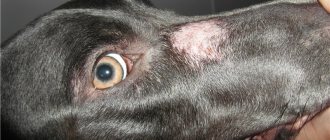
Typically, an eyesore in a dog occurs when the damaged eye membrane, during recovery, becomes covered with a whitish film (leukoma), which is connective tissue.
This pathology occurs, as a rule, on the basis of keratitis - inflammation of the cornea. It is imperative to treat this ailment, since it is unsafe and can result in blindness. Therefore, if this happens to your pet, you must urgently take serious measures, since it is almost impossible to get rid of such a disease on your own.
What it is
A cataract is also called leukoma. This is cloudiness in the eye caused by mechanical damage or infection. The cornea recovers after the lesion, but is overgrown with a white film. It also worsens the dog’s vision.
Leukoma appears as a milky white film covering an area of a dog's cornea. An aggressive inflammatory process can cause the cataract to continue to grow. So the scar can become higher than the cornea and even begin to fuse with the iris of the eye.
Connective tissue scars can be divided into 3 types.
- Central - appears in the middle of the cornea of the eye and is completely covered with a film. The dog becomes almost completely blind and can only distinguish between light rays.
- Peripheral - a cataract occurs at the edges of the cornea. The process of inflammation stopped in time preserves the pet’s vision. However, the dog loses peripheral vision.
- Total - the film covers the entire eye of the dog, which leads to complete blindness.
What is a thorn
This is a lesion of the eyeball that develops as a result of a progressive disease or injury. Before starting treatment, the veterinarian finds out which part of the eye is affected and what is causing the pathology.
Veterinarians call a thorn in dogs leukoma . There are several varieties based on the type of location:
central – affects the middle of the eyeball;- peripheral - with this pathology only the rim of the cornea becomes cloudy, the center remains crystal clear;
- total - the entire eye is covered with a cloudy, whitish film.
In all cases, the animal remains at risk of complete loss of vision.
Forecast and consequences
The prognosis for leukoma depends on the causes of the development of the pathology, the degree of neglect and the chosen treatment method. Correct and timely diagnosis allows you to start therapy at an early stage of the disease. In this case, the prognosis will be favorable.
If an advanced stage is present, then there is a high risk of undesirable consequences, including complete loss of vision.
With surgery there is a greater chance of recovery. To minimize the likelihood of complications, the doctor may temporarily stitch the eyelid to allow the cornea to fully recover.
Is it possible to cure a thorn?
It all depends on the reasons for its appearance.
If the nature of the pathology is viral or infectious, then it can be dealt with with the help of medications or folk remedies.
In advanced cases, when pathology of the lens, cornea, retina has developed, in the presence of a malignant or benign tumor, treatment is carried out using surgical methods.
Causes
There are many reasons why eyesores appear in dogs. Leukoma is a symptom that indicates inflammation. Most often, the culprit is keratitis - inflammation of the cornea, due to which it becomes cloudy and the eye turns red. The eyesore also occurs due to glaucoma - sudden jumps in intraocular pressure. Glaucoma causes various vision defects, including visual impairment.
A corneal ulcer, or ulcerative keratitis, distorts the cornea of the eye, causing pain and cloudiness. Leukoma can lead to complete blindness. Due to the inversion of the eyelid, the eye becomes damaged and its healing entails the appearance of a cataract.
Leukoma also occurs for other reasons not related to diseases. These are complications after operations, various injuries, age-related changes in the body. Sometimes a cataract appears due to pathology or abnormal structure of the eye as a whole (it does not close completely).
Types of disease and photos
A cataract is a scar formation. A type of pathology is scar spots, which differ in density and size:
- The spot is clear, transparent, small.
- The cloud is translucent and blurry.
- A cataract is a dense thick spot of gray or milky hue.
This pathology is dangerous for a dog; due to sprouted blood vessels, the cornea is subject to deformation. Vision disappears completely or partially.
