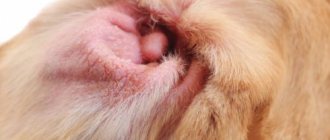
The appearance of any neoplasms on a pet’s body always causes concern for the owner. But not in all cases we are talking about a malignant tumor; it could very well be an ordinary lipoma. A dog's fatty tumor is a benign fatty growth that does not pose a serious threat to the life of a furry friend and does not cause persistent pain in him. The article will discuss in detail what a lipoma looks like, what are its causes and symptoms, and how to treat this type of tumor.
Types of wen and their features
There are 3 types of lipomas, which are classified depending on the location:
- Intermuscular. These neoplasms have diffuse properties - they are able to penetrate soft tissues, causing acute pain and discomfort when moving skeletal muscles. Cannot be treated. If a lipoma occurs in the intermuscular space of the legs, the limb swells and the dog begins to limp.
- Internal. Appear on organs: liver, gastrointestinal tract, lungs. Pathology can only be diagnosed by performing an ultrasound scan from a veterinarian.
- Superficial. They are located on the skin in the form of nodules. Soft neoplasms contain only adipose tissue and do not pose a threat to the animal. If the tumor feels like a dense lump, it is made of connective tissue.
In the absence of treatment and unfavorable living conditions, many wen may appear in one place. The accumulation of tumors is called lipomatosis.
Predisposition to lipomatosis
The disease has a genetic predisposition.
The breeds most susceptible to the disease are the Golden Retriever, Labrador and American Cocker Spaniel.
Pets are also prone to the disease:
- elderly;
- females;
- overweight pets.
Wen occurs many times more often in overfed pets
Causes of wen appearance in dogs
There are causes of lipoma in animals:
Take the Attention Test! Find 10 differences! (click right here!)
Find the answer Are you bothered by some problem or question? Enter “Breed” or “Name of the problem” into the form, press Enter and you will find out everything about the issue that interests you.
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Unfavorable environmental conditions;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Kidney and liver failure;
- Protein metabolism disorder;
- Diseases of the digestive tract;
- Hormonal imbalance and pathologies of the endocrine system.
Sometimes a lipoma is formed due to blockage of the lumen of the sebaceous gland with sebum or dirt, which causes inflammation. The swelling is subsequently overgrown with adipose tissue.
Prevention
Based on the prerequisites for the formation of wen, conclusions can be drawn regarding the prevention of this disease. The dog needs a complete diet without excess protein, with vitamins and minerals. Taking regular walks in the fresh air every day will also help you avoid obesity. After 5–6 years, the pet’s menu should be reviewed and made easier for the normal absorption of all important substances. Even if a lipoma has already formed, regular examinations by a veterinarian (1-2 times a year) will help avoid negative consequences.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Complications caused by lipoma
In the absence of external and internal irritants, superficial lipomas do not pose a threat to the life of the animal. In a benign formation, there is a risk of cancerous degeneration of cells. This phenomenon is observed when receiving burns or when an infection is introduced into the site of the lipoma, when the tumor is damaged or due to improper treatment. Wen can transform into a malignant neoplasm called fibrosarcoma. Dogs at risk include:
- With a hereditary predisposition to developing cancer;
- Regularly scratching and biting the wen - constant irritation of the skin leads to cancerous degeneration;
- With metabolic disorders;
- Those who do not receive care and live in unfavorable environmental conditions;
- With dermatological diseases.
The greatest danger is represented by wen covered with dark spots. The latter are an accumulation of melanin. The pigment appears due to the fact that the lipoma absorbs ultraviolet radiation. The risk of a fatty node degenerating into a cancerous tumor increases by 40%. To exclude the possibility of malignancy, a biopsy of adipose tissue is performed.
Sometimes wen can grow under the influence of external factors. A tumor on the skin that increases in size interferes with movement. Internal neoplasms compress blood vessels, nerves and internal organs, complicating the peristalsis of smooth muscles. When nerve fibers are pinched, the dog feels pain.
