The owner's attitude towards the small puppy in the house is compared with the attitude of parents towards their children. Particular attention is required during the period of the appearance of milk teeth and their replacement by permanent ones. This raises many questions, especially for inexperienced dog breeders. It is important to know when puppies’ teeth change, what complications may arise, and how to help your pet.
Milk teeth in puppies
Newborn puppies are helpless. They are blind and toothless. During the first 2 months on mother's milk, they become completely independent.
Baby teeth begin to cut closer to the age of one month. Their number depends on the breed: for large ones - 32 pieces, and for dwarf ones - 28 pieces. The process is completed by two months from birth.
Need to know ! Deviations from deadlines of 7-10 days are considered normal.
The incisors appear first, then the canines, and the premolars complete the row of baby teeth.
In time it looks like this:
- baby fangs appear on days 20-25;
- the incisors begin to appear after 10-15 days;
- premolars are the last to peck - by two months.
Attention ! Decorative dogs (Chihuahua, Spitz) acquire milk teeth at the age of 1.5 months.
Milk teeth are evenly distributed throughout the jaws. Depending on the breed, there may be 14 of them on each jaw or 16. In the primary dentition there are no molars. They appear only after changing to permanent ones.
What does a correct bite look like?
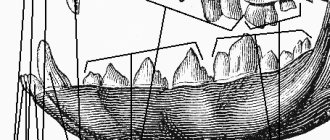
When the mouth is closed, the dog should have a normal "bite". This is very important for dogs to be able to eat and use their mouth normally (and this is assessed accordingly in show dogs). A normal bite looks like this:
- The lower canines are located in front of the upper canines.
- The upper incisors overlap the lower incisors.
- The points of the upper premolars fit into the spaces between the lower premolars.
- The upper carnassial teeth overlap the lower ones.
Malocclusion refers to the abnormal “bite” or alignment of these teeth. An overbite may be normal in certain dog breeds due to differences in the shape of the jaw and mouth.
For example, flat-faced (brachycephalic) dogs such as bulldogs have a normal overbite because their lower jaw is longer than their upper jaw.
However, this causes the teeth to misalign, which can cause damage to the dog's mouth when he chews.
Therefore, the veterinarian or veterinary dentist performing orthodontic correction must be aware of malocclusions.
In what order and at what months do puppies change teeth?
The beginning of the change of teeth starts almost immediately after the completion of the growth of milk teeth. Depending on the breed, food, and care rules, it is considered normal when this process is completed when the dog reaches one year of age.
Puppy milk teeth
The change of teeth occurs in stages, that is:
- first the incisors are replaced (3 months);
- then the fangs fall out (up to 7 months);
- premolars change.
Unlike the milk series, the permanent series is supplemented by molars. The first molars (M1) appear by 5 months, the second (M2) by 6 months, and the third (M3) by 7 months.
History of the breed
Siberian Husky began to attract the interest of professional dog handlers and breeders only at the beginning of the 20th century. At home - in the regions of the Far North of Russia - local residents used the ancestors of the husky to move across the tundra, go on remote hunts and to deer grazing areas. At that time, there was no such breed as the husky, and by the thirties of the twentieth century, the breeding of these northern dogs was considered unpromising in Soviet Russia, since they were replaced by technical means of transportation in the Far Eastern regions.
Residents of the northern regions of the United States, where gold and fur mining was in full swing, thought differently. In 1934, the breed was officially recognized there and received the name “Siberian Husky” in the registry. For the first time, representatives of the Chukchi and Eskimo sled dog breeds appeared in 1908 in Alaska. They later spread to other regions of America.
The northern husky began to return to Russian territory only in the 90s of the twentieth century, having first arrived here in 1995 from the Czech Republic and Belgium. And by the beginning of the 21st century, the number of purebred individuals had reached several hundred.
Hurry up, choose a box and find out what gift awaits you
Discount on pet insurance
Promo code copied to clipboard
Does this process depend on the breed of dog?
The timing of the appearance of all permanent teeth does not depend on the breed of the dog. All dogs grow them by the age of one year. But the change itself proceeds differently in different breeds. Small dogs are in the process for the entire first year, and large breeds have the entire series by 9 months.
That is, adults must have 42 teeth: 20 in the upper jaw and 22 in the lower jaw. The upper jaw consists of:
- molars – 4;
- premolars – 8;
- fangs – 2;
- incisors – 6.
In the lower jaw:
- molars – 6;
- premolars – 8;
- fangs – 2;
- incisors – 6.
Weeks 2-4
Narrow teeth known as incisors will begin to appear at the front of the mouth.
The incisors appear first at two to three weeks of age. Puppies have six incisors on the upper and lower jaws. Premolars and molars also begin to grow behind the canines (the pointed teeth between the incisors and premolars) at three to six weeks of age, three above and below on each side.
Four needle-like canines appear at four weeks of age and frame the incisors, one on each side, above and below.
How to help your pet during the period of teeth change
Changing teeth is a big challenge for the animal and its owner. Problems can be noticed by the pet's behavior. When dogs change their teeth, their relationship with food changes. They prefer something softer or more liquid. The owner needs:
- regularly examine the puppy’s jaw;
- provide him with rubber toys, such as sticks, bones;
- give peeled carrots (and vitamins at the same time);
- regulate the presence of phosphorus and calcium in the diet.
If necessary, you can gently loosen a loose tooth (but do not pull it out by force).
Very important ! During the period of changing teeth, the puppy should be provided with peace and protected from contact with other pets. Vaccinations are not indicated during this period.
Vaccinations
Despite the fact that huskies have a strong immune system, vaccinations are a must .
What needs to be done?
- "Nobivak KC" is a vaccination against a group of infections.
- Vaccination with DP type vaccine - against plague and bordetellosis.
- Vaccination with DHP-L type vaccine - against viral hepatitis and rabies.
- Vaccination with a vaccine like DHP-RL - repeatedly against plague and hepatitis.
When?
The first vaccination is given to the puppy at 3 weeks of age. The second at 4 weeks of life. Basic vaccinations are given at 8–10 weeks and 3 weeks after vaccination.
First vaccination
Usually at 2 months of age the first vaccination is given, but if the dog is susceptible to any diseases and if it is not possible to limit the puppy’s contact with other individuals, then the first vaccination is given before a month.