In addition to scar formations, there are other types of pathologies. Among them are:
- Corneal ulcer – can be superficial, deep, or descemetocele. A through lesion of the eye occurs.
- Keratitis is an inflammatory process in the cornea.
- Degeneration – deposition of calcium salts, cholesterol.
- Endothelial dystrophy is a disease unique to old dogs.
- Endothelial edema - the pupil becomes blue. This happens after vaccination.
- Cataract – the lens begins to become cloudy.
- Glaucoma - at the initial stage the eyeball becomes enlarged, and then clouding is observed.
Attention! The deeper the lesion, the less pain. If a pet squints and then stops, this does not mean that everything has passed.
Prevention and eye care
Prevention involves careful monitoring of the dog. Provide as little opportunity for eye injury as possible. This can be done either by another animal or by a simple twig.
It is important to pay attention to even minor symptoms (the dog squints, hides from the light). If an injury occurs, it should be treated immediately without delay.
We must not forget about eye care, especially for brachycephalic breeds, due to the structural features of the skull, they often experience profuse discharge from the eyes.
To care for your eyes, you can take a cotton pad or gauze soaked in liquid. They also use special care products that are sold in any pet store.
If this is not possible, you can use clean water, as well as chlorhexidine (not alcohol). Under no circumstances should you clean your eyes with preparations containing alcohol.
You should not wipe your eyes with cotton wool; its particles may remain on the surface, which will cause irritation.
Puppies
An eyesore is quite rare in puppies; it is a pathology of adult dogs. Treatment of a fragile body has its own characteristics and contraindications. Puppies can often injure their eyes with their claws, so a special cone or collar may be required.
Levomecithin solution can be used to treat the disease in a puppy. In this case, the dosage is reduced.
Tetracycline ointment should be used with caution. This safe antibiotic can cause a number of side effects in case of overdose:
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- loss of appetite;
- lethargy.
In rare cases, puppies may experience an allergic reaction.
Symptoms
By its behavior, the dog makes it clear that it has an eyesore. As a rule, the pet ceases to navigate in space. But the main symptoms include:
- white clouding on the cornea that does not go away on its own within 2 days;
- fear of bright light - the pet hides and looks for dark places;
- blurred vision – the dog looks lost and squints;
- purulent discharge (indicates an infectious origin);
- redness of the eyes;
- tearfulness.
If these signs are present, your pet should be immediately taken to see a veterinarian. If the dog is not given timely help, the eyesore will cause the dog to completely lose his vision.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
In addition to clouding of the pupils, the disease is accompanied by a number of other symptoms. When constantly caring for your dog, they are easy to notice:
- Watery or mucous discharge appears.
- The pet behaves restlessly, is constantly afraid of something, practically does not go outside, and during walks he walks reluctantly.
- The dog tries not to be in the sun, in a room with bright lighting, and spends most of his time in a dark place.
- The cornea becomes cloudy and the eye becomes rough.
- The disease is accompanied by pain and each animal demonstrates this differently.
Treatment of a cataract in a pet begins with a preliminary diagnosis. The veterinarian evaluates the dog’s external condition and asks the owner questions. To make the treatment process faster and more effective, it is recommended to provide information:
- diet;
- frequency of walks;
- contact with other animals;
- date of appearance of the first signs of the disease;
- diseases that the pet suffered from.
After the examination, the veterinarian prescribes treatment.
Attention! If you have self-medicated at home, do not hide this information from your doctor. Often, improper treatment is the main cause of cloudy eyes.
Classification of cataract varieties
- The location of the thorn may be central. It is mainly located in the pupil area. A sign of such an arrangement is complete or partial clouding of the pupil itself. The dog's vision decreases very sharply; unfortunately, with this location of the eyesore, dogs often become completely blind.
