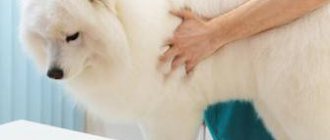
Causes Diagnosis Treatment Recommendations The mammary glands are located on the abdomen of dogs. There are usually 10 pieces in two rows of 5 pieces. Normally, in a dog that is not nursing puppies and is not pregnant, the glands should not have any thickening, swelling, discharge or hyperemia (redness). Pregnant animals may normally experience slight swelling of the glands. But if the owner notices that his pet’s mammary glands have changed shape, color, hardened, or have discharge, it is necessary to examine the animal in a veterinary clinic to determine the cause of this pathology.
Swollen mammary gland in a dog: Causes and accompanying signs
Breast engorgement in dogs occurs most often during false pregnancy. Our pets inherited this phenomenon from wild ancestors who lived in packs.
Estrus in wild canids in the same pack occurs simultaneously, and then in the body of the females, regardless of whether fertilization has occurred or not, physiological changes and preparation of the mammary glands for feeding occur.
In this way, all females of the pack can feed the cubs, which leads to a higher survival rate of the offspring, even in the event of the death of the mother. At home, such changes in the dog’s body cause a lot of inconvenience for the owner.
Signs of a false pregnancy include the following:
- Swelling of the mammary glands.
- Colostrum release.
- Change in color of the mammary glands.
- Increased appetite.
- Changes in behavior (lethargy or, conversely, anxiety and aggressiveness).
- Abdominal enlargement.
- Even false contractions are possible.
Breast swelling may also be a sign of the following conditions:
- Lactostasis is an excessive accumulation of milk in lactating animals, which leads to inflammation of the mammary gland (mastitis). This, for example, happens if puppies do not completely empty their mother’s mammary glands and leave a lot of milk.
- Galactorrhea is the secretion of milk from the mammary glands in a dog that is not feeding. In this case, the gland swells, looks swollen, and a secretion appears from it from transparent to milky and yellowish in color. This condition most often occurs due to hormonal imbalances in the animal’s body.
Recommendations
Veterinarians recommend sterilizing dogs that are not intended to be used for breeding. This procedure will significantly reduce the risk of galactorrhea and mammary tumors in your dog.
A dog nursing puppies should have its mammary glands checked for fullness and firmness. If after feeding there is a lot of milk left, it is recommended to express it by hand or place the puppies on those glands that are not completely emptied. And if there is also thickening of the mammary glands, pain and redness, then this is a reason to contact a veterinarian.
(c) Veterinary center for the treatment and rehabilitation of animals “Zoostatus”. Varshavskoe highway, 125 building 1. tel.
8 (499) 372-27-37
Swelling of the mammary glands: Treatment
If a dog develops false pregnancy syndrome, if the signs are moderate, then without any intervention the symptoms disappear within 2-3 weeks.
If you are very concerned about your dog's behavior, here are some things you can do:
- to reduce lactation (milk production), exclude all dairy products from the dog’s diet;
- limit water consumption (if you feed your dog dry food, switch it to natural food, because access to water will be temporarily limited);
- reduce the usual portion of food;
- load the dog physically, force it to move more (this is useful not only for normalizing its physical condition, but also for distracting it from caring for imaginary puppies);
- do not express the collected milk - this only stimulates its production;
- remove all toys and avoid contact between your dog and other puppies.
If the false pregnancy is “protracted,” the animal must be shown to a veterinary specialist, who will prescribe hormonal drugs to the animal according to a specific regimen, which will solve the problem.
Also, hormonal therapy will be required for galactorrhea. An alternative to the use of hormones is homeopathic therapy with Ovariovit, but it should also only be used as prescribed by a veterinarian.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to distinguish false from true lactation “by eye”. Laboratory and instrumental studies and the experience of a veterinarian are required. By the end of the 3rd week after mating, a relaxin test will confirm or deny pregnancy. After the 24th day, embryos and their number are visible on ultrasound. If the studies do not confirm pregnancy, but signs are present, then false pregnancy is diagnosed.
Anamnesis plays a great role in diagnosis. Sometimes the dog behaves as if it were pregnant, although it lives under strict control, and the owner has no doubt that there was no mating.
Inflammation of the mammary glands in a dog: Causes and clinical signs
Inflammation of the mammary glands in a dog - mastitis - is a disease that most often develops in nursing females, when stagnation of milk occurs in the glands and pathogenic microflora joins.