Rabies vaccination
It is a mandatory vaccination and is given to the puppy at 8-10 weeks. It also includes vaccination against canine distemper, hepatitis, and parvovirus enteritis.
Vaccination table by age from birth
| Vaccine name/age | 3 weeks | 4 weeks | Week 9 | 12 week | 1 year | Every subsequent 12 months |
| Nobivak KC | + | |||||
| Vaccination with DP type vaccine | + | |||||
| Vaccination with DHP-L type vaccine | + | |||||
| Vaccination with DHP-RL vaccine | + | + | + |
Caring for your dog's teeth during shifts
In order for teeth to grow correctly, you need to monitor the process of the appearance of each of them. It often happens that the permanent one begins to grow before the milky one falls out. You cannot force toys or any other object out of your pet’s mouth or play tug-of-war with it. It is better to feel the teeth every day and slightly loosen them as they sway.
When puppies lose their baby teeth, adjustments are also made to their diet. It is better to leave very hard foods until better times. The dishes must be clean and the water must be fresh. For any deviations, you should contact a specialist.
How can the process of changing teeth be complicated?
Malocclusion
Incorrect replacement of teeth or unreasonable human interference in the process can cause an incorrectly developing bite in dogs. Also, dogs with elongated muzzles, when teeth of a standard size are placed on narrow gums (Doberman Pinschers, Poodles, Rottweilers, Labradors, Scotch Terriers, etc.), are prone to this problem. To avoid malocclusion, dogs are not fed soft food, toys are not pulled out of their mouths during play during the teething period, and “stuck” units are monitored.
- Symptoms. Incorrect closure of the jaw is detected.
- Help. If the bite is broken, then for purebred dogs this is a significant drawback when they participate in exhibitions. You can try to install special braces to correct it, which are installed by specialists under anesthesia. Ordinary domestic dogs are usually not subjected to this procedure and the bite remains as it is.
Gum inflammation
Often a minor inflammatory process accompanies the entire period of tooth change. Usually everything goes away on its own. If there is a complication, you need to go to the clinic.
- Symptoms. The gums are intensely red and swollen, saliva flows heavily, and there is a high probability of decreased appetite due to sore gums.
- Help. Avoid rough food so as not to cause additional trauma and pain in the mouth.
When inflammation persists, to sanitize the oral cavity in dogs, as prescribed by a veterinarian, you can use the drug “Stomadex” C300 in courses of 10 days (cost: 400-450 rubles/pack with 10 tablets). The tablet from the package is pressed with your finger onto the dry surface of the cheek at the level of the 2nd premolar. Dry the cheek with a clean, dry paper towel. After attaching the tablet, the animal should not be given food or drink for 20-25 minutes. It is better to do the procedure before bed, half an hour after the last feeding (the period when the amount of saliva produced decreases).
Delayed change of teeth (persistent or “stuck” milk teeth)
Sometimes baby teeth don’t have time to fall out before permanent ones “make their way” into their place. In addition to malocclusion, persistent teeth threaten additional injuries to the cheeks and inflammation of the gums.
- Symptoms. Milk teeth are discovered at an age when they should no longer exist, as well as two processes from approximately one tooth socket (one of them is milk teeth).
- Help. If, with a loose baby tooth, the owner cannot help it fall out without effort, this is a reason to contact a veterinarian - it will be removed using anesthesia.
What to feed the animal during this period
When puppies change their teeth, they experience discomfort, sometimes quite severe. The pet may refuse to eat altogether. This means that the food needs to be changed. To keep your pet healthy, it should be switched to something between semi-liquid and liquid food. Sometimes the puppy can only lap or lick. In this case, he needs to be given broths and fermented milk, meat and vegetable puree.
Important! You can use special dog food. But only very high quality and in the form of pate.
Husky show standards
According to unified criteria and standards from RKF, a husky must meet the requirements:
- have average sizes;
- proportional physique;
- erect triangular ears;
- neck of medium length, moderately arched;
- slanted eyes of brown, blue or different colors;
- black or light nose;
- strong and deep chest;
- well-furred sickle-shaped tail;
- straight limbs;
- double layer wool cover.
Possible complications
When changing teeth, various complications can arise. Small breeds weighing up to 8 kg are especially predisposed to them. Troubles most affect medium-sized and long-faced breeds, such as:
- lap dogs;
- toy terriers;
- Yorkies (Yorkshire terriers, for example)
- Italian greyhounds;
- poodles;
- Sheltie
These dogs were artificially bred specifically for home keeping. They never had to look for food for themselves. They eat what their owner gives them. These are often soft canned foods. There is no need to train the chewing muscles, so the gums weaken. Moreover, they are dogs, that is, they have ordinary teeth, of ordinary sizes.
This dissonance leads to the fact that baby teeth do not naturally loosen and fall out, while permanent teeth rush to appear on time. Baby and permanent teeth sitting in the same hole lead to improper growth of the latter, and, as a result, to malocclusion. You can't do it without the help of a specialist.
With some clarifications, this problem also applies to large breed dogs. The reasons are almost the same. Complications arise with breeds:
- boxers;
- mastiffs;
- Caucasians;
- Great Danes;
- Shepherd dogs (German, Eastern European);
- Labradors;
- husky;
- miniature schnauzers;
- Dobermans;
- Rottweilers.
You can tell if there are problems by:
- improper jaw closure;
- bleeding gums, swelling in this area;
- heavy odor;
- purulent fistulas under the nose.
There is also a possibility of missing teeth. This is already a pathology, nothing can be changed here.
As for the causes of complications, these could be:
- Inflammation of the gums. It can occur when teeth erupt too large and leathery pockets form on the gums (food remains and rots).
- Persistent teeth - when permanent teeth come out in parallel with milk teeth. In this case, baby teeth begin to rot, which leads to inflammation.
- Diarrhea. This is rather a concomitant phenomenon. If it happens, you need to monitor the drinking regime and the hygiene of your pet’s household items.
- Smell from the mouth. It appears as a result of rotting food under the gums and rotting of the tooth itself.
- Poor appetite. This phenomenon is very explainable. If there is pain in the oral cavity, then the discomfort is stronger than the desire to eat. During the normal course of the teeth changing process, appetite will return very soon.