- Peripheral location of the eyesore. This discomfort may be located in one of the corners of the eye. Such a thorn usually does not reduce the dog’s vision, so this is the simplest form of the disease, which responds quite well to treatment. Once the first symptoms are eliminated, the animal’s vision quickly returns to normal.
- The most difficult form of cataract is the total location. This type of disease spreads completely, filling the entire area of the affected eye. Typically, older dogs suffer from the total form of cataract. The process is already 100% irreversible. Therefore, many veterinarians recommend euthanizing such animals to avoid suffering.
What is the pathology if a dog has an eyesore?
This disease is quite dangerous. Depending on the location of the leukoma on the cornea, the following types of this disease are distinguished:
- peripheral - the lesion occurs on the edge of the eyeball, and if time is not lost in treatment, the dog may lose only lateral vision, which will not greatly affect its life;
- central - the film covers the main part of the eye, which as a result ceases to see (only light emissions will be distinguishable);
- total - leukoma closes the eye completely and it stops seeing.
The cataract itself is usually milky white or yellowish-white in color. As a result of inflammation, it swells and rises above the cornea, and sometimes it fuses with the iris. In practice, the disease can also be bilateral.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out by an ophthalmologist. Before prescribing medications for cataracts, he determines the cause of the clouding of the eye. If an infection is suspected, the veterinarian will take a scraping from the cornea of the eye. This is the most effective diagnostic method.
Corneal scraping (cytology) is a rather traumatic procedure. This involves taking a sample from the eye for analysis. Therefore, scraping is carried out in rare cases if other methods have not yielded any results.
Electroretinography helps examine the retina of the eye. It is used to assess the light sensitivity of cells. If the doctor suspects ophthalmoherpes (herpetic keratitis), he takes tests (smears) to determine herpes viruses. Serology is used when it comes to fungal infection.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
Ophthalmological diagnosis for vision problems in dogs is based on several step-by-step steps. First of all, the veterinarian conducts a thorough examination of the eyes and determines the strength of the “growth” of the cataract, for which an ophthalmoscope (a device for determining the passage of light) is usually used. To verify the presence of a problem and determine its nature, a cytological examination of a smear from the cornea of the affected organ is performed.
You will be interested to know what patella is in dogs, signs and treatment of the disease.
Considering that the use of this technique is quite traumatic for the organs of vision, it is used only in extreme cases, for example, if the doctor suspects a bacterial infection is joining the inflammatory process. To establish the exact cause of the appearance of an eyesore, other types of instrumental and laboratory studies would be appropriate.
The list of common actions includes:
- collecting fluid from the internal cavity of the eye for a broader study for the presence of pathogenic microflora;
- serological blood test for the presence of fungi;
- diagnosis and assessment of the condition of the fundus;
- electroretinography;
- Ultrasound of the eyeball (available only in large veterinary clinics due to the complexity of the procedure).
An integrated approach to the issue of diagnosing cataracts ultimately allows you to select the most effective methods for solving the problem, thanks to which the dog will preserve its vision and will not experience discomfort.
Briefly about the main thing
- A cataract (leukoma) is a scar formation on the cornea, manifested by clouding of the eye. It is easy to confuse leukoma with other pathologies due to its similar external manifestation.
- There are several causes of the disease - injuries, other diseases and improper treatment.
- Diagnostics can only be carried out in a specially equipped clinic.
- Treatment should be prescribed by a specialist. At home, it is safe to use only tetracycline ointment and chloramphenicol eye drops.
- Prevention involves monitoring the pet’s condition and periodically caring for its eyes.
Why do eyes suffer from allergies?
The eyes are among the “favorite targets” and areas for the development of allergic reactions. The tissues and structures of the eyeball are thin, very sensitive, not very well protected from the harmful influences of the external environment - and therefore especially vulnerable. The cornea, eyelids, eyelashes, sclera, conjunctiva are in direct contact with the air, where particles of countless substances are contained in suspension, as well as with rain and tap water, with cosmetics, shampoos, creams, eye drops and gels, and contact lenses. In addition, in close proximity and in direct communication with the orbit there are many other equally vulnerable mucous membranes (nose, oral cavity, etc.). The eyes are also susceptible to allergic reactions to substances that enter the body, for example, to individually allergenic foods and medications.
