Intestinal obstruction is a syndrome characterized by partial or complete disruption of the movement of contents along the digestive tract. In dogs, it can be caused by a mechanical obstruction, as well as a violation of intestinal motility.
The syndrome is diagnosed in dogs, regardless of their age and breed. However, stray animals that may eat foreign objects are at particular risk. Read on to learn more about how intestinal obstruction develops and what the animal owner needs to do.
See this article:
Causes Signs of intestinal obstruction Forms and characteristics of the disease What to do? Diagnosis of the condition Treatment of intestinal obstruction Rehabilitation after surgery Prevention of the disease Prognosis
What is volvulus
Volvulus in dogs
Food stuck in the stomach rots, increasing the volume of the organ. If not treated promptly, the animal may die from rupture and sepsis, as well as from cardiac arrest or suffocation caused by excessive pressure on the heart and lungs.
Interesting! Dogs inherited this pathology from wolves. When predators chase prey, their stomachs contract so as not to interfere with the chase. Having caught the victim, the wolves swallow the meat in large pieces and go to secluded places to calmly digest the food. During this time, the shape of their stomachs can change up to 5 times.
Symptoms and signs of volvulus development
Volvulus in dogs develops rapidly, and its symptoms appear in an unknown sequence. However, if you notice 2-3 of the symptoms listed below together, you need to run to the vet. Time may be short and the hours are ticking.
Bloating is a serious condition and needs immediate treatment. Without treatment, this condition can be fatal within an hour. With early treatment, more than 80% of dogs will survive.
Characteristic signs by which pathology can be recognized include:
- Bloating. It becomes very tight and takes on a spherical shape. Strong pressure on the stomach can cause rupture of the insides, so it is better not to touch it.
- When the abdomen is tapped, there is a special “ping” sound. Remember what sound a table tennis ball makes? It's like you're hitting a snare drum. This information is more likely for veterinarians, so it is better to focus on other symptoms.
- Vomiting or nonproductive vomiting. Tightening of the upper digestive tract triggers the gag reflex and the dog experiences excruciating nausea. This may be vomiting white foam or unsuccessful attempts to vomit, so-called non-productive vomiting.
- Abdominal pain. To relieve pain, the dog lies on its stomach, with its limbs extended, and constantly turns from side to side. Due to intestinal colic, the dog becomes indifferent or, on the contrary, aggressive and may bite when trying to touch the stomach. The dog feels pain and may even whine if you press on its stomach.
- Lethargy. The dog arrives in apathy, trying to lie down and find a place for himself.
Other possible signs:
- Increased salivation;
- Excitement, anxiety, agitation;
- Weak pulse;
- Pale gums;
- Cardiopalmus;
- Breathing problems. The enlarged stomach puts pressure on the diaphragm, causing increased salivation, wheezing and shortness of breath. Each breath costs the dog enormous effort. Due to lack of oxygen, the animal's mucous membranes turn blue or pale. And acute hypoxia is fraught with loss of consciousness.
- Problems with bowel movements. When a dog has intestinal volvulus, fecal stasis occurs. Any attempts to defecate end in nothing and provoke severe pain.
Causes of the disease and the tendency of certain breeds
Volvulus in a dog develops as a result of maintenance errors made by the owners.
The most common factors that provoke the occurrence of pathology include:
- Errors in nutrition. Abuse of cereals, bones or low-quality cheap dry food causes increased gas formation and bloating. The absorption of unchewed food also leads to a similar result.
- Violation of feeding regime. Excessively large portions and long intervals between meals cause the dog to suffer from either oversaturation or hunger, as a result of which it is constantly in a state of stress.
- Exercise immediately after feeding. A full stomach is poorly protected and its natural position may change due to active games, jumping and running.
Permanent stress, hormonal imbalances and chronic diseases of the digestive system increase the likelihood of volvulus in dogs.
volvulus in a dog causes of the disease
Important! The predisposition to volvulus is inherited from parents. To reduce the risk of pathology, when purchasing a puppy, it is recommended to double-check information about its ancestors.
What dog breeds are at risk?
Among the breeds predisposed to volvulus are:
- Great Dane;
- shepherd;
- Saint Bernard;
- bullmastiff;
- Giant Schnauzer;
- Doberman Pinscher;
- Labrador Retriever.