Complications you may encounter
- At home, when examining the oral cavity to determine whether the dog still has milk teeth, you need to take into account the pet’s age and its size. If the change does not occur within the prescribed period, you must contact your veterinarian.
- A prolonged period of changing teeth can lead to malocclusion in an animal: permanent canines and incisors shift and grow along a different trajectory if the milk teeth do not fall out and take their place.
- Fracture is a periodontopathy in which the crown breaks and the root remains in the gum. This residue cannot resolve on its own and will remain in the oral cavity, becoming a source of infection. Inflammation, swelling and local redness develop at the affected area. The remaining part is removed surgically.
- False polyodontia is a pathology that is caused by delayed loss of temporary canines and incisors. Visually in the oral cavity it can be noted that they are located in two rows. If such a problem is detected in a dog, the baby teeth must be surgically removed.
- Impacted teeth are a situation in which there is a baby tooth, but the permanent one remains in the gum and does not grow (or it may not exist at all). In any case, the temporary one is surgically removed, leaving a space.
Prevention of dental diseases
If problems cannot be avoided, they can be minimized. Dogs' baby teeth don't last long, so they don't need care on their own. To identify problems, it will be enough to inspect them daily. Detecting violations at an early stage will help reduce risks.
The quality of food is very important when raising a dog from a puppy. Special, balanced dry food not only contains all the necessary microelements, but also gives the animal’s jaw the necessary load. By developing the jaw, they also cleanse the teeth of plaque.
If desired, you can create a diet for your pet yourself, but after consultation with a veterinarian. A person cannot know exactly the composition of a complete diet for a dog. And regularly giving her solid food such as raw carrots, apples, cabbage is quite possible.
On a note! Special treats - dry veins, pressed bone meal - will delight and be useful for your pet.
If these simple rules are followed, the shift should be completed painlessly and on time. If, after the appearance of the entire permanent row, milk remains in the gums, then only a dentist can help.
Violation of the process of changing the dentition can lead to irreversible consequences. Even if, over time, all the milk teeth fall out, the permanent ones will no longer fall into place. The bite will remain broken forever. To avoid this trouble, you need to be attentive to your pet’s health and urgently respond to violations. Then your home friend will bring only positive emotions.
What are the complications of the process?
Formation of malocclusion
The cause can be either genetic or acquired.
- Deformity is inherited.
- Microelement starvation of the mother affects the offspring.
- Exhaustion of the puppy itself.
- Deep injuries.
What does it look like?
When overbiting, the lower jaw bulges forward and the lower incisors become exposed. The rest of the teeth don't match.
Underbite is characterized by protrusion of the upper jaw. Misalignment of remaining teeth.
A straight bite is more difficult to notice because the mouth closes normally.
What to do?
First of all, we turn to a specialist to determine the cause of the pathology. If a shift of the jaws or individual teeth occurs due to retention of a primary incisor, premolar or canine, it can be removed. If the defect goes to the bones, then veterinary dentists use a set of rubber corrector rings. Braces are placed on adult dogs.
Important! For the development and formation of a bite in an animal as a whole, it is necessary to provide a complete diet and proper care.
Well-formed milk teeth in dogs provide a good basis for permanent ones. Even genetic defects can be defeated or smoothed out if the puppy eats well, moves actively, spends a lot of time in the fresh air, and receives all the necessary trace elements and minerals.
Gum inflammation
The process is accompanied by severe itching. The puppy begins to chew something and may whine at the same time, as his inflamed gums hurt. On examination, foci of inflammation are visible (cherry-pink and white at the edges). In special cases, the gums bleed heavily. A hood of tissue may form over the erupted tooth.
Corrective Actions
We relieve the itching by gnawing the puppy on beef bones, toys, and special bones. We treat the inflamed areas with chamomile decoction. If your gums bleed, see a doctor. If this is not possible, we treat it with peroxide, but so that the puppy does not swallow it, even the foam. Wet the napkin a little. The doctor will remove the tissue hood; you may damage the baby tooth yourself.
Shift delay
This is a condition in which a baby tooth has not been replaced by a permanent one. Both teeth are located together in the gum.
How does it manifest?
It happens that teeth grow in two rows. The more powerful constants push the milk ones and they stick out in different directions. The adult canine continues to grow in parallel with the milk canine. It’s as if there are two fangs at the same time - a thick one and a thinner one (milk). The teeth begin to protrude from under the lips, and the formation of an incorrect bite begins.
When do husky puppies' teeth change?
Steegle.com - Google Sites Tweet Button
Today we will talk about how to care for the teeth and mouth of a Siberian Husky. We will also consider what kind of prevention, dental treatment and dental care there are for huskies at different age periods.
To do this, the puppies need to be given bones from the tendon, or you can get by with a more natural product, give the husky puppies a large piece of raw meat (beef) - let them exercise (eat it, they won’t eat it, but they will train their jaw, there is no reason to worry, besides Raw meat contains a lot of vitamins necessary for a growing body).
Changing teeth in a husky puppy
During this period, it is necessary to check the oral cavity and monitor the loss of teeth before new ones begin to emerge. If you see that a baby tooth is on the verge of a hair, and a new molar is growing under it, help the baby tooth fall out so that the teeth do not start growing in two rows.
First of all, the front incisors are replaced. If baby teeth (incisors) do not have time to fall out and new molars grow under them, then the teeth grow in two rows. Don't let this happen.
Then the back ones come in turn - molars and premolars; there are rarely problems with them, they quickly and independently fall out.
The next line falls on the fangs. It is necessary to monitor the fangs, very often there are cases when a temporary fang does not fall out and a molar grows nearby and teeth are formed in two rows, such a temporary canine can last until the age of two, and there are cases when the permanent canine does not grow correctly (in the other direction - into the gum), this mainly concerns the canines of the lower row of teeth, so the temporary one must be removed as soon as the permanent one emerges. If you plan to show your Husky at shows in the future, you need to take care of his teeth.
Until the age of one year, huskies do not have any problems with their teeth, but starting from the age of one year, it is necessary to have their teeth brushed (regularly once a week) and have a daily oral examination.
Regular brushing of your teeth will prevent the formation of tartar. Tartar is mineral deposits on the teeth (where the tooth emerges from the gum). These deposits are not easy to remove with a toothbrush. If your husky has stones, it is better to consult a veterinarian, who will remove the stone with a special tool.