Treatment
Treatment for eyesores in dogs is aimed at eliminating the cause. It depends on the diagnosis. Unfortunately, it is very rare to get rid of leukoma completely. In most cases, the film can be reduced to a minimum and vision can be slightly improved.
Medicines are prescribed in 2 cases: for mild inflammation or after surgery. The most important thing is to remove purulent discharge from the eyes and treat them with hydrogen peroxide or boric acid. If the eye has been injured, the veterinarian may prescribe a solution of furatsilin.
To reduce the inflammatory process, the patient is prescribed ointments that contain antibiotics. These include Tetracycline, Kornegel, Oftagel and others. If the disease is catarrhal in nature, the doctor recommends Levomycetin or Hydrocartisone.
It is important! Self-medicating without knowing the reason is very dangerous! Only a veterinarian will competently explain how to cure leukoma in the eyes.
What to do if drug therapy does not help and the cloudiness does not disappear from the eyes? Only surgery will help here. The surgeon removes the film, and in severe cases will be forced to replace the cornea with an implant.
During treatment, a special collar is attached to the dog. Thus, the pet will not be able to damage the eyes with its paws and will not aggravate the situation.
What are the symptoms of leukoma?
The appearance of a spot on a dog’s eye largely depends on the root cause of its appearance. Thus, a thorn after keratitis is characterized by clouding and whitening of the cornea, which, in the superficial form of the disease, returns to normal within 1–3 days. If the disease has affected the deep layers of the eyeball, the cloudy pupil and dots on it persist much longer, and the dog experiences discomfort due to a sharp decrease in vision: the animal becomes restless, looks confused, and its gait seems awkward and uncertain.
Important! Do not try to remove plaque from the surface of your pet's eyeball yourself. Additional impact on the cornea will only worsen the situation, causing irritation and the development of an inflammatory process.
The pet may avoid bright light, and the veil on the surface of the cornea often becomes blue or yellowish, although it may well simply turn white over time. A white spot in the eye often occupies both the central part of the eyeball (next to the pupil) and is localized closer to the edge of the iris, but this area will become cloudy in any case.
It is the appearance of such a characteristic spot of cloudy or white color that is considered the main sign of a cataract, which can be supplemented by other manifestations:
- cloudy discharge from the eyes, sometimes mixed with pus;
- photophobia;
- corneal roughness;
- protrusion of the white spot outward;
- the appearance of redness as a result of burst capillaries (the dog constantly rubs its head with its paw, trying to remove the film lining the eye, thereby only increasing irritation).
Signs
Visually, the thorn, which has occupied more than 20-30% of the eye, can be seen; diagnosis is not difficult.
What the owner can see:
- Cloudy spot on the eye (may appear or disappear).
- Watery eyes, discharge of pus.
- Photophobia.
During a visual examination in the clinic, a veterinary ophthalmologist notes unevenness of the cornea, the appearance of a yellowish film, which is easily removed, but then forms again.
If there is no treatment, the last stage of leukoma is characterized by thinning of the eye membrane, the thorn begins to protrude greatly.
Cataract
This eye disease is associated with aging of the lens, a violation of its transparency - subnuclear (nuclear) sclerosis.
The development of cataracts is most likely at the age of 8 years, when the elasticity of the lens decreases, it hardens and ceases to adjust vision to different distances. It is more common in Golden Retrievers, Poodles, Yorkshire Terriers and Boston Terriers. The disease progresses over the years.
Cataract photo:
Causes
Less commonly, the causes of cataracts are heredity. Acquired cataracts occur after trauma, after inflammatory diseases, diabetes, etc.
