In this article I will talk about the main diseases in adult dogs and puppies. I will list diseases of various origins and the symptoms that accompany them. I’ll tell you what to do if you suspect your dog is unwell.
The animal body is as fragile as the human body. Susceptible to viral, bacterial, parasitic and fungal infections. The dog’s health is influenced by a genetic predisposition to certain disorders, environmental and psychological conditions. Aging of the body, injuries, and poor quality nutrition have a significant impact on the well-being of the pet.
The most common diseases of dogs
Dog diseases should never be left to chance.
The list of the most common diseases in dogs can range from infectious to genetic to those caused by parasites. The most common include:
- plague;
- ringworm;
- encephalitis;
- enteritis;
- damage by fleas and worms;
- cystitis;
- urolithiasis disease.
The most painful and deadly diseases
The most painful and fatal diseases of dogs include:
- rabies;
- plague;
- leptospirosis;
- piroplasmosis;
- parvovirus enteritis.
Today, veterinarians note the fact that cases of encounters with deadly diseases in dogs have become more frequent. Large breeds are easier to treat than decorative ones. The difficulty lies in the size. It is worth noting that some diseases develop rapidly and conquer the body, while others are completely incurable. But they are all very painful.
To avoid trouble, scientists have created vaccines, but some owners neglect vaccinations, considering them a waste of money.
Can you help your pet yourself?
No, self-help should be avoided. Many owners like to use traditional medicine and follow the advice of friends, but such treatment never gives the desired effect.
Most recipes presented on the Internet contain vodka and onions. Both products are toxic to four-legged pets and can cause death.
Herbs that look harmless are no less dangerous. They can provoke allergies and aggravate the general condition.
Despite the fact that sometimes the advice of friends really helps, it is important to understand that this is not a rule, but a survivor’s mistake. The recommended remedy will be effective if you randomly guess the disease, but it will definitely do harm if you are wrong. The latter option is observed more often, but is talked about less readily.
IMPORTANT!
Never give your pet medications from your home medicine cabinet. Most of them are toxic to pets, and the modest list of approved products requires mandatory dosage adjustment.
Taking medications is allowed only as prescribed by a veterinarian, since when giving a prescription, he takes into account the diagnosis and medical history of the patient. Taking into account the cause of the disease, the patient’s age and concomitant pathologies helps to select an effective and safe treatment regimen.
Diseases transmitted to humans from dogs
Many people keep pets. Dogs have been kept by humans for more than 14 centuries. Many studies confirm the fact that having pets has a beneficial effect on a person’s mental state. However, there are a number of infectious diseases that a dog owner may be susceptible to. The disease is transmitted even with minimal contact, through saliva, urine, and feces.
Diseases that can be transmitted to humans from dogs include:
- tuberculosis;
- rabies;
- leptospirosis;
- toxoplasmosis;
- helminth infections;
- chlamydia;
- lichen;
- acute echinococcosis.
If you find signs of disease in your dog, you must immediately contact a veterinarian to identify the disease and begin treatment. If the doctor confirms the presence of a disease that can be transmitted to humans, then it is necessary to take tests for everyone who came into contact with the animal.
Diagnostics: how to deliver an animal to the clinic and get tested
The method of transportation depends on the condition of the animal. If you witness a seizure, be sure to check with your veterinarian whether you can move the victim yourself.
The same applies to acute attacks of pain when the dog is unable to sit or stand. In such situations, it is recommended to arrange a veterinarian visit directly to your home.
If the existing symptoms do not affect the ability to move, then follow the basic rules. Bring basic equipment (leash and muzzle) and, if possible, place your pet in a carrier. The easiest way to get to the clinic is to walk, drive your own car or take a taxi.
To make a diagnosis, you will have to take a blood test - this is the most informative way. All other studies will be determined after a visual examination and medical history.
The most commonly used are ultrasound and x-ray. To prepare for the first, it is recommended not to go for a walk right before the appointment and not to limit the dog’s fluid intake. There is no need to prepare for an x-ray, but severe aggression and fear may require sedation.
“ ADVICE!
If you have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, take with you a jar of stool and a sample of vomit. They will make the diagnosis easier.
