Bad breath is called halitosis. More often caused by lack of hygiene and oral diseases. Sometimes it is a sign of more serious illnesses that require immediate treatment.
Bad breath itself is not a disease, it is a symptom that indicates that there are problems in the body.
Sooner or later, all owners experience halitosis.
Why does my dog have bad breath?
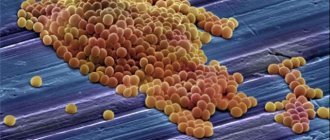
In 80% of cases, the cause of foul odor from the mouth is dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity with a predominance of pathogenic (anaerobic) microflora. Normally, immunity and normal microflora limit their numbers, and saliva washes them off the smooth surface of the teeth and gum mucosa.
Anaerobes feed on food debris and protein deposits. If there is an excess of “food”, they begin to multiply rapidly. In the process of life, they produce volatile compounds, many of which have a strong unpleasant odor of rotten eggs, cabbage, fish, feces, urine, ammonia, etc.
Colonies of anaerobes usually develop in gum pockets, thick plaque on the tongue, on the inner surface of the cheeks, and in the porous surface of tartar. Here they are protected and provided with food. The immune system tries to fight them, and an inflammatory reaction develops.
The development of dysbiosis is promoted by:
- Poor hygiene (accumulation of food residues and their decomposition, formation of protein plaque);
- Inflammatory diseases (of the gums, oral mucosa, hard and soft palate);
- Dental diseases (carious lesions, formation of plaque and stones, more often in small breeds);
- Papilomatosis;
- Injuries to the oral cavity (from chewing plastic bottles, in some dogs from dry food);
- Eosinophilic granuloma (found in huskies);
- Dental pathologies (bad bite, abnormal number of teeth, etc.);
- Dry mouth after prolonged sleep or physical activity, dehydration, or taking certain medications (diuretics).
- Unbalanced diet. An excess of meat and dairy products leads to an increase in the pH of the environment, which promotes the growth of anaerobic bacteria.
In 80% of cases, halitosis indicates problems in the oral cavity
How to remove odor
It is important for a dog owner to determine the cause of the stench from the pet’s mouth in order to get rid of it.
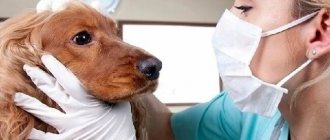
To make a diagnosis, go to a veterinary clinic, where a specialist conducts a series of tests and analyzes to determine the cause of the illness. Depending on the pathology, treatment is prescribed.
Tartar removal
The procedure is not carried out at home. You should trust your veterinarian-dentist. Stubborn plaque is removed with ultrasound, which is painless and effective. When removing tartar with a scaler, anesthesia is required.
Introduction of solid feed
If plaque accumulates quickly, the dog does not have enough solid food in its diet.
The pet is given raw carrots, apples, and small bones. Store-bought solid food in the form of granules or pads will also help solve the problem of plaque.
For the same purpose, the dog is offered treats with rawhide and special enzymes that dissolve dental plaque.
Rubber, bone-shaped chew toys prevent food debris from depositing on your teeth.
Probiotics
Violation of the intestinal microflora provokes the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and the appearance of a heavy odor from the mouth. To prevent and treat dysbiosis, the dog is given probiotics (Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin, Linex, Acipol).
Deworming
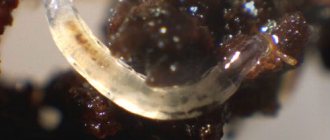
To prevent infection with worms, it is necessary to treat the animal at least 3 times a year. If the cause of bad breath is helminthic infestations, a stool test is performed to determine the type of parasite.
Based on the examination results, the veterinarian prescribes effective medications.
Other causes of bad breath
Less commonly, halitosis indicates serious illness. The type of odor combined with symptoms helps in making a diagnosis.
- Respiratory system. There is often a putrid smell - a sign of an inflammatory process with a predominance of anaerobic microflora.
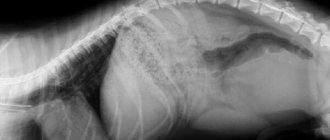
- Digestive tract. Under normal conditions, gases do not leave the stomach and intestines; this occurs when the esophagus is damaged, vomiting, belching, coughing, or severe pathologies. The smell from the mouth may be sour or rotten eggs (hydrogen sulfide). The culprits of halitosis and other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract can be helminths. In the process of life, they produce many toxins that are absorbed into the blood and poison the body. The most severe option is acute intestinal obstruction caused by a ball of parasites and the pungent odor of acetone from the mouth.
- Urinary system. In case of renal failure, toxins accumulate in the blood, which should have been excreted in the urine, but are partially eliminated through the respiratory system, and “uremic (ammonia) breathing” occurs.
- Liver diseases. The smell of acetone, rotten fish, pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Systemic diseases (dehydration, diabetes, fever). Often accompanied by the smell of acetone, which may indicate a lack or excess of glucose, appears during fasting, overeating, or elevated temperature.
- Oncology.
Bad breath may be a symptom of a serious illness
What to do if you are poisoned by fish
If you experience signs of poisoning after eating fish, such as severe diarrhea, you should consult a doctor. In case of any ailment, it is important to seek medical help in a timely manner to avoid negative consequences.
