Oral health and oral hygiene are an extremely important part of your pet's daily life. Many oral diseases can worsen over time or, in some cases, lead to other pathologies. Observation and proper medical examination are necessary for the owner to detect the problem and begin prompt treatment. The moment we realize that something is wrong, it is vital that we seek veterinary medical attention as soon as possible. It should be remembered that only a veterinarian can diagnose the problem. It may also be referred to a veterinarian with dental experience...
In this HowMeow.ru article about My Dog Has Black Gums , we analyze the causes of this phenomenon, as well as possible treatment options that may be available.
Causes
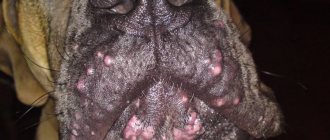
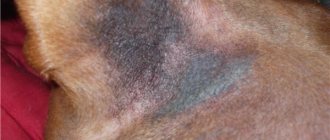
Firstly, it may be due to the color of the animal. Black wool also means black spots on the skin and even on the mucous membranes. So, pets with this color have a black sky immediately at birth, but it can also appear over time as they grow up. This is absolutely normal and is explained by the genetic characteristics of animals with this color. Owners who notice that their dog’s gums have turned black during adolescence should not worry - this is normal and does not cause any harm.
Secondly, the gums actually turn black due to disease. This may be a sign of tissue necrosis, which is very dangerous and indicates an advanced problem. Such changes cannot be reversed; you must contact a veterinary surgeon for surgery. Treatment will be quite long, including antibacterial therapy and restoration of the body's immune functions. It is also necessary to find out the reason why suppuration or tissue necrosis began; perhaps there are wounds on the gums or the help of a dentist with sore teeth is required.
Black gums are also called cases when, due to hemorrhage, the mucous membrane becomes dark burgundy in color. In this case, the gums are not only dark, but also swollen, they are probably inflamed and painful. The dog will not allow itself to be examined and will whine when you press on the darkened area. This is how the disease can be distinguished from simple details of color - by the animal’s reaction to touching a suspicious place.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used as additional ones. They allow you to quickly cope with the infection and stop the inflammatory process. The following methods can achieve good results:
- Fluctuarization. The inflamed tissues are exposed to low voltage current.
- Electrophoresis with lidase. Electrical current is applied to the tissue, allowing the drug to be effectively distributed.
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy. The method is based on the influence of an electromagnetic field.
- Ultrasound therapy. The effect of ultrasound on infected tissues accelerates their regeneration.
- Laser therapy. Damaged tooth tissue is treated with a laser beam.
How dangerous is this phenomenon?
We can say that when a dog’s gums turn black and he reacts restlessly to touch, this is a clear sign of illness or injury. In any case, the situation is dangerous and requires the mandatory intervention of a veterinarian. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to serious consequences:
- loss of teeth;
- blood poisoning;
- exhaustion (as it is painful for the animal to chew);
- spread of necrosis to adjacent tissues;
It should be understood that even a small scratch infected with an infection that the immune system could not overcome can be lethal for the animal. This is especially risky for decorative breeds that are susceptible to genetic diseases and have weakened protective functions of the body.
Dental problems in animals are not so easily solved. In certain cases, surgery at a veterinary clinic is required. Moreover, we can talk about ordinary cleaning, but it will be carried out in an operating room, because it is not so easy to “persuad” an animal to sit quietly with its mouth open for an hour or more.
Why does flux form?
Dental diseases are always the precursor to gumboil. Most often lead to suppuration:
- Untreated caries. If caries is not treated, the inflammatory process begins to spread to other tissues. Pulpitis and periodontitis gradually develop.
- Mechanical injury. Injury can lead to more than just crown destruction. Very often, an inflammatory process develops in injured tooth or gum tissues. Without treatment, purulent processes develop and gumboil forms.
- Periodontitis. In more than half of the cases, gumboil develops precisely against the background of periodontitis, as its complication. This is due to the fact that purulent processes from periodontal pockets can spread to the neck of the tooth.
- Poorly sealed canals. Before filling, the canals must be completely cleaned and the filling material must completely fill the cavity. If at least one of the conditions is violated, the infection from the canal spreads to other tissues.
Black gums on a dog photo
Rinse
They are used as an additional treatment in order to completely remove pus and ichor from an opened abscess and prevent the infection from spreading to healthy areas. Soda-salt baths and rinsing with antiseptic solutions help make treatment more effective and speed up gum healing. When rinsing, you must adhere to the following rules:
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
How not to miss a developing disease?
When examining your pet, be sure to wash and disinfect your hands. The dog should be calm, if it breaks out and is afraid, then you need to let it relax a little and take it to the veterinarian - with the help of a professional everything will work out faster. During a basic home examination, there are a number of signs to look for that are likely to indicate that dental or general health problems are present.
- An aggressive or restless reaction to examination that suggests the dog is in pain when touched.
- Refusal of food or only partial intake of it, when the animal just sits over the bowl for a long time.
- Traces of blood on the lips or in a bowl of water may also be on the gums or surrounding fur.
- A putrid odor from the mouth, which appears not only immediately after eating, but at any time.
- Lethargy, the pet’s desire to hide, but it can also be the other way around, when the dog is looking for attention and seems to be trying to put its muzzle into the owner’s hands in search of help.
