Veronica Igorevna Sharipova
veterinarian Petstory
Staphylococcus in dogs is one of the most common infections that require timely diagnosis and treatment. And in recent years, the number of diseases caused by these bacteria has only been growing. But at the same time, there are a large number of myths around this microorganism. How to treat Staphylococcus aureus in dogs? Is staphylococcus transmitted from dog to person? What is the difference between the disease in puppies and adult animals? We will answer this and many other popular questions in our article.
Features of the disease
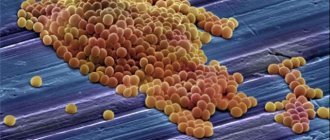
Staphylococcus in dogs is caused by spherical bacteria - representatives of the genus Intermedius.
They are present everywhere, therefore they are found on the surface of the body of animals and humans and are normal. Any damage to the skin leads to increased proliferation of microbes. If the body's immune system is strong, its cells quickly cope with infection. Otherwise, the activity of bacteria causes an acute inflammatory process, accompanied by necrotic phenomena and the formation of pus. Staphylococci are characterized by:
- resistance to external environmental factors, due to the special structure of their cell membrane;
- the ability to synthesize enzymes and toxic compounds that facilitate penetration into the animal or human body;
- resistance to many antibiotics.
Most often the disease occurs in the hot season. The risk group includes young, elderly and weakened dogs.
Content
1. What contributes to the development of staphylococcus in dogs 2. Symptoms of staphylococcus in dogs 3. Complications of the disease 4. Correct diagnosis to detect infection 5. Features of treatment 6. Is canine staphylococcus transmitted to humans 7. Preventive measures 8. Is there a vaccination against infection 9. Video about the disease
Staphylococcus in dogs is quite common. Even despite careful care, constant hygiene procedures, proper, balanced nutrition, regular scheduled vaccinations and vitamin supplements, no one is immune from the problem.
Large breeds of dogs need long walks, which have a beneficial effect on their health. But it is walks that often become the causes of infection with a disease that affects the blood. Staphylococcus spreads quickly in natural environmental conditions, and at the same time is an incredibly tenacious organism.
Bacteria are constantly present in the body of healthy animals, but are in a dormant state. With normal immunity, the disease practically cannot develop. However, with the onset of heat, the risk of infection increases many times. This is due to the increased activity of dogs. Walks become longer, and contact between pets and each other increases. Any damage to the skin allows harmful organisms to enter, causing unbearable itching. The disease should not be ignored - the infection poses a serious danger, spreading rapidly in the animal’s body, causing complications and causing pathologies in all vital organs and systems. Owners need to promptly seek help from specialists. Timely comprehensive therapeutic treatment helps reduce the risk of developing a dangerous complication and premature death of the dog.
What contributes to the development of staphylococcus in dogs?
The cause of the development of staphylococcus in dogs can be any disorder in the body that leads to a decrease in protective forces, for example:
- poor nutrition with minimal vitamin content;
- damage to the skin and/or mucous membranes;
- liver dysfunction;
- high levels of sugar in the bloodstream;
- internal and external parasites;
- past illnesses;
- hormonal changes.
If staphylococcus develops independently, it is called primary. If it is a consequence of another disorder, then they speak of a secondary form.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
Staphylococcus aureus in the nose of a child: symptoms and treatment
Staphylococcus aureus in the ear of an adult and a child, treatment methods
What diseases does Staphylococcus aureus cause in humans?
Long worms in dogs: main types, description and methods of treating parasites in dogs
Staphylococcus aureus in the stool, nose, throat and intestines: symptoms, degrees of infection and treatment
Doctor Komarovsky about Staphylococcus aureus in children (infants)
Symptoms of staphylococcus in dogs
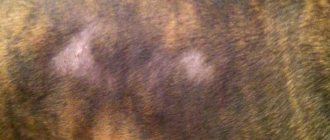
At the very beginning of infection, the symptoms of staphylococcus are concentrated on the skin or mucous membranes. These include:
- round spots of pinkish or red color;
- pus;
- hair loss in the area of the spots;
- severe itching;
- bleeding of damaged areas (the pet chews the spots due to severe itching);
- boils (when bacteria penetrate into the deep layers).