Some owners believe that a dog that chews dry food or special bones “for cleaning teeth” cleans its own teeth and does not develop tartar. It's a delusion. Additional regular teeth cleaning is necessary for any husky, especially a show husky. After all, at the exhibition, an expert will definitely examine the condition of the dog’s teeth. Imagine how embarrassed you will be if your dog has yellow, dirty teeth!
Care
Husky is considered one of the easiest dogs to care for. The main feature of caring for an adult husky in an apartment is the provision of constant physical activity. In other words, the more tired a dog is on the street, the easier it is to care for it at home. Another feature is the coat; it requires brushing several times a week, and when shedding, several times a day.
For a newborn puppy
If there is a mother, minimal care is required for the newborn puppy. You just need to provide comfortable conditions for the puppy to grow. Weigh yourself daily. On day 9, it is necessary to trim the tips of the claws, then repeat this procedure weekly.
At 1 month
It is recommended to feed 6 times a day with special food for puppies. At this age, the character of the future dog is established, so it is worth starting to educate him. Also, a husky puppy should know its place and its things:
- toy,
- two bowls,
- collar,
- special rug.
At 2 months
Vaccinations against distemper, rabies and other diseases are given. At this age, they usually begin to actively train the puppy. Periodically comb his fur and trim his nails. The puppy should eat often and drink a lot.
Is it possible to wash a puppy?
It is not recommended to bathe your puppy until his latest vaccinations have been completed. Only if absolutely necessary, but not advisable.
From what age?
The earliest time allowed by veterinarians is 4 months if the puppy is very dirty or for any other reason.
How to bathe?
Bathing is not done in hot or very cold water (about 28 degrees). The paws should be on a hard, rubberized surface. First, lather with a special puppy shampoo, and then rinse with water, avoiding getting water into the puppy’s ears and eyes. Then thoroughly dry with a towel until the undercoat is completely dry. It is recommended to avoid drafts for a few more hours. The procedure is carried out no more than 3-4 times a year.
Ear care
If there are any visible symptoms, brown discharge, swelling or strange behavior of the puppy itself, you should immediately contact a veterinarian .
Does it need to be cleaned?
If everything is fine with your ears, then you can carry out the cleaning procedure once every two weeks. Apply a special ear lotion, massage the ears for a few minutes and wipe off the released wax with a napkin. The depths of the ear should not be cleaned.
When do your ears stand up?
If the puppy’s ears do not stand up until six months of age, then this is a reason to go to the veterinary clinic. It is difficult to talk about more precise limits, because much depends on the number of puppies in the litter, the quality of food and the uniqueness of the animal.
Why don't they get up?
A common reason for ears not standing up is a lack of vitamins and calcium in the body. It is necessary to diversify your diet. External plumpness of a puppy does not always indicate good health.
Reference. The purebredness of the breed is expressed in erect ears.
My ear fell - what to do?
If this occurs before 6 months of age, the cause is most likely either tooth growth or limb development. There is nothing wrong with this, it’s just that these processes are very demanding on the presence of calcium. It is necessary to give your pet vitamins, and soon the ears will be on top again.
Why do puppies get into the refrigerator?
Huskies are northern dogs, and their ancestors are wolves that live in harsh climatic conditions. Therefore, it is not surprising if the puppy climbs into the refrigerator. He is simply more comfortable there.
When can you start walking?
You can go for full walks with your puppy no earlier than quarantine after the last vaccination. Until this time, you can go outside for a short time, holding the baby in your arms. At the same time, preventing other dogs and people from approaching the puppy.
How many walks per day?
After all age-appropriate vaccinations have been completed and the quarantine period has been completed, you can go for a real walk. During the first walks, the puppy must be on a leash. Otherwise he might run away. It is better to walk several times a day for an hour. You should not overload the dog if he is tired, it is better to give him a rest and return home.
Husky in winter
Winter walks are the most unforgettable for huskies, because snow is their homeland. The puppy will be happy to give a ride to a light skier. But don’t expect him to drag the whole family on a sled. Up to 10 months, puppies have not yet fully strengthened bones and joints; such walks run the risk of injuring them.
At what age do puppies change teeth?
The owner's attitude towards the small puppy in the house is compared with the attitude of parents towards their children. Particular attention is required during the period of the appearance of milk teeth and their replacement by permanent ones. This raises many questions, especially for inexperienced dog breeders. It is important to know when puppies’ teeth change, what complications may arise, and how to help your pet.
Your puppy is teething – how do you know what the symptoms are?
In most cases, the process of teething in a puppy is invisible and painless. The increase in temperature can be short-term and pass during sleep or rest. The owner himself must control the process. To do this, just run your finger along your pet's gums.
Important! The animal’s gums itch in any case, and the dog begins to chew everything it sees to get rid of this sensation.
For this, the owner should stock up on large beef bones (mosles) or special products from the pet store - toys, bones, etc.
The appearance of baby teeth
Puppies are born toothless, which facilitates normal feeding with mother's milk. By 3-4 weeks of age, the first barely noticeable tubercles begin to appear. The canines appear first, then the incisors. Then after 1-2 weeks the rest cut through.
Just like humans, dogs have 32 teeth; fewer teeth are considered abnormal.
There are factors that influence whether the growth of baby teeth is delayed or begins earlier. Most of them are associated with health problems. Chronic diseases, problems with the digestive system, and nutrition provoke complications. Also, delayed jaw development is common in small breed dogs.
At what age do baby teeth change?
The loss of milk and the growth of permanent milk in their place occurs at different times in representatives of different breeds:
- in large breeds - at the age of 3.5-4.5 months;
- in small ones - at the age of 6-7 months.
Let's look at the update time and features using the example of representatives of breeds of different sizes:
- Yorkie puppies are in their third or fourth month, with frequent pathology – two sets of fangs, the old ones do not fall out, new ones grow nearby;
- German Shepherd puppies – third month;
- spaniel - third or fourth month, common pathology - incomplete teeth (less than 42 molars);
- husky – third month, frequent pathology – excess of normal amount;
- French bulldog - third to seventh month;
- Spitz - fourth to eighth month.
If for some time the baby teeth border on the molars, this is normal. If this continues for a long time, then you need to contact a veterinarian.
