How to understand that a dog is pregnant and the mating was successful? In the first two weeks, this cannot be determined for sure, even by laboratory methods. And here's why: during this period, the maturation of eggs is still ongoing, sperm are still functioning in the genital tract, continue their journey to the egg, finally, fertilization occurs, then the fertilized eggs move through the fallopian tubes and are implanted (introduced into the wall of the uterus).
How to understand that a dog is pregnant
This happens 12-15 days after the first mating and only at this time the embryos begin to secrete their own unique hormones into the mother’s blood, in particular relaxin. A diagnostically significant increase in the dog’s blood occurs on days 21-25 from the moment of mating, and only on these days can you, by taking a blood test, tell with 100% accuracy whether the dog is pregnant or not. Before this, only indirect signs can be observed that may indicate a possible pregnancy.
First signs of pregnancy in dogs
The most reliable first sign of changes in the body of pregnant bitches, confirming the success of mating, is considered to be the cessation of estrus within a week after mating. Otherwise, there are no clinical symptoms of pregnancy in the first couple of weeks.
Within 14 days after fertilization, the owner can note only indirect behavioral signs of pregnancy in the pet:
- the animal seeks solitude;
- daily activity decreases;
- the female strives to dominate other pets if they live in the same territory with her;
- the dog hides its belly and can also become aggressive when trying to feel it.
However, if no changes occur in the animal’s behavior after mating, the possibility of pregnancy should not be ruled out.
During the period under review, the pet should not experience any vaginal discharge, changes in temperature or lack of appetite. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately visit a veterinarian.
Possible complications during pregnancy
Dogs can experience various complications during pregnancy. They are associated with disruption of the functioning of certain organs and systems.
Common complications also include the appearance of edema, which is a consequence of an unhealthy diet, as well as a lack of physical activity in the animal.
The most dangerous disturbances are during labor. It is quite difficult to predict their occurrence, but the help of a specialist will come in handy. Therefore, you should not delay contacting a veterinary clinic if the birth process is delayed or the owner has any doubts about the correctness of its course.
Timely contact with a veterinarian allows you to provide your dog with qualified care and preserve healthy offspring.
Main signs of pregnancy in dogs
In general, the course of pregnancy is identical for all dog breeds.
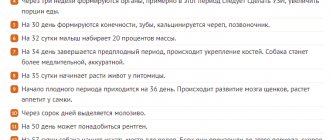
In the third week, most females notice a decrease in appetite, which is associated with changes in hormonal levels. Animals tolerate toxicosis caused by hormone imbalance in different ways. Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting.
By the end of the first month of pregnancy, the dog becomes lethargic, rests more often and longer between games and walks, and sleeps more than usual.
Also, by the end of the third week, the female may experience copious mucous discharge from the loop. Normally, the owner may not notice them and can only identify them by the fact that the dog begins to lick itself more often.
Despite the fact that in dogs, pregnancy proceeds relatively quickly and the fetus develops at a high rate, external changes in the animal are noticeable only by the middle of the second trimester.
By the end of the fourth week, the appearance of the pet’s nipples changes, and from 30-35 days after fertilization, the dog will begin to gain weight. During this period, the animal must be provided with a varied diet, enhanced with vitamin complexes and microelements, but the dog should not be overfed in order to avoid the development of obesity and subsequent complications during childbirth.
In late pregnancy, the frequency of meals often increases. As the fetus grows, the pressure on the stomach increases, the volume of food consumed per feeding decreases, and, therefore, in order to be satiated, the dog begins to eat more often in small portions.
The gestation period for puppies is on average 9 weeks, but depending on the individual characteristics of the animal or the characteristics of the breed, it ranges from 55 to 70 days.
How long does it take for dogs to give birth?
Canine labor is divided into three stages. Contractions in the first stage can last 6-12 hours. Puppies are usually born 45-60 minutes apart, but the mother dog may take up to four hours between puppies. Here's what happens at each stage.
The first stage of labor in dogs: the onset of contractions
The first stage is defined as the relaxation of the cervix and the beginning of intermittent contractions. However, you are unlikely to notice contractions at this stage of the labor process.
During this stage, your dog will become restless, going in and out of the nesting box, panting, digging, and sometimes even vomiting. This stage can last 6-12 hours.
Second stage of canine labor: stronger contractions and labor
The second stage of labor begins with stronger and more frequent uterine contractions, which ultimately lead to the birth of the puppy. Puppies are usually born every 45-60 minutes, with 10-30 minutes of vigorous straining. Expect some puppies to be born tail first, as this is normal for dogs.
The mother takes a break during whelping, and she may not exert herself at all for four hours between puppies.
If your dog strains for more than 60 minutes or requires more than a four-hour break, take him to the vet as soon as possible.
How nipples change in a pregnant dog
One of the earliest signs of pregnancy in dogs is a change in the appearance of the nipples.
In dogs that have given birth, the halos lighten (turn pink) by the end of the second week after fertilization. During the first pregnancy in a female, this symptom may manifest itself mildly. More often, the skin on the nipples thickens and becomes slightly rough.
On days 45-50, the nipples of a pregnant dog swell greatly, especially those closest to the pelvis. The body temperature around them changes noticeably. When pressed, colostrum is released. Irritation of the mammary glands can cause discomfort in the dog.
What changes occur in the second month of pregnancy
The dog's belly enlarges, the mammary glands swell and darken, and viscous mucus may be released from the loop. The pet becomes less active and quieter, and its appetite increases. Starting from the 50th day, the puppies can be seen moving.