Symptoms, treatment and diagnosis
An external sign of cataract is clouding of the lens. The cloudiness of cataracts is uneven. It is possible to recognize cataracts on your own. When a beam of light hits the affected eye, the clouding will shrink in size. In low light, on the contrary, it increases.
In some cases, this dangerous disease can develop for a long time without visible symptoms. But a dog owner may notice decreased vision by analyzing the dog's behavior.
The most reliable way to diagnose an eye disease called cataracts remains to be examined by a specialist.
Treatment without surgery
How to treat cataracts without surgical intervention at home? But no way. The use of medicinal drugs does not allow us to hope for the recovery of our four-legged pet. At best, the progression of the disease will slow down. It is possible to use drugs only at the very beginning of the development of cataracts, when surgery is not yet required. Vitamins and enzymes are usually prescribed.
Cataracts cannot currently be prevented. Do not fall for the tricks of deceivers who recommend Smirnova eye drops, vitaiodurol, vicein, catachrome, vitafacol for the treatment of cataracts . These drugs cannot prevent, slow down, or even cure clouding due to the fact that the nature of the disease is not clear.
When is cataract surgery necessary?
The only effective way to treat cataracts is surgery to replace the clouded lens with an artificial one. From a technical point of view, this operation is very complex. Its result largely depends on the stage at which the application was made to an ophthalmologist. Obviously, earlier treatment guarantees a better result.
The modern technology of lens removal using ultrasound - phacoemulsification - is finding more and more fans. But it is also effective in the early stages.
Prevention
The need for surgery is determined by the animal’s ability to navigate in space using vision. If decreased vision does not allow the dog to move without the threat of harm to health, we can talk about the need for urgent surgical treatment.
- When purchasing a puppy, you should ask whether any of the parents have been diagnosed with cataracts.
- After 6 years, it is necessary to regularly visit a veterinarian.
- Maintain eye hygiene for your pet: wipe and apply eye drops if indicated.
- A nutritious diet and adherence to the vaccination schedule are also important.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is best combined with the main course of treatment. It is advisable to consult a veterinarian before doing this. He will tell you how to cure a dog’s eyesore using unconventional methods.
Boric acid can be replaced with chamomile decoction or strong tea. They are used to wash the dog's eyes daily. Instead of chamomile, you can use calendula.
A solution of honey is instilled into the pet's eyes after washing them. A teaspoon of honey must be dissolved in 50 grams of boiled water. This method has a natural anti-inflammatory effect. Dogs do not like the burying procedure, so it is better to find an assistant.
Pregnant and nursing
The peculiarity of treating an eyesore in a pregnant or lactating dog is that many medications are contraindicated in this condition.
Tetracycline ointment should not be used in dogs during pregnancy or lactation. Lidaz drops can be used, but with extreme caution. The dosage must be prescribed by a veterinarian. A solution of chloramphenicol can be used to instill eye drops into pregnant dogs.
Treatment method for cataracts in dogs
Depending on the causes and stage of development of the disease, the veterinarian prescribes medication or therapeutic treatment.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment for cataracts in dogs is used only in the early stages of the disease. Conservative treatment with drugs is used in the initial stages of the disease and during the recovery period after surgery.
The following drugs are used for treatment:
- To cleanse the eye of pus and secreted fluid, rinsing with a solution of boric acid is used.
- In case of catarrhal lesions, an ointment or solution of levomecithin is prescribed, and novocaine or a suspension of hydrocortisone is injected into the conjunctival sac.
- Antibiotic ointments: Tetracycline, Oftagel, Kornegel. Placed under the dog's eyelid.
- Eye drops: Oftan, Dexamethasone, Lidaza, Hydrocortisone. Drop into the eye 2-3 times a day.
- Vitreous injections. Used for resorption in vascular keratitis.
- Rinsing the eye with furatsilin solution to prevent inflammation after injuries.