Characteristics of puppies
Each puppy is unique, but breeders conditionally divide all puppies into three classes:
- Pet class - puppies without pedigree; have any non-critical defects that exclude their participation in exhibitions.
- Breeding class - puppies of this class will be allowed for breeding in the future; representatives that meet all breed standards.
- Show class - puppies of titled parents with excellent pedigree that meet all breed standards.
Newborns
As a rule, newborn Siberian Huskies weigh from 350 to 500 g. Weight varies depending on the number of puppies in the litter, as well as the gender of the newborn.
In appearance, newborn huskies are no fundamentally different from most newborns of other breeds.
The eyes are closed, the paws are thick, the coat is predominantly white, but with distinctive spots of various colors. It is somewhat more interesting to observe the development of the puppy further, month by month:
- 1 month . Already 15 days after birth, the weight of babies increases more than three times. They are actively developing and by the end of the month reach up to 24 cm at the withers, and up to 3700 g in weight.
- 2 months . By this period of a husky’s life, it is already perfectly built and moves well. The ears begin to rise. He gains weight well, on average 7500 g with a height of 32 cm.
- 3 months . A transfer is made to five meals a day, as a result of which the pet’s accelerated growth rate continues. Height at the withers is about 40 cm.
- 4 months . The transition to adolescence occurs, the features of an adult dog begin to emerge, all this happens simultaneously with rapid growth in height (46 cm) and weight gain, the husky already weighs 18 kg.
- 5 months . Lines continue to form. Gains weight up to 23 kg and height up to 50 cm.
- 6 months . Already a large (under 25 kg) and tall dog (height at the withers is about 54 cm). But still, he is still far from becoming an adult.
- 7 months . There are even fewer distinctive features from an adult representative of the breed. He gains an average of about 3 kg in weight, and may not gain any height at all.
- 8 months . Sexually mature individual. Growth is slowing down. Weight is approaching 30 kg, and height can reach 58 cm.
- 9 months . The height at the withers is 58 cm - this is the height of an adult dog. Weight can reach 33 kg.
- 10 months . With proper care and proper care, by the age of ten months a husky puppy will gain 35 kg, which is the average norm for an adult. It no longer grows in height.
- 1 year . The weight of a male dog can increase up to 40 kg due to accompanying factors. Can grow up to 60 cm in height (but unlikely unless it reaches this mark at 10 months).
Table of weight, height and size by month
| Husky puppy age by months | boy (cm) | Girl (cm) | Weight, kg | ||
| Height at withers | On the back | Height at withers | On the back | ||
| 1 month | — | — | 2,7 | ||
| 2 months | 32 | 30 | 5,9 | ||
| 3 months | 42 | 40 | 10,5 | ||
| 4 months | 484 | 50 | 47 | 50 | 14,3 |
| 5 months | 53 | 54 | 51 | 52,5 | 19,5 |
| 6 months | 55 | 57 | 53 | 54 | 21,5 |
| 7 months | 57 | 58 | 55 | 55 | 24,3 |
| 8 months | 58 | 59,5 | 56 | 56,5 | 25,5 |
| 9 months | 59 | 60 | 57 | 57,5 | 26,5 |
| 12 months | 60 | 62 | 58 | 59 | 28 |
IMPORTANT! The data presented in the table has an average value. Small deviations from these values are allowed.
When do puppies' eyes open?
It happens differently for each puppy; it is impossible to predict the date of opening of the eyes down to the minute. In a properly developing dog, the eyes open 11–16 days after birth. Only one or half of both may open, maybe both entirely. It will take a few more days for the baby to be able to see fully, like an adult dog. If a month has already passed since birth and the eyes are not open, you should contact a veterinarian.
REFERENCE. Two weeks after birth, the puppy can be helped to open its eyes with boiled water.
When does eye color change?
Most Huskies are born with blue eyes, but within six months some of them may change eye color. The Husky breed is also characterized by odd eyes.
To what age do they grow?
The Husky is a large dog, and like most large dogs, it takes a long time to develop. From birth to six months, development in boys and girls is almost identical, after which some differences arise.
- Girls . The phase of active development is up to 8 months, growth continues up to 1 year and is finally formed by 2 years.
- Boys . They actively grow up to 9 months, development occurs up to 1.5 years, and formation occurs up to 2.3 years.
When do teeth change?
They are born without teeth and develop a full set of milk teeth by three months. Then the milk ones begin to gradually fall out and permanent ones appear in their place, this happens until the seventh month. By the ninth month, the puppy should have all 42 permanent teeth.
How teeth change
The order in which permanent teeth appear is different from the order in which baby teeth grow. The canines are not the first to be renewed, the incisors come before them, then all the others, then the canines are the last. There are more molars than baby teeth. By the age of one year, a healthy animal has 20 pieces at the top and 22 at the bottom.
When teeth begin to change, any owner notices this by changes in the pet’s behavior. If this does not happen, some decide to loosen the dog’s teeth themselves to speed up the renewal process. This cannot be done; the minimum harm to the pet from this is a severe painful shock. If renewal has not begun by the age of six months, you need to contact a veterinarian.
Symptoms
Symptoms of renewal manifest themselves in different ways. Their intensity is influenced by the individual pain threshold of the animal, the quality of nutrition, and the dog’s general health.
Typically, when baby teeth change, the following changes in behavior occur:
- severe itching in the gums forces the pet to chew on everything it comes across;
- eating problems, loss of appetite;
- lethargy, loss of strength, decreased activity;
- increased body temperature;
- diarrhea caused by licking everything around.
Many owners say that when a puppy's teeth change, he begins to bite. This is especially dangerous if there are small children in the house, who, out of habit, climb up to the pet to play with it. It is important to provide him with peace and his own territory in the house. It is recommended to take care in advance of the availability of special toys that the dog is allowed to chew.
Oral care
In their shape and structure, baby teeth differ from permanent molars. Basic care involves proper oral hygiene. For example, with the help of teethers, they reduce discomfort and help keep teeth clean. Healthy “snacks” made from dried meat and tendons are also great.
It is necessary to accustom your dog to brushing its teeth. This must be done starting from puppyhood. With proper care, dogs do not develop dental problems until they are 6 years of age.
Dogs need to brush their teeth every day. Despite oral hygiene, you cannot give a 100% guarantee of dental health. There are many factors that influence changes in a dog's mouth. For example, hereditary diseases, genetic predisposition, accidental injuries.