If the superficial tumor is not removed, it will continue to grow. Subsequently, the wen located on the chest, paws and abdomen begins to curl. The adipose tissue contained in it will compress the vessels that deliver oxygen and glucose to the lipoma. As a result, the part of the neoplasm that does not receive nutrients dies. Necrosis gradually develops, requiring surgical intervention.
Dangers and forecasts
If the seal does not cause discomfort to the animal and does not grow, then the only problem is loss of aesthetics. In other cases, the danger depends on the location of the formation:
- Paws. Large lumps in this area cause severe pain and lameness.
- Neck. Constant pressure on the carotid artery can lead to sudden death.
- Internal organs. They lose functionality, causing general malaise and secondary pathologies. The appearance of pain is characteristic of compression of the nerve roots.
The transformation of a benign tumor into liposarcoma is very rare and is typical for animals at risk for oncology. Despite the low probability, this diagnosis must be excluded first.
In most cases, lipoma is operable and does not recur. A cautious prognosis is given only when the formation grows into neighboring tissues. Such a tumor is difficult to remove entirely, so after surgery a new one may form in place of the old lump.
What to do first
It is necessary to recognize the lipoma as soon as possible, and then take the animal to the veterinarian. Superficial lipoma can be detected visually in short-haired dogs. The neoplasm should be examined by parting the hairline and palpated. The wen looks like a small oval-shaped swelling with a smooth surface. Pressing your fingers on the tumor should not cause pain or discomfort in the animal. Lipoma can be either soft or firm to the touch. The neoplasm remains mobile.
Long-haired pets should be examined for wen during water procedures. The thick undercoat will not allow you to examine and palpate the tumor in detail when the dog remains dry.
The difference between a benign tumor and cancer
A malignant lump is usually lumpy and has indistinct edges, unlike a lipoma, which appears as a smooth, spherical formation. Cancerous tissue grows quickly and is prone to ulceration, while wen develops slowly (if it does not grow into deep tissues) and is injured only under external influence.
A fatty cyst is usually soft, while a cancer lump is always hard and elastic.
There are other types of growths that require special attention and treatment to avoid serious complications.
It can be:
- papilloma (wart)
- Tumor
- abscess
- cyst
- hematoma
- mycetoma
- sporotrichosis
How to treat at home
Drug therapy and physiotherapy are not prescribed for the treatment of lipoma. Any drugs, electric current and magnetic waves will not be able to destroy the fatty and connective tissue contained in the tumor capsule. Folk remedies are considered ineffective for resolving tumors.
The low results from drug and alternative treatment are due to:
- Increased blood supply to lipoma;
- The location of the tumor in hard-to-reach places: between muscles, on internal organs, in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the skin;
- High risk of cancerous degeneration of cells.
The effects of drugs lead to tumor growth, so self-treatment of wen is considered life-threatening for dogs.
Associated symptoms
A wen is a small subcutaneous lump that rises on the body as a noticeable tubercle. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- softness and free rolling during palpation;
- round or oval shape;
- absence of pain, inflammation, fever, bald areas and metastases;
- slow growth.
Please note that, in addition to adipose tissue, the lipoma also contains connective tissue. When the latter predominates, the ball is denser, but still mobile.
The appearance of bald spots, redness and wounds is possible only with scratching. If an animal constantly itches and licks the formation, then it greatly bothers it.
Associated symptoms not directly related to the lump appear when internal organs and limbs are affected. In the latter case, the dog may tuck its paw and limp.
What to do if the wen is inflamed
If the tumor swells and gradually increases in size, it will need to be removed as soon as possible. It is prohibited to get rid of wen at home using a knife:
- Violation of the integrity of the capsule leads to infection. If pathogenic microorganisms get inside the tumor, a purulent abscess will begin.
- Excision of the skin to remove large tumors without the use of painkillers leads to the development of painful shock. When getting rid of small wen, the dog will experience discomfort and acute pain, constantly tear and run away from the owner.
