As soon as a dog settles in the house, it immediately becomes interesting how old it is by human standards. This helps you better understand your pet and find the key to his soul. So, how can you find out how old a dog is in comparison to a human’s life? More on that below.
How to calculate a dog's age
There are many methods that allow you to find out the age of a four-legged pet in relation to a human one. But they are all quite arbitrary, since the life expectancy of a pet largely depends on the breed, nutrition, physical activity, the presence of chronic or congenital diseases, and the attitude of the owner.
Up to 2 years, veterinarians use the following coefficients to calculate the ratio of dog and human age:
- small breeds – 1;12;
- medium breeds – 1:10;
- large pets – 1:9.
A one-year-old dog, especially small breeds, is an adult and can control its actions; for comparison, according to human criteria, this age corresponds to 10–13 years.
Table of the age ratio of people and dogs without taking into account breed
| Pet age (years) | Person's age (years) |
| 2 months | 1,2 |
| 6 months | 5 |
| 1 year | 10–13 |
| 3 | 28–32 |
| 5 | 38–42 |
| 7 | 47–50 |
| 8 | 54–57 |
| 10 | 63–66 |
| 12 | 73–77 |
| 15 | 85–88 |
| 16 | 87–90 |
| 20 | 94–97 |
Factors influencing life expectancy
1. Small dogs live a much longer life than representatives of large breeds. Why is this happening? It’s simple, because to maintain the basic functions and physiology of the body, small pets expend much less energy than large dogs. Large four-legged dogs often experience heart problems, because their heart beats much faster than that of small pocket dogs.
2. The sex of the animal also affects the average lifespan. Bitches live a little longer than males due to their physiological characteristics, endurance and body structure.
3. During sterilization and castration, four-legged companions no longer feel natural needs and joys, but they also do not expend energy on finding a partner and love pleasures. That is why their life is calmer, and therefore longer. Untreated animals often develop cancer of the genital organs.
4. The right choice of diet also plays a role in the duration of a dog’s existence. Balanced specialized food can extend the life of a pet by several years. That is why you should definitely contact a veterinary clinic so that specialists can select the optimal diet for your pet of a certain breed.
5. A healthy and proper lifestyle is important not only for humans, but also for dogs. Long walks in the fresh air, an active lifestyle, a good and friendly atmosphere in the family - all this is the key to a long life for a pet.
6. Regular examinations by a veterinarian will help identify the presence of hidden diseases and infections and promptly vaccinate the animal.
Stages of development - features
A pet goes through the same stages in its development as humans - toddlerhood, late childhood, early and late puberty, growing up, maturity, old age. But, unlike people, the formation of basic character traits and behavior is completed at 2 years.
How to determine the age of a four-legged pet:
- Milk teeth - begin to erupt in puppies older than 1 month, fall out at 4 months, the change of dentition ends at approximately 8 months.
- Molars – up to 2 years of age, dogs have sharp, intact teeth. The lower jaw wears down at the age of 4–6 years; after 7 years, teeth begin to fall out.
- Coat – young pets have a soft coat that is evenly colored. After 6 years, the coat becomes coarser and gray hairs can be seen.
- Eyes – in puppies, the eyes have a bright, uniform color, gradually the organs of vision become less transparent, and regular discharge is observed.
- Activity - up to six months, puppies are in motion almost all the time; with age, active games and long walks attract dogs less and less.
According to veterinary statistics, the average age of domestic dogs is 12–13 years.
Periods of a dog's life
The entire life of dogs can be divided into several periods:
- Lactic;
- Puppy;
- Teenage;
- Youthful;
- Mature;
- Elderly.
The dog experiences growth during the milking, puppy, and teenage years. So the smallest dogs, for the most part, fully grow by 10 months. Well, the largest breeds stop growing by 2 years.
Adolescence in tiny breeds begins at 10 months and ends on average at 8 years. However, in larger four-legged animals, adolescence ends much earlier; already at 3 years old, some dogs can be called mature, while medium-sized dog breeds go through the stage of adolescence at about 4 - 5 years old.
A small breed dog becomes full-fledged and mature after 8 years of age, and this period continues until the 12th year of life. The largest breeds reach maturity at 3 years old, and remain so for up to 6 years. The duration of maturity in average representatives of tetrapods ranges from 7 to 10 years.
Naturally, old age also comes to dogs; there is no escape from it. The youngest dog breeds may experience some age-related inconveniences only after 12 years. By the way, pocket dogs, which are constantly in the arms of girls, can live even more than 20 years, which cannot be said about other pets.
Medium-sized dogs begin to age rapidly after 8 to 10 years of age and can live in this state for about several years. Well, the largest four-legged animals already after 6 years enter the phase of old age and the duration of their future life will depend only on proper care.