Staphylococcus aureus is especially dangerous - in addition to the above symptoms, it causes disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. The clinical picture manifests itself in vomiting, intestinal upset, and rapid onset of dehydration.
Main symptoms
Staphylococcus aureus can easily be confused with some other disease. Most often it is disguised as dermatitis. The owner should be alert to the following symptoms:
- fever of a constant or intermittent type;
- vomiting and diarrhea leading to dehydration (in the intestinal form);
- inflammation, swelling around damaged skin;
- discharge of purulent exudate from the wound;
- matted fur and hair loss;
- itching;
- damage to mucous membranes;
- unpleasant odor from the skin and ears;
- slow healing of wounds.
In some cases, the wounds turn into boils or poorly healing, very painful ulcers. As the infection progresses, the animal’s condition worsens, which is why it is so important to show your pet to a specialist in a timely manner.
Complications of the disease
If even a small infected area is detected, immediate action must be taken. Ignoring the disease can cause serious complications.
- Development of inflammation in the ears. The animal develops an unpleasant odor from the ear canal, and pressing on the auricle leads to a squelching sound. At the same time as the ears, the organs of vision and nasal mucosa may become inflamed: characteristic discharge, swelling, and redness appear.
- In bitches, staphylococcus is complicated by vaginitis, endometritis, and pyometritis. Males suffer from inflammation of the prepuce. Pathologies quickly become chronic, which subsequently complicates treatment.
- The spread of staphylococcus through the bloodstream is fraught with the formation of numerous boils, carbuncles, and inflammation of the follicles. Located in the area of the interdigital folds on the paws, they especially worsen the dog’s condition.
Characteristics and features of the microorganism
Staphylococci belong to a group of organisms that includes thousands of subspecies and are shaped like a bunch of grapes. These bacteria surround people and animals in everyday life. Since staphylococci exist almost everywhere, they can greatly affect the weakened body of animals, especially dogs. In the summer, the risk of developing a staphylococcus infection increases, since the pet walks a lot and often comes into contact with other individuals. Animals kept in ideal conditions are also susceptible to the influence of this microorganism.
Treatment of staphylococcus
Treatment of staphylococcus in dogs is carried out comprehensively. First of all, it is necessary to destroy the pathogen. To do this, the pet is injected with a staphylococcal bacteriophage. In addition, they activate the animal’s own immune system using nonspecific and specific methods. In the first case, the use of immunostimulants is indicated, causing an increase in the number of immune cells. For specific treatment, staphylococcal toxoid (active immunotherapy) or antistaphylococcal serum (passive immunotherapy) is administered. The latter option is applicable only at the beginning of the development of pathology. Both cannot be used at the same time.
The complex of therapeutic measures necessarily includes antibacterial agents. Staphylococci quickly develop resistance to antibiotics, therefore, as a rule, several drugs are prescribed one after another or in combination (according to indications). The following drugs are widely used in the treatment of staphylococcal infections: Enroxil, Tsiflox, Enrosept, Quinokol, Baytril. In some cases, taking antibiotics continues for about a month or more.
In parallel, symptomatic treatment is carried out.
- To dry the wound surface, it is irrigated with various solutions. For this purpose, enzymatic and antibacterial drugs are used: potassium alum, dermalot, tribasc, lysozyme.
- Dimexide or novocaine lotions help relieve itching. Suprastin or tavegil are used for the same purpose.
- If the infection has spread to the inner ear, a powder mixture of novocaine and dermatol is injected into the ear canal. For high intensity symptoms, novocaine is used intramuscularly.
- Inflammation of the intestinal mucosa requires not only the use of antibacterial drugs, but also agents that restore the microflora - probiotics, for example, lactobacterin.
- Strengthening the immune system and increasing the body's resistance is facilitated by the introduction of vitamin complexes into the diet.
If the cause of staphylococcus in a dog is diabetes, thyroid disease or allergies, then appropriate medications are prescribed at the same time.