Why are fatty cysts dangerous?
The location can be any, but more often it is the subcutaneous tissue of the back, neck, chest, and limbs. A small growth on the body, in the singular, does not cause much harm to the pet, but as the growth increases, discomfort and a deterioration in the quality of life are possible.
Located on the neck, the lump can compress large blood vessels that supply the brain, which leads to oxygen starvation of the tissues.
Large wen on the limbs or armpits cause inconvenience when walking, which is why the animal moves little and refuses to walk.
As the growth grows, the skin stretches, causing itching. Trying to get rid of it, the pet licks the surface, chews out tissue, as a result of which pyogenic bacteria enter the wound, causing an inflammatory process.
In females, a lipoma can form in the mammary glands. The neoplasm is injured and is also prone to degeneration into cancer.
Often fatty cysts appear inside the abdominal cavity, causing functional disruption of organs, their displacement and compression.
Diagnosis of lipoma in a veterinary clinic
To determine the type of tumor, a specialist uses diagnostic methods:
- Performs an external examination: excludes tissue pigmentation, identifies other neoplasms on other parts of the body;
- Palpates the skin;
- He takes a piece of tissue for a biopsy: using a syringe, the veterinarian pierces the wen capsule and collects cells from the deep layers of the lipoma for analysis;
- Excises the tumor with a scalpel if necessary.
The last diagnostic method is used only if the wen capsule has been damaged. The veterinarian strives to obtain information about the tumor quickly, because an infection could have entered the open wound. If the tissue begins to fester, the dog requires urgent surgical intervention.
Causes of the disease
It is worth saying right away that in most cases the exact etiology of the appearance of lipoma remains unknown. Even a qualified specialist, without additional diagnostic methods, will not be able to say for what reason the tumor arose. However, there are factors that can provoke this neoplasm to a greater extent, we list them:
- Metabolic disorder. In the animal's body, there is insufficient production of the enzyme responsible for protein.
- Inactivity of the pet. This is especially true for those animals that live in cramped spaces, for example, in a small apartment.
- Age. According to statistics, older individuals who have crossed the threshold of 7-8 years are more likely to suffer from wen.
- Dysfunctions in the functioning of the internal secretion organs (gallbladder and liver).
- Genetic predisposition.
- Gender. According to statistics, wen appears 45% more often in females.
Having dealt with the reasons, let’s move on to the question of what symptoms are characteristic of a lipoma, and how to determine that an animal has a wen.
How is a wen removed?
Lipoma is treated with surgery. The operation is performed in a hospital and is not complicated - the dog is sent home immediately. The cost depends on the size of the tumor and its location. Veterinarians often set prices from 1,500 to 4,000 rubles for removing a wen.
Small tumors are removed using a local anesthetic, larger tumors are removed under general anesthesia. In order for the operation to proceed without complications, the dog should not eat food the day before the procedure. You can give your pet water.
The surgical intervention takes place in several stages:
- The veterinarian disinfects and excises the skin over the tumor. The wound is washed with water to remove excess blood.
- Adipose tissue is located in a capsule, which is penetrated by many capillaries. After excision of the skin, the specialist separates the lipoma from the vessels and surrounding skin.
- The main vessel supplying the tumor is ligated.
- After cleaning the capsule from adipose and connective tissue, the skin is sutured. Air is first removed from the cavity and washed with antiseptics.
Intermuscular and internal lipomas require layer-by-layer dissection of soft tissue. To detect this form of neoplasm, veterinarians use ultrasound. After surgery, the tumor may reappear. Relapse of the disease can occur as a result of stress received during surgery or metabolic disorders in the dog’s body.
During the postoperative period, the owner must follow the recommendations for caring for the pet:
- Treat seams with an antiseptic;
- Apply antibacterial and anti-inflammatory ointments to the wound;
- Give the animal wound-healing drugs, vitamins;
- Put a collar on your dog to prevent him from biting or licking the stitches.