How to help a dog
To help your pet survive this difficult period, you need to surround it with attention and care. At six months of age, the first scheduled visit to the veterinarian is recommended; it occurs at the time of teeth change. The doctor will be able to detect any violations and suggest how to solve them.
If your puppy has completely lost his appetite, you should not force him to eat. Usually after a few days, when he feels better, he starts eating again. Otherwise, you need to contact your veterinarian to prescribe medications that normalize the functioning of the digestive system.
It is also recommended to use vitamin complexes that strengthen the body's immune system. They prevent the occurrence of many diseases that are extremely undesirable during a difficult period for the animal.
The puppy should have a sufficient number of objects that he can chew. It is best to buy them in clinics, where they offer toys specifically designed for the time of teeth change. If you select toys yourself, they should not be too hard or sharp so as not to damage the gums.
A caring owner must understand at what age the puppy’s teeth will begin to change and prepare for the growing up stage. It is important to be patient; your pet can be capricious, like a small child. If there are any abnormalities, you should immediately contact a veterinarian to prevent irreversible complications.
Ailments
Puppies of this breed are characterized by various ailments, both funny and unpleasant.
Why does he hiccup frequently?
Puppies may hiccup frequently for a variety of reasons. If the hiccups are short-lived, then most likely the pet is thirsty after a vigorous game, or he filled his stomach too quickly, or the dry food was too dry. In any case, you need to give your pet something to drink.
REFERENCE. Before feeding the puppy, it is better to soak the dry food in water.
Hiccups can also be caused by a foreign body stuck in the stomach. If your puppy is prone to frequent bouts of hiccups, you should contact your veterinarian.
Breathes quickly
If the puppy, being in a static position, has rapid breathing, then most likely he is sleeping. The fact is that sleeping dogs, when their sleep reaches the rapid phase, tend to dream. In these dreams, they can experience the same emotions as in real life, and rapid breathing is proof of this.
But if your pet breathes more often than 10-30 breaths per minute while awake, this is a reason to show it to the veterinarian. Since this is already a symptom of respiratory disease.
Diarrhea
If diarrhea is not accompanied by vomiting, fever, dizziness and drowsiness, it is necessary to change the puppy’s diet. In cases where all the symptoms are together, the only vital decision is to take the dog to the veterinarian.
Dandruff
One of the reasons for the appearance of dandruff may be the presence of parasites in the puppy, such as worms and hair mites. Regular deworming will help get rid of them. If your pet does not have any of these, then there is a lack of vitamin A. High-quality food, shampoo and vitamin supplements will correct the skin condition. In a situation where a vitamin-enhanced diet does not produce results, you should think about skin fungus. In this case, only a veterinarian can get rid of the disease.
Stages of tooth change in puppies and related problems
All dog breeds have two types of teeth - molars and milk teeth. Puppies have 32 teeth before they fall out, and adult dogs have 42. Teeth are the main criterion for determining age. A dog's beautiful teeth are a source of pride for the owner. And in order to prevent their improper development, it is worth knowing all its stages, as well as the dog’s well-being, behavior at this time and possible problems.
The role of teeth in the life of an animal
The dental system of dogs is the main device for the primary mechanical processing of food; its importance is difficult to overestimate. It is adapted for cutting meat like scissors. All breeds, without exception, have sharp and large fangs that are saber-shaped to tear food or prey into pieces.
We recommend this article:
How many teeth should dogs have at different ages?
Cheek molars are necessary for quickly cutting food and gnawing bones. They have a triangular shape and a jagged end that resembles a blade. Premolars are used for tearing and grinding. The incisors are used for biting. Dogs use their front incisors to perform various auxiliary actions, such as catching fleas.
Stages of development
Puppies are born toothless, and the first teeth begin to appear only after a month. The jaw and teeth do not grow at the same rate, so you may feel like there is too much space between them. This will be corrected when they are replaced by permanent ones. The animal either swallows or loses its milk teeth. The first molars begin to emerge in the third month. At this time, the rudiments of permanent teeth are formed, and the roots of milk teeth weaken and dissolve, which causes their loss.
The last thing to fall out is the fangs. They have a pointed shape and are fragile. With normal development in decorative dogs, the shift should end by the seventh month; in large breeds this happens somewhat faster.
Teething order
The first teeth to appear are the baby teeth. This occurs on the 20-30th day from birth. Dogs are predators and first of all they grow 6 incisors on each jaw, 12 in total. Canines - 2 canines on each jaw. The last to erupt are the 16 premolars. The total number of baby teeth is 32 in a puppy aged 2-3 months (in some breeds – 28).
Large breeds
In large dog breeds, this process is fairly quick and painless. The huge mouth provides space for proper eruption and further development of the dental arch. Problems occur when the animal is exhausted, has suffered a deep maxillofacial injury, breeding control and breed line are not maintained, or close mixing of blood has occurred.
The process is similar to large breeds, but the closer to the lower limit of medium-sized dogs, the greater the likelihood of pathologies (delayed shifts, missing teeth, etc.).
Small breeds
This group of dogs is most susceptible to dental risks. The process itself is very slow and delayed compared to other large dogs. Breeds with flattened faces often suffer from missing teeth. Access to the oral cavity is limited and control is difficult.
Behavior of dogs during teeth changes
You won’t notice much of a difference, only your pet’s desire to chew on something will increase. For these purposes, it is better to buy him a special rubber toy and teach him not to touch the furniture. You can also give him large natural bones and crackers. During this period, the puppy needs to chew as much as possible - this speeds up and facilitates the process of changing teeth.
Immunity is declining, so dogs should not be vaccinated or subjected to heavy stress. Also, you should not place your puppy in an environment with too low a temperature, which risks deteriorating your pet’s well-being.
Quite rarely, it turns out that a puppy goes through a difficult period of replacing teeth: diarrhea, lethargy, and fever begin. If this happens, it is best to consult a veterinarian before self-medicating. But in general, such complications happen to very few people, and you will most likely remember the stage as increased energy and gnawing on everything that gets in your way.