Lebeau's theory
In the middle of the last century, a veterinarian from France A. Lebo developed his theory to calculate the age of a dog in relation to a human, which is based on the accelerated development of four-legged pets in puppyhood. In his calculations, he compared the period of puberty, maturity and average life expectancy in pets and people.
According to his calculations, the development of a dog at 12 months is the same as that of a teenager at 14–15 years old, 2 years correspond to 23–25 years of a person, each subsequent year of an animal’s life is equal to 4–5 human years. But in his calculations the doctor did not take into account the size of the pets.
Separation of dogs depending on body weight
| Group | Representatives | Weight, kg) |
| Small dogs | Toy terrier, pugs, Yorkshire terrier, Pekingese, Pomeranian. | No more than 10 |
| Average | American, English cocker spaniel, basset hound, bulldogs, dachshunds, husky. | 11–25 |
| Large | Labradors, greyhounds, Staffordshire terrier, German shepherd, husky. | 26–45 |
| Gigantic | Great Danes, Newfoundlands, Mastiffs, St. Bernards, Deerhounds. | More than 46 |
Calculation formula
The very first and simplest calculation method is still popular among many owners.
The calculation method is that 1 year of a dog’s life is equivalent to 7 years of a person’s life . In order to calculate the age of a four-legged friend, you need to multiply the number of years he has lived by a coefficient equal to seven.
Where did this figure come from? Back in the middle of the 20th century, veterinarians compared the average human life expectancy of 70 years and the average life expectancy of dogs, 10-12 years. Based on these indicators, it was concluded that a person lives 7 times longer than a dog.
A significant drawback of the “seven-year theory” is the simplicity, even primitiveness, of calculations without taking into account the stages of the animal’s physical and mental development and breed indicators.
Kleiber's Law
Klaiber put forward the theory that the rate of metabolic processes in a dog’s body is directly related to its weight - the larger the animal, the longer it will live. But in practice, everything happens the other way around: small dogs live about 4–5.5 years longer than representatives of large and giant breeds.
The rule of correlating the number of years lived with the heart rate does not work on dogs either - small dogs have a faster heart beat, but they live longer. The weight of an adult mastiff is almost 40 times the body weight of a Chihuahua, according to Kleiber's theory, a large dog should live longer, but in fact, a small dog will live 1.5 times longer.
Scientists have not yet been able to identify the exact reason for this discrepancy, but many veterinarians believe that this is due to some hormonal characteristics of the dog’s body. Representatives of small breeds produce more of a specific hormone that slows down the aging process than large pets, and the concentration of growth hormone is lower. All this leads to the fact that small dogs are less likely to suffer from age-related diseases, which also has a positive effect on the total number of years they live.
The ratio of 78 human years and the age of small dogs and large pets
| Size | Approximate age (years) |
| Small breeds | 14–17 |
| Medium breeds | 14–16 |
| Large breeds | 11–14 |
| Giant dogs | 10–11 |
For all other warm-blooded animals, Kleiber's law works - large individuals live much longer than small representatives of the fauna.
Why do small dogs live longer than large dogs?
This phenomenon still puzzles scientists, and they have yet to explain the relationship between a dog's body weight and lifespan. Generally speaking, large mammals like elephants and whales tend to live longer than small ones like mice. So why do small dogs live longer than large dogs?
Some researchers believe that the lives of large dogs are accelerating over time. Scientists have concluded that every 2 kg of body weight reduces a dog's potential life expectancy by about 1 month.
One likely reason for this is that larger dogs may become more vulnerable to age-related diseases more quickly, and that the increased growth of larger dogs may lead to a higher likelihood of abnormal cell growth and death from cancer. The researchers plan to conduct additional future large-scale experiments to better explain the relationship between size and mortality.
The Internet is simply teeming with requests from curious owners “how to determine how old my dog is by human standards?” Indeed, every pet owner, no matter if it is a dog, a cat or a guinea pig, is trying to figure this out.
Dog age table
Until about 3.5–4 years of age, dogs of all breeds develop equally, but then large pets begin to age rapidly. Therefore, modern gerontologists have concluded that the life expectancy of pets directly depends on its weight and size.