If the size of the lipoma does not exceed 1 cm, then the operation is not performed. Swellings do not cause pain or discomfort and have a low risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor. Surgical intervention is not performed on puppies and elderly pets - they may not survive anesthesia. Old pets are prescribed intramuscular injection of Ligfol in an individual dosage. The drug helps reduce the rate of tumor growth and prevents cancerous degeneration of cells.
Prepare before going to the vet
In the office, you may have to provide the veterinarian with all possible assistance (hold the animal while they take blood for analysis, give an injection, extinguish aggression, calm your voice, scratch its ears, stroke it). If you know that you are terrified of blood, IVs, or definitely cannot withstand the type of medical interventions, then perhaps you should ask a friend or relative for help.
Find a veterinary certificate, veterinary passport.
https://dog-care.ru/zdorove/bolezni/zhirovik-kak-lechit-domashnih-usloviyah.html
Take:
- Leash;
- Collar;
- Muzzle;
- Carrying;
- A pack of napkins;
- litter;
- Bowl, water (at the veterinarian's discretion)
Prepare answers to possible questions from the veterinarian:
- Are all vaccinations up to date on the animal?
- Pet’s behavior in recent days, appetite;
- His diet;
- What drugs and medicines did you give to the animal;
- Latest test data (if available).
It’s better to make an appointment in advance - you’ll save time and be able to calculate when you’ll have to take time off. This does not apply to life-threatening situations where you will have to take an animal to a veterinary clinic without an appointment.
Be affectionate with your pet, play, talk to him. You can take his favorite toy with you so that while you wait for your turn at the reception, you can distract your friend from the new environment.
Furry, feathered or scaly ones also need to be prepared. No matter how much you want to treat your little one with something tasty, remember: you need an empty stomach. Feeding is prohibited!
You can wash your animal without using detergents. But it is important not to touch your pet if there is nasal discharge, watery eyes, salivation (salivation), dandruff, scratching, rashes, skin scabs, loss of hair/feathers/scales, wounds and other external manifestations of a potential disease.
If the veterinarian has instructed, collect the animal’s urine in a sterile container, and pick up the feces with a stick (no blades of grass, specks, or debris). Transfer the feces into a sterile container. Send to the biochemical laboratory within 6 hours. The feces are examined for eggs of roundworms, pinworms, tapeworms, liver flukes, echinoccus, alvecoccus, pork tapeworm, bovine tapeworm, and gastrointestinal bleeding is detected.
At the veterinary hospital, the animal’s blood will be analyzed for antibodies to allergens, viruses, bacteria, and parasites.
Choosing a veterinary clinic
We determine the veterinary clinic where you plan to go. A big PR company doesn't promise quality. The price is explained by the huge amount of money invested in advertising and “signboarding” of the establishment.
It’s great if you can ask your friends about clinics where their pets were treated “humanely.” If you travel far from them, it may be worth sacrificing time for the health of your pet.
A few more tips on how to spot an unverified veterinary clinic:
- Refusal to provide certificates and licenses for veterinary activities.
- Strange and suspicious behavior of the veterinarian (inconsistency, flattery, attempts to intimidate, shouting).
- Prices are too low (compared to other organizations).
- Refusal to freely visit the veterinary clinic.
“We have a sanitary day”
Beware of scammers!
When you contact the veterinary clinic, you are informed: “we cannot accept you at this address, sanitary day/repair/inspection.” How much intelligence does a dispatcher have? The client is persuaded to have a veterinarian come to his home. The price does not change.
A veterinary clinic can exist purely nominally. And the invited “Aibolit” will not bear responsibility. There is a high probability of running into a person without a veterinary diploma or simply an unprofessional.
It is better to find time to visit the veterinary clinic on your own. This is safer for the animal.
Games on feelings
In real veterinary clinics there will be elements of “divorce”.
