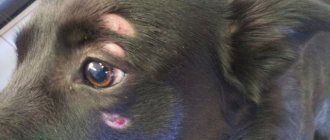
The third eyelid is a vertical fold of mucous membrane near the inner eye. Its main function is considered to protect and moisturize the eyes without losing the ability to see. Let's consider a disease such as third eyelid adenoma, its treatment without surgery and the causes of its occurrence. The name adenoma indicates a benign tumor. Therefore, formations develop in this tissue, but infrequently.
The pathology usually affects animals in childhood or at five to seven years of age. The owners pay attention to the swelling and redness of the third eyelid. Mostly the swelling is round or in the form of a roller. The disease can affect representatives of any breed. But it is more often observed in Pekingese, Pugs, Chihuahuas, Toy Terriers, English and French bulldogs, Mastino, Canne Corso, and Cocker Spaniels.
What is a third eyelid adenoma in a dog?
Adenoma of the 3rd eyelid is a common ocular pathology in which the lacrimal gland of the third eyelid falls out. Dogs have the following lacrimal glands:
- Accessory gland (gland of the 3rd century). It is located inside the stroma of the eyelid and is clearly visible in all pets.
- Accessory glands. They are localized near the free edge of the eyelid.
- Main gland. It fits tightly to the eyeball and is located under the upper eyelid.
These groups form the tear film - a thin layer covering the conjunctiva and cornea. It has a nutritional and protective function.
Sometimes prolapse of the third eyelid gland is observed. The ligament attaching it to the periorbita weakens. This is often influenced by hereditary predisposition.
The pathology does not spread to the eyeball, but in any case it is dangerous. The disease cannot go away without medical intervention, so if you detect a hypertrophied pink formation in your pet’s eye, you must contact a veterinarian. Typically, therapy consists of surgery, that is, its removal.
Third eyelid: where it is located and functions
The third eyelid is a crescent fold located at the inner corner of the eye. It performs protective and auxiliary functions.
When you touch the eyelid and if you tilt your head, protection is immediately triggered - the cornea is covered by the third eyelid. This prevents all kinds of damage.
In the thickness of the third eyelid there is a lacrimal gland that produces about a third of all tear fluid. Also on its surface there is lymphoid tissue, which consists of numerous follicles. They are the most powerful immune defense for the eye.
Main symptoms
It is quite easy to identify diseases because the symptoms are characteristic. An oblong or round formation is observed near the medial canthus. The shade varies from pink to bright red.
The enlarged gland is then damaged when blinking, injuring the eye cornea. Uncomfortable sensations appear, which is why the pet begins to scratch the problem area. This leads to infection and damage. Follicular hypertrophy also develops, purulent-mucous discharge and lacrimation appear.
Initially, the pathology is observed in one eye, but after one to three months the second eye may be affected. If the necessary medical intervention does not occur, there is a risk of developing dry eye syndrome and pigmentary keratitis.
Types of neoplasm
There are several types of adenomas:
- Cystic. Its structure is bag-like, closed.
Papillary. With this form of pathology, growths appear, which are papillae protruding into the lumen of the gland.- Polypoid. This is a kind of polyp formed as a result of hyperplasia.
Adenomas are of solid and tubular type. The first form is characterized by weak development of the stroma and fusion of the glandular epithelium into a single whole. In the second type of adenoma, narrow tubules are lined with epithelial cells.
Depending on the number of formations, the disease is divided into single and multiple. In the first case, only one node appears. With adenomatosis there are many of them.
Surgery to eliminate the disease
Treatment methods for this pathology have been controversial among doctors for many years. Ten years ago they came to a consensus that there is one way - this is surgical intervention, removal of the prolapsed gland. But it was soon discovered that the dog then developed dry kerato-conjunctivitis, which progressed for a long time and disappeared only after two years. The gland also produces approximately 40% of tears.
Therefore, they put forward a decision that the gland should be returned to its place so that it continues to work normally - to produce tears, which have the function of protecting the eyeball. Surgeons must prevent the eye and gland from drying out and becoming inflamed.
If the pathology has not reached a serious stage, it is possible to realign the gland by a specialist using ordinary tweezers. This option is not considered effective, since there is a high probability of repeated loss. The procedure is carried out if no more than a day has passed.
Surgical reduction of the gland remains the current method. If it is severely inflamed, treatment with antibiotics will be required before surgery. Therapy can last several days.
The dog's affected eye is instilled with a 0.25% solution of Levomycetin. The procedure is carried out once a day. Experts advise laying a special film with Kanamycin. At the same time, 1-2 drops of a 1% Dicaine solution are instilled.