How to cure a dog
The basis of therapy is medications for external use and oral administration. Treatment with folk remedies can only be used in addition. Drug therapy involves:
- Treatment with antibiotics. Drugs are selected that are suitable for the individual animal and are effective against gram-positive microorganisms. Usually, antibiotics of the quinol group are chosen - Tsiflox, Enrosept, and others. If the disease progresses, several drugs from different subgroups are prescribed.
- Immunostimulants. Strengthening the immune system increases the body's internal strength to resist infection. A separate drug was created for dogs - polyvalent staphylococcal toxoid (SPT). It is effective only at the beginning of infection, when only a small area of skin is affected.
- Staphylococcal bacteriophage. This is a virus that is specifically introduced into the animal’s body. It provokes the death of pathogenic microorganisms. It is considered one of the most effective treatment methods and is performed only by a specialist. The disadvantage of the procedure is the relatively high price.
Along with the main therapy, medications are prescribed to eliminate itching, redness, and inflammatory processes on the skin. An effective ointment for staphylococcus on the skin - Lysozyme. The wounds are washed with Dimexide solution, and novocaine compresses are made for relief.
Treatment with home remedies using traditional recipes complements the basic therapy. The following tips are popular:
- add apple cider vinegar to the bathtub (half a glass per 5 liters of water);
- make lotions out of it, keeping them on the wounds until dry;
- wash the affected area with burdock tincture;
- Use tar soap when bathing.
Until the dog experiences relief, he will feel lethargic. Provide peace and protection from external irritants and other pets.
Can a person become infected?
Is canine staphylococcus dangerous for humans? Experts have different opinions. Some argue that a sick pet is not contagious to the owner and animals living nearby. Others believe that the dog needs to be isolated from others.
Mainly, staphylococcal infection poses a danger to weakened organisms. If there are small children, elderly people in the family, or those who have recently suffered or have any illness, then, of course, their risk of contracting an infection is much higher. The same applies to our smaller brothers.
Healthy people and animals have nothing to fear, since strong immunity quickly copes with bacterial invasion. This explains the fact that staphylococcus is normally found on the surface of our skin, but does not lead to disease.
Diagnostics
In the modern world, making a diagnosis of “staphylococcosis” is not difficult. In case of skin forms of the disease - for example, in the presence of staphylococcus in the dog’s ears or in case of skin lesions (when staphylococcus is found only on the skin), to make a diagnosis, the doctor only needs to take a cytology of a smear-imprint. But in case of systemic lesions, as well as in inflammatory diseases of the bladder (that is, when staphylococcus is detected in urine tests), a comprehensive examination of the pet is required: a general blood test, blood biochemistry and sampling from affected organs for bacteriological culture with mandatory titration of the results to antibiotics.
Home Safety Measures
You can reduce the likelihood of infecting others with staphylococcus from your dog, as well as avoid the development of complications in it, if you take appropriate measures from the very beginning of the disease:
- ensure the isolation of the pet;
- treat the room where the animal is kept with disinfectants several times a day;
- regularly replace the bedding with a clean one; when washing, use boiling water for at least half an hour;
- Wipe the dog during the day with a solution of tar soap (lightly, over the fur), do the same with nasal discharge - soap particles remaining on the surface of the animal’s body prevent further proliferation of pathogenic microbes.
What to do at home
The dog owner must strictly follow the veterinarian's instructions. In addition, we must not forget that Staphylococcus aureus can be transmitted to humans, so when caring for a sick pet, you must take the necessary precautions:
- Wash your hands with laundry soap, using a brush to treat the area under the nail plates.
- Use disposable medical gloves. After handling the dog, they must be thrown away.
- Isolate the sick animal from other family members and pets.
- Collect and destroy dog feces by burning.
- Disinfect the room where the pet is located, its toys, bedding, etc. It is better to burn things that are not of great value.
A sick dog should receive a complete, balanced diet, enriched with vitamins and macroelements. If the animal experiences vomiting and diarrhea, gastric lavage and cleansing enemas are performed. A fasting diet is indicated - at least 12 hours.
Since the body is exhausted, parenteral nutrition is performed. During the recovery period, low-fat broths and water porridges are gradually introduced. Products should be introduced into the diet gradually, feeding in small portions.