- High temperature, which indicates the presence of infection in the body.
It is not necessary that all these signs will be present at the same time. They can appear either one at a time or in any sequence. The owner must use his or her own common sense in assessing whether the pet's behavior and condition have changed.
Having noticed that your dog’s gums have turned black, you need to examine them to determine whether there is pain when touched and pressed. If it is not there, then do not be nervous, because most likely this is only a manifestation of the color of the animal, determined genetically. But if you have a restless reaction to examination and refuse to eat, you should definitely go to the veterinarian. When a pet doesn't want to eat, this is one of the most dangerous signs. This is like giving up the fight for your health; here you need to react as quickly as possible.
General treatment
Methods depend on the reasons that caused the flux. The only exception is periostitis, which develops against the background of periodontitis. In this case, immediately after opening the abscess, the doctor begins periodontal treatment. No medical manipulations with the tooth are required. In other cases of dental disease you need to treat:
- Pulpitis. First, the dentist drills out carious cavities and performs pulp removal. After this, endodontic canal treatment is performed.
- Periodontitis. Treatment depends on whether depulpation and canal filling have been previously performed. If periodontitis has developed for the first time, the doctor will remove the pulp, clean and fill the canals. If filling of the canals has already been performed previously, they need to be unfilled and treated again. Since it is very important that the pus comes out of the flux completely, when treating complicated pulpitis and periodontitis, a temporary filling is not placed.
- Tooth after restoration. At the first stage, the doctor is faced with the task of completely removing inflammation. After this, the damaged tissue of the root apex is removed. If the condition of the root allows, the tooth is restored again using a core tab or pin and an artificial crown. When the damage is very severe, it is more advisable to remove the tooth.
Types of gingivitis
Gingivitis in dogs is classified according to the severity of symptoms, location of occurrence and form of manifestation. Depending on these factors, 6 types of pathology are distinguished.
Acute and chronic
The acute form is characterized by vivid symptoms and rapid deterioration of well-being, while the chronic form is characterized by a smoothed clinical picture, periodic improvements and relapses. The chronic form is more dangerous because it is difficult to diagnose early.
Localized and generalized
In the localized form, the inflammation manifests itself as a point, and in the generalized form the process covers all soft tissues. In the latter case, the treatment still affects the entire oral cavity.
Catarrhal (serous) and hypertrophic
The catarrhal form occurs due to the influence of external factors (trauma, bacteria and viruses, allergens), the hypertrophic form - due to the influence of internal factors (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system, hormonal disorders, blood diseases).
In the hypertrophic form, inflammation is localized on the canines, incisors and molars. Depending on the symptoms, it can be edematous or fibrous. In the second case, in addition to redness and swelling, ulcerations appear on the mucous membrane. The fibrous form is often found in older dogs, large breeds and collies.
Prevention of stomatitis in dogs should be aimed at compliance by dog owners with feeding and maintenance rules. You should not give dogs food that is too hot or too cold, as well as medications that have a strong irritant effect on the oral mucosa.
Prevention of secondary stomatitis of infectious etiology should be aimed at timely vaccination of the dog against these infectious diseases. For non-communicable diseases, it is necessary to prevent and promptly treat these diseases.
Breed standard
Professional dog breeders generally point out that a pigmented mouth is often a breed standard. For example, chow chows should have not even a dark, but a bluish-black palate. In Newfoundlands with a light mouth, this is considered a serious drawback and can become an obstacle to the participation of this dog in mating and further club breeding. But neither Chow Chows, nor, especially, Newfoundlands are aggressive dogs; on the contrary, their breed characteristics include agreeableness and love for people and children. And here the concept “black palate is a sign of innate anger” does not work at all. So it's just a myth?
The mechanism of caries occurrence
Dental caries in dogs is usually one of the signs of a general painful condition of the body. The trigger for the disease is the appearance of dental plaque, which contains a large number of pathogenic bacteria (mainly staphylococci). Plaque settles on the teeth, resulting in close contact between the microbial flora and enamel.
The chemical composition of saliva facilitates such contact. The minerals contained in saliva, interacting with dental plaque, increase its density. This formation is tightly fixed to the enamel and is called a dental plaque. The product of this interaction is lactic acid, which has a destructive effect on the enamel, demineralizing it.
The surface of the tooth suffers especially severely in the presence of microscopic damage to the enamel. In this case, its destruction occurs especially quickly.
Diagnostics
A completely correct diagnosis can only be made in a clinical setting. As mentioned above, gingivitis rarely occurs alone, and during diagnosis, all associated problems should not be missed. Only by seeing the full picture of the disease can you help your dog efficiently.
The diagnosis is made based on:
- General examination of the animal.
- Examination of the oral cavity . This point should be approached carefully. When a dog is conscious, especially when experiencing painful sensations, it will resist examining the mouth, and it is unlikely that it will be possible to fully examine all lesions in the oral cavity. Therefore, sometimes the doctor will only be able to see the full picture when the dog is under sedation.
- Special research methods - for example, use the Schiller-Pisarev test. Using a specially prepared iodine solution. The solution is applied to the gums and the color changes are monitored. Thus, the area of inflammation is determined.
- Sometimes an x-ray .