Description of the Siberian Husky breed
The most successful husky standards and characteristics of the breed are given using the example of dogs of British selection. This variety was not chosen by chance. Since the beginning of the registration and description of the Husky breed at the beginning of the 20th century, three directions have been developed:
- sled dogs - they are also called working dogs. Nowadays, they are used to deliver mail, take children on rides, and entertain tourists. These dogs are hardy, have moderation and proportionality in all parts of the body;
- racing dogs - although they are used in sleds, like their working relatives, they are used exclusively for the sporting interests of the owners. In this category of huskies there are two subtypes: dogs for skijoring (sport riding in small teams - up to 4 dogs in a team) and dogs for competitions in sixes and sleds with a large number of dogs. In the first version, the husky’s exterior is distinguished by greater height at the withers and muscular legs;
- show category husky, or show breed - this type was bred to participate in entertainment programs and dog shows. Two subgroups have been formed here - European and American type. American representatives of this breed look larger, with a massive chest; European relatives are more elegant and graceful, and the characteristics of the breed are more clearly visible in them.
Since there are still differences in the three categories of these dogs, British Huskies were chosen as a sample of the breed, so it is worth focusing on their description.
All types and categories of Siberian Husky are characterized by common features: a slightly shortened muzzle, dense coat and thick undercoat. All dogs are medium in size, with excellent running qualities and well-developed muscles. All types of dogs have a compact build. When looking at a husky from any angle, you immediately notice the ease of gait, smooth lines, proportional addition of the body, legs and head.
Features of the proportions of the Husky breed are as follows:
- the length from the stop to the back of the head is identical to the length from the stop to the nose;
- the length from the shoulder joint to the ischial tuberosity is greater than the height from the ground to the highest point at the withers.
Head
The husky's skull is absolutely proportional to the size of the dog's body. The head of Husky dogs is medium in size, slightly rounded closer to the ears and widened to the maximum in the eye area. Gradually the shape of the head narrows from the eye sockets towards the nose.
The dimensions of the Siberian Husky skull, from the stop to the extreme point of the occipital bone, are the same as the dimensions from the stop to the tip of the nose. The nose shape is round. The structure of the nasal tissue is elastic. The nostrils are well developed and open.
The eyes of Siberian Huskies are almond-shaped, with a distinct slanted cut, and the color varies from brown to blue.
The ears of Husky dogs are tightly set, medium in size and slightly rounded at the ends. Closer to the head, the ears have a wide base. Both ears are close to each other and point vertically upward.
Husky lips are characterized by the same pigmentation as on the nose. The structure of the lips is dense and massive, but the lips themselves are not thick.
The dentofacial apparatus is highly developed and has massive, but not long teeth with a characteristic scissor bite.
Neck
Siberian Huskies of any type - working, sporting or show dogs - have the same neck that stretches proudly above the body. The shape of the neck is slightly curved. When moving, especially with a load in a harness, the husky characteristically stretches its neck forward, forming an almost perfectly even straight axis with the entire body.
At the same time, the head also extends forward.
Frame
Since Husky dogs have a fairly large heart, it requires more space in the chest. This anatomical feature explains the narrow, but strong and deep chest.
The deepest point of the Husky's sternum is located just behind the elbow joint, on its horizontal axis.
Other features of the case are:
- wide arrangement of ribs;
- massiveness and strength of the rib bones;
- oblique type blade;
- The bevel angle of the scapula is no more than 45 degrees relative to the axis of the back;
- the shoulder joint is slightly beveled relative to the vertical axis;
- the line of the back, starting from the croup and ending with the top point of the withers, is absolutely straight; the husky's back appears to be very strong;
- back size - medium length.
The width of the back of purebred Siberian Huskies is also of medium size. The proportional ratio of length and width of the upper back gives the dog a compact appearance. This makes the exterior feel tightly built and durable.
Closer to the rear, a slight slope is noticeable in the croup area, which is necessary so that the dog can limit the pushing movements of the hind legs.
Front legs
The stance of the forelimbs complements the dense build of Siberian Huskies. The legs are positioned straight and parallel, at an even distance from each other.
If you look at the dog from the front, you can see that the front legs are slightly apart. Although the bones of Siberian Huskies are quite massive and strong, they are lightweight. The muscles of the front legs are moderately expressed.
Both elbow joints are evenly and tightly pressed to the body of the body. They are located straight, without internal turns and do not turn back either at rest or when moving.
The characteristic structure of all joints of the husky's forelimb is well-developed ligaments, cartilage tissue and muscle fibers. In addition to the strength and density corresponding to the Siberian Husky standard, almost all the tissues of the front paws are resilient and elastic.
The structure of the wrist joint is particularly flexible.
A slight slope is noticeable when viewed from the left or right at the metacarpus of the front paws. The shape of the paws of the forelimbs is regular oval, without distortion. The pads are dense and thick. A husky's front paws usually have dewclaws, which are necessary for grooming. But since they are often injured in working-type dogs, breed standards allow their removal.
When running fast, the front paws are noticeably brought forward, while the distance between the tracks of the front and hind limbs is practically absent. With free, slow running, the gap between them increases.
The toes of the front paw of a Siberian Husky have good fluff. There is some hair between them and the paw pads.
Hind legs
The stance of the Husky's hind legs is as straight as the front legs. They are also parallel and slightly spaced below when assessed from the front of the body.
The texture of the muscle tissue is strongly expressed on the hind legs. This is especially noticeable in the area of the knee, hip and hock joints.
Other features of the Husky standard in the hind limbs:
- tight articulation of the knee joint, with a slight angle;
- low position of the hock joint;
- massive hip joint, strong and durable.
All joints of the hind limbs have well-defined angles and slight slopes.
The paws of the husky's hind limbs are straight and of medium size. They do not turn back when moving. In a state of rest, the toes are tightly adjacent to each other. The shape of the hind legs is oval, with pronounced compactness. The pads are adapted for movement on loose snow and hard crust - they are durable, quite elastic and have a thickened sole.
Thanks to the anatomical structure and physiology of the hind and forelimbs, the Siberian Husky has an even gait and uniform running in a characteristic gait style. The dog can also move at a moderate trot. If necessary, speed develops quickly, with the hind paw moving after the front limb of the same name.
The hind limbs are evenly pubescent; there is dense undercoat even between the toes and paw pads.
Tail
Northern Huskies have a tail located below the horizontal axis of the upper back. It has a fox-like shape, with a rich coat of fur. In normal condition, the tail is carried slightly raised above the level of the upper back or may be lowered. During the active or alert stage, the tail may be curled slightly to one side or forward, taking on a sickle shape.