Dogs of these breeds weigh more than 30-40 kg. Constant pressure leads to weakening and stretching of the mesenteries, increasing the risk of volvulus due to improper feeding and excessive physical exertion.
Intussusception (telescopic bowel)
This is a condition in which one segment of intestine protrudes or invaginates into the lumen of an adjacent segment of intestine.
This “telescoping” effect causes complete or partial obstruction of the intestine, impairing its circulation. This provokes the development of edema followed by necrosis, release of toxins and translocation of bacteria, which ultimately leads to septic peritonitis and shock.
Intussusception can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract from the stomach to the colon. However, the most commonly involved segments of the intestine are the middle of the small intestine or the place where the small intestine joins the large intestine.
Is it possible to provide help at home?
In case of intestinal volvulus, only a veterinary surgeon can save a dog from death. Therefore, when the first signs of illness appear, the animal must be immediately taken to the clinic. To alleviate the dog’s condition, you can give it an anesthetic (Ketonal or Baralgin) before the trip.
Important! If you suspect a volvulus, you should not give your dog a laxative. Instead of normalizing stool, they will only aggravate the disease and hasten the death of the pet from intoxication. It is also useless to give the animal sorbents and vasoconstrictor drugs.
We recommend reading:
- Enterosgel for dogs with diarrhea and vomiting
- Signs of dog poisoning from rat poison
- Is it possible to feed a dog fish?
Volvulus in dogs: phases of pathology development
Volvulus (GDV, in English GDV) is not just a banal gastritis, but something more serious and dangerous, or rather, even deadly for your dog.
Watch for the following signs and symptoms:
- Your dog may be very agitated, tense, or anxious shortly after walking and eating.
- She may have a bloated stomach due to gas buildup in the stomach.
- She may struggle to have a bowel movement, sometimes even whining in pain.
- It may be unpleasant and painful for her.
Phase 1: In the initial stages of this condition, the dog's behavior may seem normal. Simply being there for her when she is uncomfortable can help calm her down. At this stage, she can recover on her own without medical intervention. The fact is that a dog’s stomach itself can change shape up to 5 times after eating (dogs inherited this ability from wolves), so the problem can solve itself without the help of a veterinarian.
Phase 2: In the next phase, her belly will begin to expand and curl, the restlessness will be a little more pronounced, and you may see her pacing and drooling. The blood supply to part of the stomach is cut off. Her stomach becomes swollen and/or painful. Be sure to call or, better yet, visit your veterinarian to have your dog checked.
As the condition worsens, the twisting gets worse and she may go into shock. This will increase her restlessness, whining, and panting. Excessive drooling will be accompanied by her standing with her legs spread and her head down. You may see your gums turning dark red. She may need surgery to fix her stomach.
Phase 3: As the disease progresses, shock becomes severe and this can affect the dog's intestines. She will have difficulty standing and breathing, her stomach will become more distended, and her gums will become pale. This is a pretty critical condition. Although surgery can be performed, your dog may not survive this stage.
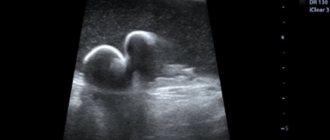
volvulus on x-rays
Veterinarians recommend that you do not feed your dogs large portions, but distribute the food and feed it intermittently. Also, teach your pet to eat slowly. Ensuring there is enough water to drink and rest after eating so that the stomach can digest food slowly.
To avoid this problem, you need to take a 2-hour pause after eating, before an active walk with games and training.
Disease prevention
The most common cause of intestinal obstruction is improper feeding of dogs. Do not give your pet bones, food from the table, or flour products. Make sure your dog does not eat household items or garbage. Train your pet so that it takes food only from its owner and in a certain place.
Basic preventive measures:
- To avoid developing intestinal obstruction , monitor physical activity. Consult with your veterinarian which load will be most optimal for your pet, taking into account its weight and body characteristics;
- Don't forget about deworming . It should be carried out once every 3 months to prevent the development of helminthic infestations. Its implementation is mandatory, even if your pet does not go outside and does not come into contact with other animals;
- For training and playing with animals, use only special toys . Do not give your pet pebbles, sticks or foam objects under any circumstances. He may swallow them, which will cause intestinal obstruction;
- While walking, make sure that your dog does not try to swallow foreign objects. Be sure to use a leash. It is possible that even trained animals, sensing an attractive odor, swallow foreign objects.