You may observe the following symptoms in your animal:
- swelling of the mammary glands, redness of the skin in the affected areas;
- increase in local and general body temperature;
- tenderness of the mammary glands on palpation;
- change in discharge from the mammary glands (appearance of lumps, color change to yellow and green).
Diarrhea in a dog after childbirth - Causes, treatment methods, diet: Caring for the dog - Cutting nails and ears: https://strazhchistoty.ru/cleanup/cleandogs/strizhka-ushej-nogtej-sobake.html
Classification of pathology
Symptoms and treatment of mastitis in dogs depend on its form. Based on the degree of damage to the mammary glands and the nature of discharge from the nipples, the following varieties are distinguished:
- TOataral
. Breast milk sours, curdles and blocks the holes in the nipples. Nodular formations form in the glandular tissue, disappearing after pumping. Moderate pain and a slight increase in temperature are possible.
- Serous
. The secreted milk turns yellow and becomes watery. Flake-like impurities appear in it. The milk bags swell and become hot. Pain on palpation is absent or mild.
- Hemorrhagic
. Develops as a result of complications of the catarrhal or serous variety. It differs from them in severe pain and fever, as well as the appearance of red spots on the glands.
- Fibrinous
. Accompanied by the release of white threads of coagulated protein, swelling of the lymph nodes and acute pain. When palpated, the affected glands make a crunching sound.
- Purulent
. The released exudate has a cloudy consistency and an unpleasant odor. The ability to lactation worsens or disappears completely. The swollen lobes take on a bright red hue and are very painful when pressed.
- Abscess
. It is a complication of the purulent form. Abscesses grow inside the glands. Their rupture is fraught with death from blood poisoning.
- Phlegmonous
. Another complication of the purulent variety, characterized by inflammation of all milk bags. Without timely treatment, it develops into sepsis.
- Gangrenous
. The affected lobes gradually decompose, becoming blue or dark brown. As a result of necrosis, multiple bleeding ulcers appear on them.
Due to its development, the disease is divided into lactational and non-lactational types. The first occurs when breast milk stagnates, and the second occurs when the milk bags are injured or pustular.
Inflammation of the mammary gland in dogs: Treatment
Treatment of mastitis must be carried out as prescribed and under the guidance of a veterinary specialist.
It includes the following activities:
- weaning puppies and transferring them to artificial feeding (specialized nutritional formulas, but regular baby food may also be suitable);
- carrying out Novocaine blockades;
- antibiotic therapy (Ampicillin, Bicillin, Cefazolin);
- homeopathic treatment (Mastometrin);
- regular expression of milk from the affected lobes;
- in advanced cases, surgical opening of abscesses.
Trauma or accidents
If your dog has been in an accident or has recently been kicked, his chest may be swollen due to the injury. This is a natural process that allows the damaged area to recover. In this case, only some bitches are likely to swell, since the blow usually causes an actual reaction. You may also notice bruising or injury near the swollen area.
Again, we remember that it is very important to take your dog to the vet to check his health after a stroke or accident.
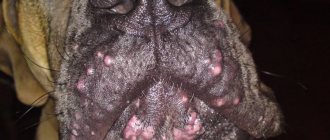
Lumps on the mammary glands of a dog: Possible diseases
If you notice that your dog has a lump on the mammary gland, this may be a sign of one of the following diseases:
- Breast adenoma.
- Breast fibroadenoma.
- Papilloma of the milk ducts.
- Mixed neoplasm.
The neoplasms listed above are benign.
Below we name the malignant forms:
- Papillary adenocarcinoma.
- Armor cancer.
- Carcinoma.
- Sarcoma.
- Tubular cancer.
The sexiest veterinarian has been announced on Instagram. Wow! You've never seen anything like this before. Look here: https://woman.rambler.ru/beauty/41684688-v-instagram-nashli-samogo-goryachego-veterinara
What is mastitis
Pathology is a gradual increase in the size of the mammary glands. The inflammatory process can spread to only one pair - or to all five at once.
It is very easy to notice such changes. The problem is that this disease has several varieties. Each of them is treated in a different way, so you should not try to cope with the problem on your own. At best, your efforts simply will not bring results, and at worst, they will aggravate the existing condition.
Mammary gland neoplasms in dogs: Diagnosis and treatment
If a dog has a lump on the mammary gland, you should immediately contact a veterinary clinic.
In Moscow, you can contact the veterinary clinics of the network “Your Doctor” or “Bely Klyk”, as well as the Innovative Veterinary Center of the Moscow Veterinary Academy (IVC MBA).
In St. Petersburg, competent specialists will help you at the clinics “Dog and Cat”, “Lucky”, “Your Doctor”.
