There are diseases of pets that, at first glance, are not dangerous for the animal, being just a cosmetic problem. Among them are papillomas in dogs. What is it, how dangerous are neoplasms, and are they a harbinger of more serious health problems?
Causes and treatment of papilloma in dogs
What are papillomas?
The reasons for the formation of papillomas in our little brothers are viruses. Currently, eight types of pathogen are distinguished. They are the cause of the development of papillomatosis - a disease as a result of which papillomas develop on the mucous membranes and skin - growths in the form of a small process, a polyp. Certain strains of the virus can be transmitted from a sick to a healthy individual.
What are papillomas?
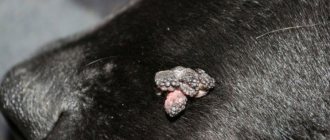
Papillomas are single growths, and they can have different sizes. In appearance, the neoplasms look like large warts with a loose structure and a cone-shaped shape. There are blood vessels inside the growths, so they are often injured, bleed and hurt.
If a pet has a lot of such growths, a diagnosis of papillomatosis is made. Multiple accumulations of such warts are not uncommon in dogs. Such neoplasms are benign and most often appear in young individuals. Neoplasms on the mucous membranes of the mouth (ulcers, gums, cheeks, lips) are contagious and are transmitted from a sick pet to a healthy pet.
At a more mature age, pathological formations develop in the ears, eyes, neck, paws, and eyelids. These are denser, more mature growths that are not contagious to other dogs.
Diagnostics
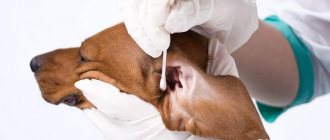
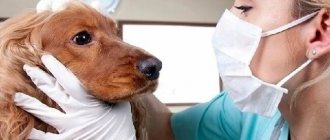
Externally, it can be difficult to distinguish papilloma from any malignant formation, therefore, in any case of a pet’s appearance of any skin formation on the skin or mucous membrane, it is necessary to show the pet to a veterinary oncologist. At the appointment, the doctor will visually examine the lesion, take the lesion for a mandatory analysis - histology, and to confirm the diagnosis, you can take blood for PCR (this test detects the virus antigen). It should be noted that degeneration of a harmless papilloma into a malignant formation also occurs, so diagnosis should not be neglected.
Hurry up, choose a box and find out what gift awaits you
Discount on pet insurance
Promo code copied to clipboard
Papillomas are primarily distinguished from transmissible venereal sarcoma, squamous cell carcinoma, fibromatous epulis and other skin neoplasms. Confirmation of the diagnosis is made exclusively by biopsy of the affected area followed by submission of the material for histology.
What can it come from?
This is a viral disease. To become infected you need contact with a sick animal. Infestation often occurs in nurseries where animals are kept together in confined spaces. Domestic dogs can become ill as a result of using unsterile needles for injections, during mass dog walks, and also as a result of using common household items.
What can it come from?
The incubation period of the virus lasts about 2 months. The pathogen makes its way into the mucous membranes through skin lesions. Once in the cells, the virus begins its activity - it multiplies, moves through the epithelial skin layers, and also releases into its environment special proteins that transform cells. It acquires the ability to actively divide and grow, resulting in the development of a tumor. As a result, papillary papillomas come to the surface.
Most animals are carriers of the virus in a “dormant” state, that is, it is present, but does not manifest itself. The transition to an active state can develop due to severe stress, illness, decreased natural defenses, use of potent drugs and other factors.
Formation of warts
The papillomatosis virus penetrates the basal layer of cells through micro-wounds on the skin and mucous membranes. From the basal cells it passes into epithelial cells, which then slough off (dandruff) - this is how the virus spreads in the external environment. Particles of skin falling on objects, the ground, or the owner’s clothes are transferred to a healthy dog.
As an infected cell moves through the body, its ability to divide into other cells changes. The pathogen is “not satisfied” with this and begins to stimulate metabolic processes and reproduction with the help of specific proteins. As a result, normal healthy cells become tumor cells and they can now multiply without restrictions. Growths (warts) grow on the skin and mucous membranes.
Symptoms of papillomatosis
Manifestations of virus activity are observed in animals no older than four years of age. The growths develop on the lips, and in the absence of adequate therapy they spread throughout the oral cavity, including the pharynx.
Symptoms of papillomatosis
At first, the papules are pink with a smooth surface. Over time, the pathological tissues grow and large warts of all shapes develop. Veterinarians also report papules affecting the mucous membrane of the esophagus and the area around the nose.
Multiple papillomas in the animal's mouth cause pain when drinking and eating. The pet may be sick from food, and there may be traces of blood on the food. Not eating leads to weight loss. As papillomas grow, it is difficult for the dog to close its jaws; the growths are often injured, becoming an excellent gateway for the development of other infections. There are often cases when bacteria and fungi are attached.
In weakened and old individuals, the growths degenerate into a malignant neoplasm - squamous cell carcinoma.
Methods for treating infection in animals
Removal of papillomas in dogs occurs under local anesthesia. There are several ways to rid your pet of an unpleasant illness:
- cryosurgery;
- surgical excision;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser.
Treatment of human papillomavirus disease by surgical removal is carried out by a veterinarian. Surgical excision is often performed because this method is the most accessible, safe for the animal and will definitely get rid of the wart. After surgical removal of a wart, it requires good care and regular dressing changes.
The natural resistance of the animal’s body will be strengthened by immunomodulators. They are prescribed to increase the pet's immunity. Stimulants are used as a complement to the main therapeutic agent. Has proven itself well:
- Gamavit;
- Interferon;
- Immunofan;
- Transfer Factor.