Wool
These dogs, resistant to low temperatures, are characterized by a thick and dense coat - it allows them to maintain a stable body temperature, preventing the animal from freezing at rest or in strong cold winds.
The Husky's coat is of moderate length, with a dense and dense undercoat. It, like wool itself, has a soft, pliable structure. During shedding, there is practically no undercoat on the body. The fur is straight, smooth and close to the body.
The Northern Husky's coat color ranges from completely white to perfectly black. The standards allow the presence of marks in the head area.
This is usually a mask-shaped color on the animal's face, the opposite shade of the main coat color. As a rule, such a mask has light colors.
The standards and characteristics of dogs of this breed allow several types of coat color:
- black and white color, with color proportionality 50/50. In the lower part of the body with this color, a white tint predominates, and on the top - black. Often the white fill starts from the muzzle. This is one of the most common colors - with a black nose and eye rims of the same color;
- Gray Coated Husky - A common Husky color, with an even shade and a silvery undercoat. The color of the nose and the lining of the eye sockets is purely black;
- silver coat color is less common and is characterized by the presence of white or silver undercoat and light gray wool;
- Agouti color is characterized by uneven filling of the coat and undercoat. The color range of this color is from black to gray, sometimes with spots of a reddish tint. The muzzle has a dark mask;
- The wolf color of the Husky is notable for its dark black color and red patches in the eye area and behind the ears.
Less common colors are absolutely black and absolutely white. A little more often at exhibitions you can see Siberian huskies of fawn, copper, red color, as well as Isabella and sable.
During the process of age-related molting, the color of a husky may change. More often it changes only the shade, becoming lighter or darker.
Size
The following husky sizes correspond to breed qualifications:
- Male huskies can reach up to 54-60 cm at the highest point of the withers;
- The height of bitches of this breed should not exceed 51-56 cm.
These dogs are characterized by proportionality of body weight and height. The average weight of males, according to the standards established by dog handlers for these dogs, is up to 20.5-28 kg. In females the weight is 15.5 kg - 23 kg. The weight of animals depends on the type of breed - working, sporting or exhibition. In the latter case, body weight may be greater. The slenderest are the sporting huskies.
Possible problems
Dogs can develop a problem called double rows of teeth. This happens due to the fact that the permanent tooth does not grow under the milk tooth in order to displace it in the future, but next to it.
Problems when changing teeth lead to:
- incorrect location of emerging teeth;
- small jaw or too rapid development;
- genetic predisposition;
- lack of calcium.
You can deal with this by giving your puppy objects to chew on. Carrots are good for such purposes. It must be given every day. In addition to being a tasty treat, it is also an excellent way to loosen teeth. The puppy is also allowed to chew rags and soft toys, but in no case should he pull objects clamped in his mouth - this will cause the bite to shift.
Sometimes it happens that, despite all the precautions and no matter how you loosen your teeth yourself, they sit firmly and tightly in the jaw (this is called false polydentia). In this case, you will have to discuss their removal with your doctor. Make sure that the operation is performed under general anesthesia.
The reverse disease is hypodontia, in which the number of teeth has grown less than it should. An x-ray will help determine whether this is true, and if confirmed, incisions in the gums made by the surgeon will help to cope.
This kind of problem does not occur often and mainly occurs in dwarf breeds. The most important thing is to constantly monitor the change of teeth and give the dog specially designated objects for biting, then you will not have any difficulties during the period of teeth replacing each other.
Types of bite
The following types are distinguished:
- bulldog (also called undershot);
- undershot;
- normal (or scissor);
- straight (pincer-shaped).
The standards for each variety vary widely, and what is common in breeds like the Pekingese is considered pathological in other species.
bulldog
This overbite is typical in Bull Terriers and Bulldogs, as the name suggests, but is also normal in Pekingese and related breeds.
The structure of the oral cavity is characterized by excessive development of the lower jaw, which protrudes forward. The canines are often exposed with this structure.
Underbite
This type of bite results in insufficient development of the lower jaw, resulting in a large gap remaining between the upper and lower incisors.
This type causes the most problems, as it provokes a number of dental pathologies.
In particular, the most common problem with underbite is the formation of tartar.
Normal
This structure of teeth is determined historically. The ancestors of modern domesticated dogs were forced to get their food by hunting, and for this they had to not only track and overtake prey, but also hold it. This explains the scissor bite.
With this structure, the incisors of the lower jaw are closely adjacent to the back of the upper ones, as a result of which a kind of “lock” is formed. A normal bite is typical for Dobermans.
Among all the varieties, it is recognized as the most “non-problematic”, since the owners of these breeds rarely seek medical help for their pets during the period of tooth loss.
Straight
This type of overbite is unacceptable for most breeds and is considered a serious defect at shows. With a pincer-like arrangement of teeth, the incisors of the upper and lower jaws are located on the same line, as a result of which their ends quickly grind down from pressure on each other.
With this type of bite, molars and canines develop without pathologies.
Expert opinion
Anna Abramenko
An avid dog lover. Experience in veterinary medicine since 2009.
Ask a Question
A pincer-like structure of teeth is normal if it is genetically determined, but it often happens that dog owners themselves develop a straight bite - this happens due to frequent games of tugging with objects.
Recommendations for education and training
Any dog of this breed loves affection and attention. Therefore, during training, excessive praise should not be allowed. Moreover, manifestations of such attention and admiration on the part of strangers should be excluded. Huskies can deliberately provoke this behavior by getting underfoot and begging for treats. From the first days, the dog must understand the primacy of its owner and the need to obey his commands. Being a herd animal, where it is customary for the entire pack to obey the leader, the Siberian Husky will easily accept this state of affairs and will unquestioningly follow the wishes of the owner.
General training recommendations:
- during training, you cannot pick up the animal;
- communication with other dogs should be allowed;
- It is unacceptable to overload with one command for a long time; it is better to repeat these skills after some time or the next day;
- Fairness to your pet is one of the main conditions for successful training. It is necessary to show strictness for sabotaging given commands and generously reward with treats for zeal in their execution.
You should start training with the dog getting used to its own nickname, performing the most primitive commands: “Come to me!”, “Lie down!”, “Nearby!”, “Walk!”, “Sit!”