Therapeutic methods
It is almost impossible to cure an overgrown cataract using conservative methods, so veterinarians perform surgical removal of the film. In severe cases, the affected cornea is replaced with an artificial one.
Important. After surgery to remove the cataract, the dog is given a special collar to prevent it from damaging the stitches with its paws.
Folk remedies
At the initial stage of the disease, you can use traditional methods of treatment. In the initial stages, a cataract in a dog can be cured using traditional methods. The most successful are the following:
- Onion gruel. 1 teaspoon of grated onion is poured into 100 ml of hot milk. Leave for 8 hours. Instill 1-2 drops 2 times a day.
- Fir resin. Instill 1 drop of juice per day.
- A mixture of celandine and propolis. Mix celandine juice with 1% propolis solution in a ratio of 1X3. Instill 2 drops every other day for a week.
- Rinse the eyes with chamomile decoction.
- Rinse with boiled honey. 1 teaspoon is diluted with a glass of water and heated over low heat for 5 minutes. The eyes are washed with the cooled solution 2-3 times a day.
- Powdered sugar. Injected into the eye three times a day. The powder must first be sifted to remove large pieces. After the procedure, lacrimation increases, this is a natural process
Attention. The action of some folk remedies is aimed at resolving the cataract film under the influence of acids, so they must be used with caution. Improper use may result in burns to the dog's cornea.
Treatment options
Depending on the cause of the disease, drug treatment is prescribed. In advanced cases, surgery cannot be avoided.
Medication
At the first stage, the secretions that accumulate under the lower and upper eyelids and around the eye are removed.
Washing is carried out with a solution of boric acid up to 5 times a day. If an infection is detected, such as conjunctivitis, topical antibiotics must be used. They are produced in the form of ointments (Tetracycline, with chloramphenicol). Gauze swabs are soaked in the ointment and the animal’s eyes and the area around them are treated with them.
If the dog has age-related changes, it will not be possible to remove the thorn, but you can preserve the animal’s vision. When the first signs of disease appear, the veterinarian prescribes antibiotic therapy, treatment with antioxidants and vitamin preparations.
If all measures are unsuccessful, an operation is performed, after which the animal’s condition improves, but the quality of vision may suffer.
If an animal suffers from glaucoma, in which a white veil appears on the cornea of the eye, the following medications are prescribed:
- diuretic Mannitol - administered intravenously to reduce intraocular pressure;
- Timolol - reduces the amount of secretion secreted by the eye;
- Dorzolamide is maintenance therapy.
If intraocular pressure continues to increase, laser cyclocoagulation is used.
Traditional methods
At home, you can prevent the development of conjunctivitis. Folk remedies help cope with the infection.
As soon as purulent discharge begins to accumulate on the animal’s eyeball and around the eyelids, they are removed. You can wash your eyes with boiled warm water.
After rinsing, infusions of chamomile, calendula, and sage will help remove inflammation. You can buy them at the pharmacy or prepare them yourself: pour 1 tbsp. l. herbs with a glass of boiling water, wrap and leave for 30 minutes.
As soon as the liquid has cooled, it is used to treat the animal’s eyes.
If infusions do not help, make a weak solution of Furacilin and wash the animal’s eyes with it.
During the period of infection, the dog should not be walked in cold or windy weather and should be protected from drafts and contact with other animals.
The bedding must be washed frequently and the house must be wet cleaned.
For cataracts, it is recommended to use onion pulp: grate a quarter of the onion on a fine grater, take 1 tbsp. l. onion puree and pour half a glass of milk, leave for 24 hours.
The resulting solution is instilled into each eye twice a day, 1 drop.
Powdered sugar also helps . It’s better to buy it at the grocery store and sift it.
The powder is blown into each eye of the dog 2 times a day - in the morning and in the evening after washing. The product disinfects the inflamed organ well.