To understand the nature of the formation and choose further treatment tactics, the following measures will be taken:
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands.
- Radiography.
- Biopsy of breast tissue followed by histological examination.
After clarifying the diagnosis, the veterinarian will make a decision: if the formation is benign, then surgical removal of the tumor will be performed, if it is malignant.
Depending on the stage and extent of the process, either a total mastectomy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these treatments will be chosen.
In severe, advanced cases in old weakened animals, the doctor may suggest euthanasia (euthanization of the animal) for humane reasons.
Establishing diagnosis
As a diagnostic measure, a veterinarian can take material secreted from the mammary gland for cytological analysis. Such an analysis will show the presence of inflammation in the gland and determine the sensitivity of the infection to certain types of antibiotics.
If a tumor of the mammary gland is suspected, the animal must undergo a chest X-ray to exclude metastases in the lungs, and undergo clinical and complete biochemical blood tests. Next, the dog is sent for surgery to remove the mammary glands - mastectomy. After surgery, the removed material must be examined for the presence and type of tumor process to determine the need and choice of further treatment (for example, chemotherapy).
Prevention of mammary gland diseases in dogs
- Balanced diet, clean bedding, daily exercise for at least 3-4 hours a day.
- Regular examination and palpation of the dog's mammary glands.
- Careful care for a nursing dog: daily washing of the mammary glands with antiseptic solutions, trimming puppies’ claws, changing bedding.
- If false pregnancy syndrome occurs, limit the dog's consumption of water and dairy products, increase physical activity, and reduce feeding portions.
- Do not use hormonal drugs to suppress estrus (Sex control, Stop-intim and others).
- The most effective measure to prevent diseases of the mammary glands is sterilization of a young female before her first heat (at the age of 6-7 months).
Quantity
Psychological pregnancy
False pregnancy (or psychological pregnancy) is very common among fertile dogs. In general, the picture appears when a female has had sexual contact with a male, but fertilization has not been completed. However, pregnancy can develop without prior mating.
The symptoms of psychological pregnancy are almost identical to the symptoms of real pregnancy: the bitch has swollen mammary glands, the belly and nipples increase in size, and their appetite increases. They also usually produce and pass through the breasts whey, which is lighter and thinner than breast milk. Therefore, it is not surprising to observe a bitch with swollen mammary glands after estrus, and also to see that the bitch has milk and is not pregnant. To prevent this from happening, the best option is sterilization, since long-term psychological pregnancy can lead to serious health problems.
© shutterstock
The essence of the condition, the causes of its occurrence
Experts tend to be of the opinion that symptoms of false pregnancy arise due to disorders of a psychophysiological nature. Not a single female is protected from this if she is already sexually mature and has even been sterilized.
Among all the reasons, veterinarians identify the following most common:
- a sterile mating was performed, with both partners being sterilized, or only one of the pair;
- the pet has problems with the reproductive system, and this is an ovarian tumor or inflammation;
- the pet was placed in the same room with pregnant or postpartum women, even if they are not of the same species;
- the female was very frightened by someone or something;
- the owner does not provide adequate attention or abandons the pet altogether;
- she met a human cub or child.
Additional Information! False pregnancy does not last long. On average, symptoms last for a month.
When to contact a veterinarian
As soon as the symptoms begin to worsen, the female becomes restless and the temperature rises, you should consider consulting a doctor - otherwise everything could turn fatal.
When the owner decides to contact the veterinarian, you need to provide him with information about the first heat, how old the dog is, whether there was a pregnancy, whether the mating was accidental or purposeful.
Note! If she has previously experienced such cases, it is important to mention this. There is no need to be afraid to tell your doctor the truth.
Before treatment, the doctor does a special test to determine whether the dog is pregnant or not. The analysis is carried out based on the blood taken. If all the dog’s hormones are normalized, if there is any doubt, the doctor will prescribe an ultrasound. Thus, he understands that it is not necessary to treat the dog, everything is fine with it. All lower limbs and the body are in normal condition - and as a result, the patient is allowed to go home.
Symptoms of the disease
Since the mammary glands are located in plain sight, warning signs are not difficult to spot.
You should pay attention to the presence of:
- compactions and redness;
- softness, friability or, on the contrary, density of formations;
- changes in the shape and color of the nipples, as well as discharge from them;
- hyperemia in the affected area;
- anxiety of the animal during the examination (due to pain and discomfort).
If the condition is advanced, the formations open and a fistula appears. The animal refuses to eat, walk and play.