When keeping dogs at home, various problems may arise related to the health of the animal and the management of natural needs. It is often believed that urinary incontinence in dogs is limited to older or seriously ill animals. But this is not always fair.
Very young animals also suffer from this disease. Owners need to know what to do if their dog is incontinent and be able to distinguish a true health problem from other situations.
Only a veterinarian with extensive experience knows exactly how to cure urinary incontinence in domestic dogs, so any amateur activity can only do harm. For adequate treatment, it is necessary to have an accurate diagnosis, and it can only be made in a modern veterinary clinic with appropriate high-tech equipment.
When can you talk about incontinence?
With incontinence, the dog has no fear or shame about urinating in inappropriate places. Wet spots appear not only on the floor, but also on her sleeping place. Because of this, excessive cleanliness develops. The animal constantly licks its genitals, trying to keep its bed dry.
Problems with involuntary urination can be constant or periodic. The amount of urine released is always individual. It depends not only on the characteristics of the pet itself, but also on the true cause of the disorder.
Depending on it, incontinence can be true or imaginary (forced). In the first case, it is explained by a real violation of the bladder sphincter, and in the second, it is a consequence of another pathology, physiological or behavioral characteristics.
Without timely assistance, a urinary burn may develop on the animal’s body. It is accompanied by redness and ulceration of the skin, as well as hair loss in the groin area. The resulting wounds are fraught with infection and inflammation of the bladder.
What to watch out for: Excessive water consumption
Excessive drinking is another common problem in dogs. As a result of this, their bladder is not able to withstand such a load, and urine begins to leak. There are more serious reasons that can explain this desire to drink:
- diabetes;
- infectious diseases;
- Cushing's disease;
- diabetes insipidus;
- renal failure.
The problem is easily detected in a laboratory setting. The specialist compares the “specific gravity” and the amount of biochemical substances in the urine with respect to clean water, which does not contain any. If the specific gravity is almost the same as the specific gravity of urine, then excessive fluid intake is confirmed. Next, a blood sample is taken to determine the disease that is causing the dog to be constantly thirsty.
Natural and harmless causes
Natural causes do not require serious medical or surgical intervention. In most cases, they go away on their own or are corrected with the help of training. These include:
- Sexual hunting
. Animals use scent marks to attract the opposite sex. This is a natural process that you just need to wait out.
- Polydipsia
. Increased thirst is a symptom of many diseases, but if it is explained by heat, everything is normal. In this case, it is enough to simply increase the frequency of walking.
- Lack of education
. If your pet is not accustomed to going outside due to his age, then this behavior is completely normal. Otherwise, the problem may be explained by resentment or other negative emotions. This behavior needs to be corrected.
- Excessive emotionality
. Small breed dogs often urinate with joy when they greet their owner returning from work.
- Weakening of the sphincter as a result of aging
. After 8 years, muscle tone decreases, weakening control over urine output. Despite its naturalness, you should not turn a blind eye to this problem. The animal's condition can be improved with the help of hormone therapy, avoiding lifelong use of diapers.
Regardless of the cause of incontinence, avoid punishment. They will not solve the existing problem, but will only aggravate the situation due to stress.
Main symptoms
If a dog in the house involuntarily urinates, it may be accompanied by:
- Joy. Dogs love to wag their tail, jump up, or spin around in one place. This mainly happens at the sight of the owner.
- Frightened. If a dog is afraid of something, it squats on its hind legs or rolls over on its back.
- Site label. Some male dogs mark their territory when they smell another dog or hear barking. This shows their self-confidence.
- A demonstration of superiority. Young males who have not undergone training can show their superiority over their owner in this way.
Pathological causes
If, in addition to urinary incontinence, your dog exhibits other alarming symptoms, be sure to take him for examination. This will help avoid complications in case of pathology.
Urinary tract infections
The most common infection is cystitis, which is inflammation of the bladder. The disease develops against the background of a sharp drop in immunity caused by hypothermia or an unbalanced diet.
The following symptoms will help you recognize inflammation:
- fever and lethargy;
- nausea and loss of appetite;
- abdominal tension;
- restless sleep with frequent turning over in an attempt to find a comfortable position;
- whining during urination;
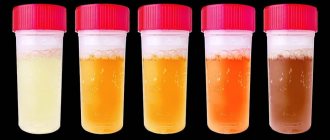
- cloudiness of urine due to mucus and pus, change in its smell, as well as scarlet coloring due to blood impurities.
The advanced stage of the disease is fraught with renal failure and peritonitis, so try not to delay the examination at the first alarming signs. The acute form can be successfully treated, excluding relapses.
Urolithiasis disease
Urolithiasis, or urolithiasis, is often confused with cystitis. Most of their symptoms are indeed similar, but there are also obvious differences. Blood in the urine appears much earlier, since stones in the urethra constantly injure the mucous membrane.
Increased salt deposition is typical for animals that consume too much protein. Due to blockage, urination may disappear completely. In this case, there is a risk of death due to bladder rupture.
Bladder sphincter problems
Weakening of the sphincter muscles is not only due to old age. Additional causes include chronic illness, excess weight, improper medication use, and ectopic ureter.
The latter pathology is included in the group of congenital defects. It involves an abnormal position of the ureter, opening directly into the urethra. With ectopia, urine does not collect in the reservoir and is immediately released out. Because of this, it comes out drop by drop on an ongoing basis.