Honey (1 tbsp) is dissolved in a glass of water. Place the liquid on the stove and heat for 1–2 minutes. The resulting syrup is used to wash the animal's eyes.
You can buy fir resin at the market or in departments with handicraft products. This remedy is famous for its wound-healing and antibacterial effect, and restores impaired blood circulation.
The product is applied to cosmetic sponges and wiped over the dog’s eyes twice a day.
Also, 2 drops of fir resin are instilled into each eye in the morning and evening. This substance promotes the rapid restoration of inflamed and damaged corneas.
Folk remedies help only with infectious eye lesions. In more serious cases, if there is a suspicion of the development of glaucoma or leukoma, more serious medications are required.
Prevention
It is very important to get your pet vaccinated annually. Some of the diseases that cause eyesores in dogs are due to infections.
If a dog has injured its eye, you should not expect it to heal on its own. It is necessary to immediately show your pet to a veterinarian to avoid leukoma and subsequent blindness.
The brachycephalic breed group has a high risk of eye injury. These include bulldogs, boxers, pugs, etc. Their eyes have a special structure - they are quite large and protrude slightly forward. In addition, they are poorly protected for centuries.
An eyesore in a dog is not a separate disease. This is a signal that indicates the beginning of the inflammatory process in the pet. White clouding rarely goes away on its own, so the dog needs the help of a specialist. If leukoma is ignored, it will lead to complete loss of vision.
Causes
White eyes in a dog are not normal. This is an alarming symptom. It is important to determine what disease caused it.
The reasons for this condition are as follows:
- Age-related irreversible changes (degeneration of corneal tissue). Old dogs are often affected. Such changes cannot be treated; you can only maintain the animal’s vision with medication.
- Diabetes mellitus provokes the development of cataracts.
- Weak immunity, frequent infectious diseases.
- Injuries: blows, scratches, chemical burns.
Genetic predisposition: diseases that cause eyesores, such as glaucoma, are inherited.- Poisoning (especially from chemicals and alcohol) can lead to irreversible changes in the lens of a dog's eye.
- Malignant or benign tumors. Treatment is surgical or medicinal.
- Infection of the eye with viruses or bacteria (infection may result from injury).
- Congenital pathologies in which the animal cannot close its eyes, the cornea constantly dries out or is injured.
- Previous operations on the organs of vision and complications after them.
- Glaucoma, keratitis, conjunctivitis, leukoma are eye diseases or infections that need to be treated immediately.
- Autoimmune pathologies: the organ of vision is affected by its own immunity. Determined only in a clinical setting. In a very short time, the dog can become completely blind.
- Entropion of the eyelids: eyelashes grow into the cornea, constantly injuring it, which is why a protective film grows on the eye.
- External irritants: sudden changes in air temperature, exposure to toxic vapors, acrid smoke.
The pet's treatment regimen depends on the reason why the pathology developed. It can only be diagnosed by an experienced veterinary ophthalmologist after clinical studies.
Features of care
There are no special care difficulties. The most important thing that the owner must remember is to prevent injury to the eye from paws; for this, the dog is wearing a protective collar.
It is necessary to follow all the doctor’s instructions and carry out the prescribed procedures in a timely manner. If the cataract can be treated with medication, the pet is kept at home.
Predisposition
In breeds
According to veterinarians, some dog breeds have a genetic predisposition to leukoma, for example:
- French Bulldog;
- boxer;
- toy terrier (usually in old age);
- lapdog (Russian color, Maltese or Maltese, Havanese, etc.);
- chow-chow;
- Golden retriever;
- Shar Pei;
- basset hound;
- Saint Bernard;
- Cocker Spaniel.
Other
Also at risk are dogs that are unattended by their owner most of the time (for example, while walking), where they can come into contact with sick animals or even get into a fight (with subsequent eye injury). But older individuals are most susceptible to the disease.