There are two options for surgical reduction: the “pocket” technique and its modifications and fixation of the gland to different orbital structures using non-absorbable sutures and their modifications. The first option is the most common. The operation is carried out quite simply without special equipment.
Video: surgical treatment of third eyelid adenoma in dogs
After immersing the pet in anesthesia, applying antiseptics, and fixing the eyelid speculum, the eyelid is secured by the edge with clamps. Then it is pulled out of the conjunctival sac so that the bulbar region of the conjunctiva and the prolapsed gland are turned towards the doctor. Incisions are made under and above the lacrimal gland, maintaining a distance between them.
The specialist immerses the lacrimal gland deep into the orbit and closes the conjunctiva in the incision areas. Their edges are sutured using absorbable sutures, the lacrimal gland remains in the pocket, preventing its appearance on the surface. At the end of the surgery, the dog requires a week of simple care.
Removal of the third eyelid is necessary only in particularly advanced cases - with degenerative or necrotic changes. During the operation, general anesthesia is used. There is no need for deep anesthesia.
The process involves a microscope and specific ophthalmons. The specialist uses them to “package” education. This prevents injury and the appearance of rough scars. The procedure usually lasts a quarter of an hour. It is allowed for dogs of any age, but the consequences for older pets can be unpredictable. The price of the operation depends on the size of the animal, the region and the specific clinic.
Recommendations for caring for your pet after surgery
Sometimes after surgery, pets are left under the supervision of a doctor. To relieve swelling, antimicrobial drugs and antibiotics are prescribed. If the procedure is carried out correctly, no relapse is observed. Great Danes are an exception; they often develop new formations.
After surgery, the owner must provide the dog with proper care at home. A special protective collar will be required. It is used for no more than 15 days. It is recommended to use eye drops and ointments. With proper treatment, signs of the disease disappear within a month.
Removal
There is no drug treatment program for problems with the third eyelid. The only way out is surgery to remove the third eyelid.
Purpose of surgery:
- do not disturb the anatomical structure of the third eyelid,
- preserve the mobility of the eyelid as much as possible;
- exclude the development of the disease in order to preserve the animal’s vision.
What does the eyelid look like after surgery?
The specialist will inform you about the need to remove cartilage or part of the lacrimal gland only as a last resort, if the consequence of maintaining the tumor may be loss of vision.
The operation is performed under general or local anesthesia, is not complex, and does not require a long recovery period.
How to feed after surgery
After the operation, to prevent the dog from injuring himself with his paw, he needs to wear a protective collar . During the first 7-10 days after surgery, you should prevent the development of bacteria by using antibacterial medications for the eyes.
You should not trust the operation to a novice veterinarian. Resection errors can cause functional disorders of the eyeball.
How to cure adenoma without surgery?
Many owners wonder whether it is possible to do without surgery. Drug therapy regimens are quite rarely prescribed. Medicines help get rid of swelling of the third eyelid. But usually there is no significant improvement.
It is important to distinguish an adenoma from lacrimal gland prolapse. The first is a benign tumor that needs to be excised. Before the procedure, the specialist recommends a biopsy.
You can do without surgery in the following cases:
- There is swelling of the eyelid, but the diameter of the formation is small and does not cause discomfort to the pet.
- The dog does not rub its eyes; the third eyelid extends beyond its edge by no more than 25 percent of its size.
- Education does not increase in size.
To provide first aid, eliminate the inflammatory process, reduce pain and anxiety in your pet, you can take the following measures:
- Instillation of Dexamethasone. These are corticosteroid-based eye drops that have anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory properties. A couple of drops in the third eyelid area twice a day is enough for your pet. The active substance quickly enters the tissues, but it should not be used during purulent processes. After the procedure, tear fluid may begin to leak.
- Eye rinsing with Tsiprovet. The active ingredient of the drug is the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. It has a broad spectrum antimicrobial effect and quickly eliminates inflammation from infection. An anti-inflammatory effect is observed. Two drops lead to a burning sensation and anxiety for the pet, but improvement soon occurs.
- Use of a special protective collar. It is necessary to prevent further damage to the visual organs.
Disease prevention
Since the main cause of third eyelid adenoma is considered to be genetic predisposition, before purchasing a puppy of the breed in which the disease occurs most often, you should carefully study its pedigree.
Hunting and guard dogs are also at risk, since pathology often occurs due to mechanical injuries. For preventive purposes it is necessary:
- Choose places and times of day for a walk with a minimum of dust, smoke and bright sunlight.
- Combine medications with vitamins and immune-strengthening medications.
- Treat eyes with antibacterial solutions.
Only a veterinarian can diagnose the disease and begin its treatment. The sooner the owner goes to a medical facility, the greater the chance of a favorable outcome and no consequences.