Preventive measures
Unfortunately, it will not be possible to completely prevent the development of staphylococcus in dogs, since any injury to the integumentary tissue provokes the growth of bacteria. However, through preventive measures it is possible to reduce the likelihood of illness to a minimum.
- To reduce the risk of microbes penetrating deep into the body, bloodstream and lymph, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system in every way: provide a diet rich in vitamins (if necessary, give them additionally), and regular long walks.
- If there are sick animals in the house, it is important to limit contact between them as much as possible. Dogs should not communicate with stray homeless relatives and cats.
- Monitor your dog's vaccination schedule carefully. Timely vaccinations will not only prevent many diseases, but will also increase the pet’s immunity.
- Pay attention to the condition of the skin and fur of your four-legged friend: regularly carry out hygiene procedures, avoid the formation of crumpled hair, the appearance of adhering particles (grass, feces and others), inspect the skin for injuries, especially in the folds.
- It is necessary to identify and destroy external and internal parasites in a timely manner, use prophylactic agents against fleas and ticks, and regularly carry out routine deworming.
- If you find even minor damage to the skin or mucous membranes, immediately treat them with antiseptic drugs.
- In the summer, do not allow your pet's body to overheat.
Stress can reduce immunity, so it is recommended to protect your pet from negative situations as much as possible.
Attentive attitude towards your pet and a quick response in case of detection of an illness will serve as the key to the destruction of microbes and the prevention of their spread to others.
Prevention measures
The bacterium is not only deadly for dogs, but is also transmitted to humans, so it is important to take care of prevention. The main measure is vaccination. Antistaphylococcal drug (ASP) is used. The solution is administered twice with an interval of 15-20 days; the required amount of the substance is calculated based on the weight of the animal.
I practice vaccinating pregnant bitches, this will protect the puppies. In this case, the dog is vaccinated on the 20th and 40th day of gestation. It is better not to violate the timing of drug administration; increasing the interval reduces the therapeutic effect, and reducing it increases the risk of infection.
Other preventive measures are aimed at strengthening the immune system and reducing the possibility of infection. Among them:
- Balanced diet. If the animal is naturally fed, add vitamin complexes to the diet; if not, choose good quality dry food.
- Give your dog adequate physical activity and walks in accordance with the animal’s needs. Remember that different breeds have high or low activity requirements.
- Monitor your pet's health, conduct regular inspections of the skin for damage, allergic rashes, and insect bites. If your pet has a lot of folds, wipe them every few days.
- In spring and summer, be sure to protect your pet from ticks (drops, collars).
- Avoid contact with sick dogs.
- Provide timely assistance for other diseases and exacerbations of chronic processes.
- Protect your dog from stress, it reduces the body's protective functions. This is especially important for small breeds, their nervous system is unstable.
Staphylococcus on the skin is a common occurrence; it lives in the environment, but should not enter the bloodstream. Otherwise, the dog will suffer from dermatitis, inflammation of the mucous membranes, and intoxication. All symptoms bring suffering; an animal experiencing constant discomfort will instinctively aggravate its condition. Left untreated can lead to death.
Modern medicine can successfully combat infection, so if it cannot be avoided, act immediately. Do not limit yourself to your own efforts; home treatment will not be enough.
Reasons for the development of infection
Each animal has individual resistance or predisposition to the pathogen. Under the influence of certain factors, the risk of inflammation increases.
Causes of staphylococcal infection in dogs:
- Poisoning that adversely affects the functioning of the kidneys and liver, damage to these organs by infection;
- Problems with the animal's immunity;
- Lack of vitamins A, E, B in the body;
- Increased level of carbohydrates in the body, presence of diabetes mellitus;
- Skin diseases, such as demodicosis, fleas and ticks, allergic reactions;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
- Insufficiently balanced diet, lack of minerals and vitamins to ensure a normal level of vital activity of the body;
- Absence or low level of resistance of the animal’s body to the pathogen of staphylococcus;
- The presence of injuries on the dog’s skin that become inflamed and affected by harmful microflora;
- The predisposition of certain dog breeds is genetic.