Veterinarians say that this is often determined by the client’s wallet. The greater the opportunity to pay for services and the more the owner worries about his pet, the more likely the animal will be prescribed additional immunostimulants, dietary supplements, water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins, and special food. There are cases when this is really necessary (pedigreed, show animals, weakened after a serious illness). But it will be good if you ask your veterinarian in detail about the need for each appointment. Find out in detail about the results of the examination and analysis of your pet’s condition. Be persistent. Do not give in to attempts to intimidate you, be consistent in your questions. Consult a specialist who does not work at this veterinary clinic. If it turns out that half of the prescriptions are prescribed to enrich the veterinarian’s pocket, and not for the health of the animal, feel free to leave. And do not forget to leave a negative review about the organization - other owners may also suffer.
How to find out the truth
Another possible way for veterinarians to make dishonest money is to conceal the diagnosis. Let's say a veterinarian discovers a malignant tumor in a cat. But if he says that the tumor is benign and treatable. A housewife who dotes on her pet will give money for already useless procedures, medications and surgical interventions.
The veterinarian may deliberately “downplay” the diagnosis in order to earn more money. If something doesn't add up, insist on clarification. There is no need to be intimidated by unfamiliar terms - take a short break and try to find information on the Internet.
You are free to leave (or threaten to do so) to another clinic at any time.
Make sure that the veterinary clinic is honest - get tested in an independent laboratory.
Justice
What to do if an animal was injured as a result of unprofessional actions of a veterinarian:
- Write an official complaint addressed to the head of the clinic.
- File a complaint with the city veterinary department.
- You can contact Rospotrebnadzor.
- Contact a lawyer for help
The Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” and Article 245 of the Criminal Code “Cruelty to Animals” are the grounds for considering claims regarding the work of veterinary clinics.
Saving
What to do if funds are limited and your pet needs medical care:
- Some procedures can be carried out independently. Giving a drug injection to a cat or dog is not difficult. Dressing uncomplicated wounds is also sufficient. Ask your veterinarian to teach you.
- How to properly give a pill to an animal: hide it in a lump of tightly rolled minced meat. If the animal bites through the decoy, you can crush the tablet and dissolve it in water, milk, liquid porridge, or food.
- If an animal has been prescribed a course of vitamins or some other non-medicinal but expensive drugs, it may be worth finding analogues at a lower price.
- There are various benefit programs in which you can participate. This could be, for example, sterilization, castration, or vaccination of an animal.
Important points
- Refusal to vaccinate. This is dangerous for the animal and all those who will come into contact with it (people). Vaccination is a scientifically proven method of preventing many infectious diseases. Get your animal vaccinated by a trusted veterinarian (or with his approval yourself). It is important to get vaccinated against rabies - this is a fatal disease induced by the Rabies lyssavirus virus, which cannot be cured, but can be prevented.
- Anesthesia - inhalation, intravenous, anesthesia - epidural, conduction. They are necessary so that the animal does not suffer, to prevent painful shock. The veterinarian’s “hands on” are important here - both overdose and weak anesthesia lead to serious consequences (shock, poisoning, death) for the animal.
- Sterility, antiseptic. If you see that the veterinarian does not follow the rules of antiseptics (reuses disposable syringes, diapers, bandages, does not treat hands with antiseptic after contact with the previous animal), the best choice would be to contact another veterinarian.
- Important medicines:
- Antibiotics - amoxicillin, tilozil, trimethoprim, sulfadiazine, lincomycin, marbofloxacin;
- Antipyretics - paracetamol, salicylic acid preparations, antipyrine, butadione, amidopyrine;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - vedaprofen, choline salicylate cycloferon, aspirin;
- Anesthetics - novocaine, lidocaine, dicaine, trimecaine;
- Hemostatics - fibrinogen, thrombin, vikasol, phytomenadione, calcium chloride, etamsylate;
- Antiparasitic - praziquantel, aversectin, albendazole, ivermectin, fluralaner.
If you care what happens to your pet, you should not neglect appointments.
Don't let unverified veterinary clinics endanger your pet and profit from their owner's feelings! If you have time and desire, it is worth trying to achieve justice in case of violation of ethical or legal standards.