Glaucoma
Increased intraocular pressure leads to an imbalance between the production and outflow of moisture. There are primary and secondary glaucoma. Primary can be congenital or acquired. Secondary - is the result of inflammation of the anterior chamber of the eye.
Photo
Symptoms
The main signs of this pathology include:
- Increased tear production.
- Redness of the whites.
- Swelling, “bulging” of the eye - it seems to have become larger.
- Apathy, lethargy.
- Decreased corneal brightness.
- The dog constantly whines when the area near the eye is touched.
- Loss of appetite.
- Reluctance to establish contact with other animals and people.
- Sometimes the pet seems to be lost in space.
- The desire to constantly be in the dark.
There are enough reasons for the development of the disease:
- Displacement of the lens;
- Inflammation of any part of the eye;
- Neoplasm in the eye;
- Accumulated blood after injury or surgery;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Keratitis or conjunctivitis if not treated.
How to treat: the best drugs
As in all cases of deciding on treatment methods, the decisive question is the timing of contacting a specialist.
In the early stages of glaucoma, drug treatment with drugs . The process is long and, at best, can stabilize intracranial pressure. A cure cannot be expected - the disease affects all components of the eye. Medications will slow down the process of clouding of the eye, but it will not be possible to restore vision or even stop the development of the disease.
Beta blockers, osmotic diuretics, miotics and inhibitors are used as therapeutic drugs; they will be prescribed by a veterinarian.
- To urgently reduce intraocular pressure (during an attack), a drug from a series of osmotic diuretics, “ Mannitol ,” is recommended. Application allows you to retain water for about 4 hours.
- What drops are needed to treat glaucoma? The external use of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors is aimed at reducing moisture production and, as a result, reducing blood pressure. Systemic drugs Dorzolamide and Brinzolamide have no side effects and are recommended for daily use.
At a late stage of the disease, the doctor’s task is to avoid complete loss of vision and reduce the pain that the dog experiences when IOP increases. When the disease is advanced, the only correct solution is surgical removal of the entire visual organ.
The results of glaucoma treatment in animals are incomparably lower than in humans . Surgeries to increase the outflow of aqueous humor (they are associated with the implantation of drainage tubes into the eye) or, conversely, to reduce the production of moisture (partial destruction of the ciliary body with a laser) quite often do not give the expected effect. In the end, when choosing between the painful inevitable loss of vision for a pet and removal, the doctor chooses the second. A prosthesis is implanted for cosmetic purposes.
Prevention
In order to prevent such a serious disease with irreversible consequences, dog owners are advised to monitor the condition of their pet’s eyes, promptly and completely cure conjunctivitis and keratitis, and conduct regular examinations with a veterinarian.
Contacting a veterinarian
Often, dog owners seek qualified veterinary help too late, when the animal has already begun to lose its vision..
You must respond immediately if the following signs appear:
the animal's eyes become cloudy;- a white spot appeared on the eyeball;
- the dog is bothered by liquid or purulent discharge near the lower eyelid;
- There was an injury to the organs of vision - chemical or mechanical.
If the owner notices that the dog’s vision is deteriorating for some reason, especially at a young age, this is an alarming symptom that requires diagnosis.
Only in a veterinary clinic after a thorough examination and all research will an accurate diagnosis be made. Self-medication in this situation is not worthwhile.
Some features of the defect
Belmo in medical terminology means “leukoma.” This defect gradually covers parts of the visual organ (retina, pupil, corneal epithelium), covering them with a whitish veil (film). This condition leads to loss of vision up to absolute blindness. The location of the cloudy spot is classified into three types:
- Total - the eye is completely covered with a cloudy spot.
- Central - the cataract covers the entire pupil or part of it.
- Peripheral - leukoma affects the protein and part of the iris.
If a dog's eye is covered with a white film of the total or central type, this is a death sentence for the animal; there is practically no chance of returning the ability to see. At least, animal medicine does not know of a single case where a dog was cured of such a pathology.