After 50 days of pregnancy, the female begins to look for a secluded place for herself and her puppies. Owners should monitor the nesting and find a cozy corner for the pet. If your pet's size allows, offer her a large cardboard box lined with moisture-absorbing diapers. Keep in mind that in such a “kennel” the dog will spend a lot of time with the puppies; there should be enough space for everyone. If necessary, trim one side to make it easier for your dog to enter his shelter. Be prepared for the fact that your pet will drag your “nest” to another, more convenient place for her. You'll have to come to terms with this.
First signs of pregnancy in small breed dogs
For small breeds, pregnancy causes more discomfort than for large dogs. Since there are usually many puppies in a litter, the dog begins to gain weight early.
- By the time of birth, the pet's weight may increase by half. The abdomen is significantly rounded; in the later stages, the outline of the fetus in the womb can be easily guessed, and the heartbeat and tremors can be felt.
- Because of its vulnerability, the pet becomes more affectionate, and sometimes intrusive. Insistently requires the owner's attention.
- The animal quickly becomes clumsy. At the first signs of pregnancy, small breed dogs should limit physical activity and replace intense activity with frequent quiet walks.
- A large volume of gestating puppies, as a rule, affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The pet cannot consume large amounts of food; it needs crushed food and frequent meals.
- Also, due to the strong pressure inside the abdominal cavity, the animal’s urge to urinate becomes more frequent; in the later stages, the dog cannot tolerate it, and it has to be walked more often.
- In addition, the more puppies in the litter, the faster intrauterine development occurs; as a result, pregnancy in small breeds of dogs lasts on average 58-63 days.
Signs of pregnancy in large breed dogs
Pregnancy in large breed dogs does not manifest itself externally for a long time. The dog maintains grace and mobility, avoiding only jumping and increased stress on the hind limbs.
- The female gains weight slightly, in direct proportion to how many puppies are expected. If the pregnancy is small, then the volume of the abdomen practically does not increase.
- Large breeds carry puppies on average 3-4 days longer. Since the puppies are quite large, there are few cubs in the litter, most often 2-3.
Puppies care and nutrition
Follow these guidelines for caring for newborn puppies.
Approach puppies carefully
Although you can pet and hold puppies constantly, it is important not to interfere too much in the first week or two of their life as they are very susceptible to illness and this can be stressful for mom and babies.
Be careful when approaching puppies, as some mothers may become aggressive towards people or other pets if they feel threatened.
As puppies get older and more rambunctious, your dog will want more and more time to sleep, sleep, exercise, or interact with family members. Give your dog a chance to get away from the puppies, but make sure he comes back often to check on them.
Provide warm bedding
Puppies cannot regulate their own body temperature until they are 3 to 4 weeks old. For the first four weeks of their lives, you should provide mother and puppies with a warm, clean crate or bedding.
Use a heating pad under the puppy crate or a lamp above it to keep the puppies warm. Make sure there are unheated areas as puppies will need to move away from the heat source if they get too hot. The temperature in the warm zone should be around 36°C.
Start socializing your puppies
At this point, if the mother dog allows it, you can get the puppies accustomed to your presence. Interacting with them at an early age can help them fit into the household well.
Keep an eye out for "poor workers" or "puppies" (puppies that are much smaller and don't grow as quickly as their littermates) as they may have health problems that affect their ability to grow. If you notice that one of your puppies is smaller or has less energy than the others, consult your veterinarian.
Puppies should not be taken away from their mother and sent to a new home too quickly, as they learn very important social rules and behaviors from their mother and siblings.
Puppies should not be separated from their mother if they are less than 8 weeks old. Wait until they are 10 weeks old so they can get the most benefit from social interaction with their mother and littermates.
Start weaning at 3-4 weeks of age
Once the puppies are 3-4 weeks old, you can begin the weaning process by giving them access to puppy food. You can mix dry food with water or canned puppy food to make it easier for them to eat.
They should still have constant access to their mother as she will continue to breastfeed them. Over the next few weeks they will rely more and more on puppy food rather than being fed. Most dogs wean their puppies between 5 and 6 weeks of age.
Contact your veterinarian immediately after the puppies are born.
Contact your veterinarian for his or her recommendations on when puppies should be examined first.
They may want to see them right away to evaluate for cleft palate, umbilical hernia and other health problems, or they may advise you to wait until they are a little older.
Many veterinarians recommend deworming at regular intervals, starting at 2-4 weeks of age and vaccinating at 6 weeks of age.
How to test for pregnancy in a large dog
In large breeds, abdominal tone increases to protect their young. For this reason, it is almost impossible to feel pregnancy until later stages.
Not even every specialist can detect the fetus of a large dog by palpation. In addition, if pressure is unsuccessful, the embryo can be damaged, which will most likely lead to the death of the fetus, and with it, provoke premature birth and the loss of the entire litter.
To ensure the safe and healthy development of the offspring, you should contact your veterinarian at the first signs of pregnancy to have the animal examined.
What to do after determining pregnancy
DogWhat kind of pet do you have?Add a pet and get access to free consultations and advice!Cat
After the veterinarian confirms the pregnancy, he will select an individual observation plan for a specific dog. Veterinarians strongly recommend carrying out modern diagnostics of the pet and monitoring it during the entire gestation and not being content only with improvised means at home.
Throughout the entire period, it will be necessary to do ultrasound several times. And after the 40th day, using the same study, it will be possible to calculate the amount of time before birth. Also periodically take blood tests (biochemical and general clinical). And on the 40–42nd day, the veterinarian will recommend deworming to exclude intrauterine infection.
Next, all that remains is to wait for the upcoming birth, prepare the apartment space for the arrival of the puppies and talk in advance with the veterinarian about how the birth will be carried out and who exactly will do it.
And let the replenishment be happy!