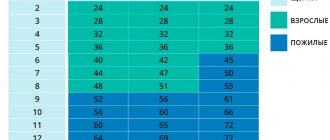
Table of the ratio of canine and human age indicators, depending on the size of the pet
| Dog age | Small dogs | Medium sized dogs | Large dogs | Giants |
| 1 | 13–15 | 14–16 | 13–16 | 11–13 |
| 2 | 21–24 | 23–26 | 21–23 | 19–21 |
| 3 | 26–28 | 27–30 | 27–31 | 26–27 |
| 4 | 30–33 | 33–35 | 34–36 | 3–37 |
| 5 | 34–36 | 35–37 | 38–40 | 40–43 |
| 6 | 39–40 | 40–42 | 43–45 | 47–50 |
| 7 | 43–45 | 45–47 | 49–51 | 54–57 |
| 8 | 46–49 | 49–52 | 53–56 | 63–66 |
| 9 | 50–53 | 54–57 | 59–62 | 68–72 |
| 10 | 54–57 | 58–61 | 54–67 | 75–79 |
| 11 | 57–60 | 63–66 | 69–73 | 84–88 |
| 12 | 62–65 | 67–70 | 74–78 | 90–94 |
| 13 | 65–67 | 72–75 | 75–78 | 98–102 |
| 14 | 69–73 | 75–79 | 85–89 | 105–110 |
| 15 | 74–77 | 80–83 | 90–93 | |
| 16 | 77–81 | 84–88 | 95–100 |
Dogs, especially large ones, do not live long, very rarely reaching 15 years of age, which corresponds to 100 human years. How long a pet will live largely depends on the owner. To prolong the life of a pet, it is necessary to feed it only high-quality products, timely vaccinations, antiparasitic treatment, more walks, and regular visits to the veterinarian.
Main causes of premature death
Dogs often die due to poisoning from pesticides used in everyday life. All a dog needs to do is eat a poisoned rodent or lick a chemically treated surface. For this reason, it is better to avoid using such tools.
Dachshunds are also prone to the following diseases:
- slipped disc syndrome;
- paralysis;
- epilepsy;
- chest deformation;
- cataract;
- glaucoma;
- ear infections;
- diseases of the genitourinary system.
Most of the listed ailments do not lead to the death of the dog. But they lead to restrictions in the dog’s normal life. And owners often come to the decision to euthanize the animal so as not to expose the dachshund to suffering.
With age, dachshunds often experience exacerbation of chronic diseases that previously occurred in a latent form. What Causes Sudden Death of a Dog.
For your information! A common cause of death in dachshunds is accidents due to the owner's carelessness and back injuries received while jumping.
Walks and games
Before you go for a walk, you need to purchase a collar and leash. It is better to choose a medium-hard collar that is not too thick, this will reduce the likelihood of injury to the animal’s neck.
Dachshunds are difficult to train; they are hunters by nature. Therefore, it is important to teach your pet at least basic commands and constantly educate it. The dog must understand that chasing vehicles and rushing at stray dogs is dangerous, and that you should not eat everything that lies on the ground. In addition, the owner should remember that dachshunds are not allowed to jump.
Important! Before a winter walk, the dog needs to be warmed up and the chest protected from the cold. This will help avoid colds, which representatives of this breed are prone to.
Before walking in cool weather, your dog should be wearing a collar and a warm suit.
Rules of care
Before you get a dachshund, you need to prepare everything you need for it. It is better to place the recreation area close to people, but away from heating devices and drafts. Due to their body type, dachshunds are recommended to rest on hard mattresses and beds.
Dachshunds are bathed as they become dirty. Intensive washing once a trimester is quite enough. Special shampoos are used as detergents. To dry the coat, the dog is soaked with a dry towel. To protect your ears from water getting into them, you should plug the shells with an oiled cotton swab before bathing.
For your information! Based on the quality of their coat, dachshunds are divided into 3 types: rough-haired, short-haired and long-haired. The first ones are combed as needed, the second ones - every day. Wire-haired representatives of the breed are scratched several times a day and shaved with a trimmer. For combing, use medium-hard brushes.
Wipe the eyes with a damp cotton swab or napkin. It is necessary to moisten the cotton wool in warm water. If your eyes are watery, you need to wash them with a 2% solution of boric acid or strong tea leaves.
You should carefully monitor your pet's ears and clean out dirt and wax. To do this, use cotton swabs or swabs soaked in warm water, a solution of boric acid or hydrogen peroxide. In addition, there are special drops for cleaning ears.
To avoid the formation of tartar, your dog's teeth need to be brushed with a special paste. It is applied to a toothbrush or a piece of hard cloth. Dog toys that your pet chews on and specially designed treats also help clean your teeth.
You can brush your dog's teeth yourself
Nails should be trimmed with a nail clipper twice a month from bottom to top. This should be done carefully. If the skin on the paws is accidentally damaged, the wound should be treated with an antiseptic. After walking, it is recommended to clean the space between the pads.
Note! If your dachshund's nails are not trimmed promptly, its paws can become deformed and cause lameness. Particular attention should be paid to puppies. Due to low activity, their nails wear down more slowly than those of adult dogs.
If the dachshund is used for breeding, the female needs careful care during estrus. You should not mate too often, as this exhausts the body of both sexes.