Stress
Single or multiple uncontrolled urination can occur under severe stress associated with fear or other negative emotions. A similar reaction can be caused by traveling on public transport, moving, losing an owner, getting a haircut or visiting a veterinary clinic.
Additional symptoms of nervous tension include:
- drooling and slight trembling;
- gnawing or biting fur;
- excessive intrusiveness or unusual isolation;
- reluctant execution of commands;
- sleep disturbance;
- running in circles or fanatical digging;
- pica.
Prolonged stress has mental and physiological consequences. The animal may develop ulcerative lesions of the stomach and intestines - or heart pathologies.
Postoperative complication
If there is a surgical error or improper care during the rehabilitation period, an infection can get into the wound. This is fraught with inflammation of the urinary tract.
In addition to infection, uncontrolled urination after surgery can occur due to a lack of hormones responsible for the activity of the sphincter. Most often, castrated animals who are faced with global hormonal changes suffer from this problem. This outcome is individual and does not depend on the work of the surgeon.
Injuries
The process of urination is controlled by the brain, which transmits and receives signals through nerve impulses. Injuries to the spinal cord or spine can cause pinching or paralysis in the lumbar region. With such damage, it becomes impossible to perform usual functions.
Treatment
Inflammatory processes in the urinary system are treated with antibiotics. The course of treatment is long, about two weeks. Positive results can be observed within a few days, but even with such dynamics, therapy cannot be interrupted. The prescribed course must be completed to the end, otherwise relapses are possible.
In case of hormonal disorders or weakening of the sphincter, hormonal therapy is prescribed. There are options when hormonal medications are combined with antidepressants. All these drugs have side effects, so the possibility of treatment with such medications, doses and duration of use are prescribed by a qualified specialist in a veterinary clinic.
In case of spinal deformation and pinched nerve, you will have to resort to surgical intervention. It happens that the spinal cord, damaged in the event of an injury, cannot be restored, and urinary incontinence cannot be stopped. Surgery is also necessary when a congenital pathology is detected in the functioning of the urinary system.
If urinary incontinence occurs against the background of another disease, then additional diagnostics are carried out, a diagnosis is established and a set of measures is prescribed to treat the primary disease.
Diagnostics in a veterinary clinic
If you seek help in a timely manner, the prognosis for urinary incontinence in dogs is favorable. Treatment methods depend on the cause of the disorder, so the four-legged pet will have to undergo a full examination. Diagnosis may include the following studies:
- a general urine and blood test that monitors changes in baseline values;
- bacterial culture, which allows you to select an effective antibiotic to combat an infectious disease;
- vaginal smear to study microflora for bacteria and other pathogens;
- Ultrasound to determine the condition of internal organs;
- X-ray to reveal the presence of injuries.
If the occurrence of the disorder is explained by lack of education, non-pathological polydipsia or excessive emotionality, specific treatment is not applied. The listed situations can be eliminated by training and timely walking.
Treatment of urinary incontinence in dogs
Depending on the diagnosis, the four-legged patient is prescribed special medications or undergoes surgery. The existing diet and care are being reviewed in favor of medicinal feed and more thorough genital hygiene.
Drug therapy
If there is an infection, antibiotic therapy is used, and if stones are detected, a special diet is used to dissolve urinary stones by alkalizing or oxidizing the urine. The choice of dry food will depend on the type of formations found.
For age-related urinary incontinence in dogs, medications are prescribed that increase the tone of the smooth muscles of the sphincter. As an alternative, estrogen hormone therapy is used.
Nervous disorders are treated with sedatives. They stabilize the psycho-emotional state and help reduce anxiety in tense situations.
When is surgery indicated?
Surgery is used for congenital anomalies, postoperative complications, injuries and large formations in the bladder. Depending on the situation, the surgeon changes the position of the ureter, restores muscle tone with collagen injections, eliminates existing nerve compression, or removes stones.
The operation is also indicated for sexual hunting, but only when the animal is not of breeding value. Taking hormonal drugs to suppress instincts is possible, but not recommended. This treatment has many risks, so it is much safer to sign your pet up for castration.
Care and hygiene products
If your dog has urinary incontinence, it is necessary to avoid salt. It retains water, increasing pressure on the bladder. They also limit the amount of protein.
In addition to reviewing the diet, you should also take care of the maintenance of the animal. For the pet to recover, it is necessary to protect it from drafts to prevent secondary infection. Place the bed in a quiet and warm room, remembering to keep it clean.
Until the functionality of the sphincter is restored, you will have to use absorbent diapers or diapers. The animal must be washed regularly to prevent the development of a urinary burn. In addition to plain water, you can use alcohol-free sanitary napkins. They can be purchased at a veterinary pharmacy or pet store.
Why does your pet urinate frequently?
Frequent urination indicates that an inflammatory process is occurring in the urinary organs.
The dog experiences discomfort or pain when trying to empty its bladder, often sits down, but cannot squeeze out more than a few drops.
This condition may be the result of normal hypothermia, urethritis or cystitis. Also, frequent urination indicates the development of urolithiasis, which may be accompanied by the appearance of blood in the urine.
For adequate treatment it is necessary to have an accurate diagnosis