other liquids on the tick so that “it will die and fall off on its own.” This does not work.
- After removal, be sure to take the little scoundrel to the laboratory.
- Treat your pet for external parasites in a timely manner.
Have we answered your question fully enough? If not, post your question in the comments below and our veterinarian will answer it.
Did you like the article? Share it with your friends on social media. networks. This will help them get useful information and support our project.
Diagnostic methods
To make a diagnosis, the veterinarian must take a medical history and examine the patient. Thanks to the owner's answers, he can find out the cause of the disease even before conducting research.
The symptoms caused by Demodex are similar to other mites, allergies, trichophytosis, microsporia, nutritional dystrophy and some infections. The type of pathogen is determined by scraping.
Scraping
Scraping is the main test for demodicosis in dogs, which is taken from the affected skin. To do this, it is pre-squeezed, provoking the release of parasites from the tunnels closer to the hair roots. Biomaterial is taken from several lesions at once to increase the accuracy of the analysis.
Other tests
In addition to scraping, other studies are also carried out. These include:
- general and biochemical blood and urine tests, revealing intoxication by waste products of parasites;
- bacteriological culture, used in the presence of a secondary infection to determine the type of bacterium and its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- trichoscopy, which determines the condition of the hair follicles;
- Ultrasound and x-rays recording the condition of internal organs.
After determining the cause and form of the disease, the veterinarian draws up an individual treatment plan. The owner must strictly follow all his recommendations. Acaricides are very toxic, so an overdose can lead to very unpleasant consequences.
How to treat demodicosis in dogs
Treatment of demodicosis in dogs is carried out at home using anti-tick medications. The list of necessary medications is quite extensive, since some of them affect only adults, while others affect larvae. Also, for recovery you will need to take a course of symptomatic medications.
The duration of drug therapy for localized pathology is 1-2 months. In case of generalized disease, the period is determined individually, since the disease very often recurs. Recovery is confirmed upon receipt of 2 negative tests in a row.
Acaricidal injections
Injections are prescribed exclusively for generalized pathology, since external treatment is sufficient to treat localized pathology. The injection solution is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly every 7-10 days until the parasites completely disappear.
Shampoos
The use of shampoos is necessary to remove dead epidermis, eliminate itching and unpleasant odor. Thanks to preliminary cleansing, acaricidal and healing ointments penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin, which increases their effectiveness.
Acaricidal ointments
For more convenient application of ointments, the hair is cut or shaved. Dried scabs are removed with a cotton pad soaked in chlorhexidine or miramistin. Only after this acaricidal preparations are applied to the affected area. Many of them have antibacterial properties, which is very important in the presence of a secondary infection.
It is recommended to cover ointments that are too greasy with a bandage to prevent licking until completely absorbed. The Elizabethan collar copes with the same task.
Healing ointments
Tissue regeneration is stimulated with levomekol, panthenol and ichthyol ointment. They reduce irritation, preventing the appearance of new scratches. These drugs are applied directly on top of the previous ones 5-7 times a day.
Drops
In addition to ointments, it is necessary to use antiparasitic drops. They cope very well with single lesions. Please note that the applied layer must be renewed after each wash, and long-haired pets will require a larger dosage.
Pills
Another possible form of antiparasitic drug is tablet form. The effect of using tablets is similar to injection, but occurs a little later. This method of treatment is suitable for shy pets who are very afraid of injections. To kill ticks, it is enough to use the drug once every 4 weeks for 3 months.
Folk remedies
As an additional therapy, the use of folk remedies is acceptable. Most often used:
- tar soap;
- oatmeal baths;
- sea buckthorn oil;
- lotions made from grated apples and juniper berries;
- decoctions of wormwood and celandine.
Please note that herbs often cause allergies. Before applying the product, be sure to test it on a small area of skin.
Other drugs
Other drugs include immunomodulators and vitamin supplements that help boost immunity. The dog is also prescribed probiotics and hepatoprotectors, which restore the intestinal microflora and liver after taking antibiotics and intoxication with parasites.
Homemade repellent with citrus fruits
Ticks don't like the taste of citrus fruits at all. So this is another great natural remedy to eliminate them. You can use them to prepare a homemade repellent. So buy yourself a sprayer. The best citrus is lemon, but you can also use oranges or any other.
To prepare this home remedy for eliminating ticks on dogs, you must follow these steps:
- You need to boil half a liter of water with two sliced lemons.
- When it reaches boiling point, leave it for a minute and reduce the heat to low.
- Let it simmer for an hour. After some time, let it rest and cool down.
- Inject it into the sprayer and apply the product to your dog, being careful not to get it in the eyes.
Remember that it is also a good idea to vacuum the rooms of your home to keep them free of ticks. When using this natural tick remover on your dog, be careful not to inhale it. Because the smell of citrus is one of the smells that most dogs hate.
Features of nutrition during the treatment period
The vital activity of ticks is accompanied by the active production of toxins that disrupt the process of food digestion. To restore the functions of the gastrointestinal tract, the patient is put on a gentle diet. It provides:
- Elimination of fatty and heavy foods. The main emphasis is on chicken breast, beef tenderloin and oatmeal.
- Refusal to reheat. Don't cook several days ahead. Food should not only be of high quality, but always fresh. It is also worth monitoring her temperature. When served, it should correspond to room temperature.
- Transition to fractional meals. Reduce the single portion, increasing the number of feedings to 4-5 per day.
- Monitoring adequate fluid intake. Change the water in the bowl regularly and include rosehip infusions in your daily menu.
When feeding dry kibble, it is recommended to switch to a special line for allergy sufferers. It can be found from manufacturers that produce products of at least premium class.