What to do if your dog has a volvulus: treatment
If a volvulus occurs, the only way to save a dog is through surgery. When the first dangerous symptoms appear, the pet is urgently taken to the clinic.
Treatment of volvulus includes several stages:
- Administration of steroid hormones, antispasmodics, analgesics, antiemetics and anesthesia.
- Removing excess gases and reducing pressure on the abdominal cavity by puncturing the stomach through the peritoneum with a long surgical needle.
- Repositioning the stomach in the right direction and getting rid of stagnant food masses.
- Removal of dead areas, sometimes along with the spleen.
- Rinse the gastric cavity with saline solution.
- Sewing part of the stomach to the abdominal wall to prevent recurrent volvulus and applying sutures.
Over the next 5-7 days, the dog remains in the hospital under round-the-clock supervision of specialists. For the first 24 hours, the animal is shown a starvation diet with the introduction of nutrient solutions through droppers. During the postoperative period, the dog is prescribed antibiotics and gastroprotectors. After the stitches are removed, the animal is discharged home.
Rehabilitation after surgery
After surgery, careful monitoring of the pet's condition is necessary. A fasting diet is recommended for the first 24 hours. Make sure your pet has free access to clean and fresh water. Then broth and liquid porridge are gradually introduced into the diet. The main thing is to feed your pet in small portions.
In parallel, parenteral nutrition is used. Plasma substitutes and nutritional components in the form of solutions are administered intravenously to the dog. A course of antibiotics is prescribed, which must be given to the pet at the same time to prevent the development of a surgical infection. In addition, it is necessary to monitor the progress of recovery and undergo repeated ultrasound examination.
Other features of rehabilitation after surgery:
- 14 days after the operation, it is necessary to include fermented milk products (low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir) in the diet,
- gradually you need to introduce oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, as well as boiled vegetables, with the exception of potatoes and cabbage,
- it is important to ensure complete rest for the dog, even short walks on a leash are allowed no earlier than 7-10 days after the intervention,
- the duration of walks after receiving permission from the veterinarian must be increased gradually: from 5-10 minutes or more,
- Additionally, immunomodulators and mineral-vitamin complexes are prescribed to improve the pet’s condition after the intervention.
Dangers and mortality rate from volvulus
As a result of intestinal volvulus, the dog develops tissue necrosis. Moreover, necrosis affects not only the intestines and stomach, but also adjacent organs. All dead areas must be removed. And the speed of the animal’s recovery depends on the area of the lesion.
If the dog is treated within the first 1-1.5 hours from the moment the symptoms of volvulus begin to develop, then the probability of a tragic outcome is only 20%. If there is a delay in contacting the clinic and sepsis, the prognosis is unfavorable. In this case, the probability of death increases by 4.5 times.
Preventive measures
Volvulus in dogs is an uncommon and easily preventable pathology.
To prevent the development of the disease, it is enough to follow a few simple recommendations:
- Avoid stressful situations or use sedatives to relieve anxiety.
- Prevent the rapid absorption of food by pouring it into a bowl with protruding elements.
- Provide adequate nutrition with the correct ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates (50%, 10% and 40% respectively).
- Organize feeding in small portions and strictly after walks.
- Completely cure all diseases of the esophagus and intestines.
- Stop physical activity for 1.5-2 hours after eating.
On a note. If a dog is at risk due to its impressive size or has a history of chronic diseases of the digestive system, it is recommended to show it to a veterinarian every six months. Systematic examinations and tests will help reduce the risk of complications.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
Due to the rapid nature of the development of the disease, a specialist often does not have enough time for a full diagnosis. Surgical intervention is prescribed already with signs of intoxication and rapid heartbeat. For an accurate diagnosis, a gastric tube is used, the obstruction of which indicates intestinal volvulus. In addition, the animal’s abdominal cavity can be examined with x-rays to determine the type of pathology and the degree of its progression.
We advise you to find out the causes, symptoms and treatment of different types of ataxia in dogs.