The best treatment for papillomatosis is Fosprenil. This medicine is used in a dosage of 3 ml per 10 kg of weight, it is used once daily. The course of treatment is 5 days. Fosprenil is used to treat benign growths in the oral cavity. After 1.5–2 months, it is necessary to repeat the treatment.
What to do if your dog has papillomas?
In most cases, the problem goes away easily and ends in recovery without human intervention. But if the tumors do not go away, but on the contrary, they increase in size, you should consult a specialist, since the immune system is not able to cope on its own. The veterinarian will determine the exact diagnosis and also prescribe treatment tactics. Today there are many known ways to eliminate papillomas, both scientifically based and quite exotic.
What to do if your dog has papillomas?
Surgical method
Specialists in veterinary clinics are reluctant to perform the surgical method. This is explained by the fact that after the procedure there is a risk of papillomas spreading to other parts of the body. However, sometimes this is the only way to relieve the dog of discomfort.
Basic methods of surgical treatment
- cryodestruction - neoplasms are frozen using liquid nitrogen;
- burning out papilloma using high-frequency electric current;
- use of laser.
The last method is the safest. However, not every animal clinic can afford such high-precision and expensive equipment.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine offers the following treatment methods:
- Intravenous injections of novocaine. A solution with a concentration of 0.5% is used. Three injections are given at intervals of three days. The dose is selected individually, taking into account the dog’s weight.
- Novocaine injections into the base of the papule. The operation is performed three times with a break of two to three days.
- Injections of novocaine and iodoform ether. A single injection is made into the base of the papilloma, and then iodoform ether is injected.
- Taking fosprenil. A new drug that is effective against most strains.
- Novocaine blockade. Placed under the jugular process.
- Immunomodulatory drugs. Prescribed to enhance immunity.
- Antiverrucin paste. The tumor is treated regularly until the growth is completely rejected.
- Immunoparasite with comedones. Injections are carried out according to a certain scheme.
If the treatment involves the use of pastes or ointments, it is recommended to put a cardboard collar on the pet so that it does not lick the medicine.
Surgical removal of papillomas is not always appropriate. As practice shows, this can lead to an acceleration of the spread of the disease. But if the growth is large and leads to difficulty in eating and swallowing, they resort to removing the tumor using minimally invasive methods. Apply:
- Cryodestruction. As a result of exposure to low temperatures, tumor cells die and are rejected.
- Electrocoagulation. Pathological cells die under the influence of a current of a set frequency.
- Laser removal. The focused laser beam performs a directed action.
Vaccination
The most effective method of treating papillomas is vaccination. To prepare the product, virus-infected tissue from a sick dog is used. The drug is administered subcutaneously with a certain interval. As a rule, it is 7-10 days. The effect of vaccination occurs after 3 weeks.
Vaccination
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine presents its methods to combat the disease. You can resort to treatment with folk remedies in the initial stages, when the lesion is characterized by single neoplasms :
- Use a nylon or silk thread to tighten the base of the papule, having previously treated the area with iodine. Pathological cells die off as they are deprived of nutrition;
- Rub celandine juice into the affected areas. You will need freshly squeezed orange juice, which is collected at the roots. As a result, the neoplasm turns black, it is cut off and treatment is continued until the growth is completely eliminated;
- Dandelion juice is used to eliminate papillomas;
- rub the affected areas with garlic;
- Vinegar is used in the treatment of tumors. One drop is applied to the affected areas every day before bed;
- dry ice is applied to the sore spot at intervals of three hours;
- for quick treatment, pureed rowan fruits are used;
- papillomas turn black and die from the juice of Euphorbia vine.
It is much more difficult to treat degenerative papilloma - fibrosarcoma. This tumor most often develops on the gums, the mucous membrane of the gums of dogs. Unlike a benign neoplasm, a tumor is characterized by a dense, ulcerated surface. Treatment is excision, but in most cases relapses occur.
Consequences of the disease
If recovery occurs on its own, the pet is no longer susceptible to the disease. However, it becomes a carrier of the disease, being dangerous for weakened dogs.
When deciding to carry out treatment at home on your own, it is worth carefully observing the animal. If you cannot achieve the desired effect, the growths grow, affecting more and more healthy areas, you should seek qualified help. Formations on the body cause anxiety in the dog; he will try to scratch or chew them. Papillomas under the collar are more difficult to treat at home.
With the right approach and proper attitude, papillomas will disappear quickly, will not cause consequences, and will not bother your pet in the future.
Prevention
The most effective preventive method is to vaccinate your dog. Science cannot yet offer anything more effective. In addition, the conditions in which the dog is kept still play an important role. It is necessary to monitor not only its hygiene, but also the cleanliness of all items intended for care.
Animal dishes, brushes, bedding - everything must be kept clean. The dog's sleeping area should be dry and warm. The dog should not be allowed to live in a damp room.
To keep your dog's immune system working well, watch his diet. You should not overfeed your dog, but it must receive every day all the vitamins, minerals and other nutrients necessary for the normal functioning of the body.
In addition, you must adhere to the following rules of prevention׃
- the dog should not be allowed to play with stray animals;
- Walk your dog enough;
- periodically check the entire body of the animal;
- watch the dog’s behavior - he may constantly lick some place or scratch with his paw.
If you find papillomas in your dog, you should seek help from a veterinarian.
Currently reading:
- We fight warts on the face and body of dogs
- The American Cocker Spaniel is an adroit hunter and loyal friend.
- What do tumors on a dog's body and tail mean?
- Is it worth it or not to include natural food in your dog’s diet?