How to help in case of poisoning before doctors arrive? First of all, you need to try to remove the spoiled or toxic product from the stomach. To do this, you can provoke vomiting: drink two or three glasses of warm water with salt and press on the base of the tongue. After this, you can take a sorbent that will help remove toxins from the gastrointestinal tract and slow down their absorption into the blood. The most affordable products with a mild effect include “Fitomucil Sorbent Forte”. The drug consists of psyllium seed shells, probiotics and prebiotics. It has a gentle effect on the gastrointestinal tract and does not provoke pain or spasms.
In addition, frequent and abundant drinking will help remove toxins. Weak sweet tea, rosehip infusion, or plain boiled/filtered water will do. You need to drink in small portions, but often.
Bad breath in puppies
Halitosis in puppies rarely indicates serious illness, but requires monitoring. Usually appears during the change of teeth (3-7 months). During this period, immunity may decrease. There is severe itching, sore gums and a desire to chew everything. As a result, the gums and palate are injured. An unformed or incorrect bite, extra teeth, or the simultaneous absence of several contribute to the formation of dental crevices in which food debris gets stuck and begins to rot under the influence of microorganisms.
The period of teeth change is the best time to accustom your puppy to hygiene procedures.
Causes of temporary halitosis
If bad breath appears suddenly, the following reasons should be considered:
- The dog ate something. In this case, halitosis does not require treatment, but the owner should think about behavior correction and other precautions. Most of the “treats” that a dog “vacuums” on the street are potentially dangerous and can cause severe poisoning.
- Inflammation of the paraanal glands. They are located on either side of the anus. They are sacs in which a strong-smelling secretion accumulates. Normally, it is transparent, low density, and is excreted during bowel movements. But in some dogs, often small breeds, it is more viscous and foul-smelling, brown in color, which complicates the natural elimination process. The dog is trying to help itself: it bites under its tail or rubs its “butt” on the ground. She licks off part of the secretion that comes out, and as a result, the same fetid smell of rotten fish emanates from her mouth.
- Binge eating. Halitosis disappears when the diet is normalized.
How to properly care for your oral cavity
Cleaning molars begins with purchasing the necessary supplies from a pet store: special toothpaste and a soft brush. The procedure is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Place a small amount of paste on the brush.
- When cleaning, special attention is paid to the upper jaw - plaque is most often deposited on it.
- The final stage is cleaning the tongue.
The manipulation is carried out twice a week, it helps to remove repulsive odors from the dog’s mouth.
Important! Do not use baking soda or human paste. They contain components that can be harmful to your pet's health.
What should the owner do?
First of all, you should take a responsible approach to the issue of preventing dental problems. The measures listed below can easily be incorporated into a weekly practice and made part of basic care.
- Proper nutrition. A balanced diet, feeding at the same time, free access to drinking water and no “treats” from the table. Frequent snacking on unhealthy foods “clogs” the oral cavity and creates conditions for the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Systematic inspection. Allows you to identify problems at an early stage.
- Regular brushing of teeth using a soft brush and a special toothpaste for dogs. Brachycephalic dogs (Shih Tzu, Pugs, French Bulldogs, Pekingese), as well as small breeds predisposed to tartar formation (miniature poodle, Chihuahua, Jack Russell), are recommended brush your teeth every day. If not with a brush, then with the help of alternative means:
- Preventive treats. Regular raw bones (large beef bones) and industrial delicacies help clean the enamel. The most popular brands on the market: Nylabone, Biff, Trixie, 8in1, Purina, Pedigree, Stuzzy, Flamingo.
- Preventive toys. Their shape and relief promote natural and gentle brushing of teeth, development of jaw muscles, and additionally massage the gums. The largest number of positive reviews can be found about toys from the following companies: Tropiclean, Trixie, Hartz.
- Preventative supplements. Available in the form of tablets, sprays, ointments, drops in water. When choosing them, you should pay attention to the purpose. Some are used only to combat unpleasant odors. Others prevent the formation of tartar, which is the cause of halitosis in most cases. Pastes, gels and sprays are quickly washed off with saliva, and therefore give a short-term effect. Feed additives in the form of tablets or drops are absorbed by the body and excreted in saliva, providing a round-the-clock effect.
Dental care is the responsibility of the owner
Treating bad odor in dogs
Oral diseases are easily diagnosed visually. It is better to remove plaque and tartar on teeth in a clinic using ultrasound. For calm dogs, the procedure is performed without sedation; for nervous and aggressive dogs, the procedure is performed under anesthesia. For severe inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, antimicrobial agents, analgesics, vitamins, locally antiseptic solutions and herbal infusions are prescribed. In most cases, it is advisable to prescribe immunomodulators. Often therapeutic regimens include injections, and owners who cannot often take their dog to the clinic learn to give injections themselves.
If the oral cavity appears healthy, the veterinarian will order additional tests to help make a diagnosis:
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Clinical urine analysis;
- Instrumental examination (ultrasound, gastroduodenoscopy, radiography of the sinuses).
Bad breath is a very common problem among pet dogs. Not paying attention to it or masking it with sprays is a big mistake. Halitosis should be considered as a “bell” that indicates problems. It is better to resolve them with the attending veterinarian.
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of a fishy odor, do not be lazy to spend time on your dog’s hygiene. Groom six, use the right dog bath products, and brush your dog's teeth two to three times a month to avoid plaque and dental problems.
Inspect the dog's body and ears after each walk. For hygienic treatment of ears, use the correct products for animals.
Important! Keep the bowls, bedding, and house where your pet sleeps and rests clean.
Don’t forget to drive away worms and treat the fur against ectoparasites. Take your pet to the clinic twice a year for a comprehensive examination.