Diseases of dogs according to symptoms, their causes and course
If your pet still gets sick, then it is necessary to clearly determine what changes have occurred. Perhaps he refuses to eat or has a fever. Some diseases are characterized by disruption of the gastrointestinal tract or disruption of the mucous membrane. All dog diseases have certain symptoms and development patterns; if you clearly name the main symptoms, the doctor will prescribe the necessary tests and make the correct diagnosis.
Viral
This group of diseases is most common among quadrupeds. Viral diseases are characterized by 4 periods of disease development:
- incubation - entry of the virus into the blood;
- preclinical - rapid development with minimal symptoms;
- clinical - it is at this stage that the signs become obvious;
- The outcome of the disease is recovery or death.
Read Symptoms of Bordetella in dogs: 3 stages of treatment
Rabies is a dangerous, fatal disease that can also be transmitted to humans. In animals, this disease cannot be treated, but an infected person is given 40 injections. Infection occurs through saliva from the bite of a rabid animal. The virus enters the animal's brain through the cerebrospinal fluid.
The dog is experiencing a change in behavior. She becomes much more active, and the bite site causes discomfort (the dog scratches it vigorously, literally gnawing it out). Over time, activity gives way to aggression, which can even manifest itself towards the owner. Salivation increases and vomiting begins. At the peak of the disease, the dog suffers from convulsive seizures. Just before death, the dog is struck by paralysis.
Canine plague is another serious disease that has a high mortality rate even with timely treatment.
There are several types of the disease, but all are characterized by lethargy, apathy, elevated body temperature to 39.5 - 41 degrees and above, and lack of appetite.
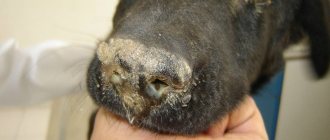
- Pulmonary - disruption of the mucous membrane, namely souring of the eyes, copious discharge from the nose.
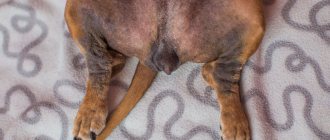
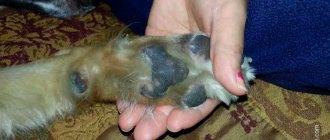
- Skin - the animal’s eyes become very watery, the nose can secrete mucus abundantly or, conversely, crack from lack of moisture, and the paw pads also crack.
- Intestinal - accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea, sometimes mixed with blood.
- Nervous is the most severe form. It is characterized by tics, paralysis of limbs or epileptic seizures.
Parvovirus enteritis is a dangerous viral disease that often ends in the death of the animal. The virus affects the gastrointestinal tract and heart. The body becomes severely dehydrated.
Infection occurs through contact with a sick animal, as well as through environmental objects, namely toys, the owner’s shoes, and his clothes.
The intestinal form involves the gastrointestinal tract. It is characterized by loss of appetite, diarrhea and vomiting of blood. With the right treatment, the animal can recover.
Cardiac is characterized by a decrease or absence of appetite. The animal is weakened, has a weak and uneven heartbeat, shortness of breath, and heart failure. Death occurs within a couple of days.
Piroplasmosis is a disease whose virus is transmitted through a tick bite. Characteristic condition: vomiting, fever, refusal to eat, lethargy, yellowness of the mucous membranes.
If you find a tick on your pet, then you need to strictly monitor the symptoms for a couple of weeks and visit a veterinarian at the first suspicion. Untimely treatment can lead to death.
Coccidiosis is a disease caused by protozoan microorganisms (coccids). The parasite can exist in the body of both animals and humans, settling in the intestines, liver and blood cells. Sources of the virus: feces of an infected animal, dirty bowls and even water.
The symptoms are similar to poisoning, dysbiosis or helminthic infestation. The disease causes indigestion in dogs, metabolic disorders, decreased immunity, stunted growth and development in puppies.
Skin
Skin diseases are diseases of non-infectious origin. The most common is Atopic dermatitis.
Atopy is a condition of the body that is characterized by the formation of antibodies to allergens.
Breeds most predisposed to the disease: terriers (Scottish, Fox), Labrador retriever, cocker spaniel, boxer, Dalmatian, German shepherd, English bulldog, Shar Pei, miniature schnauzers.
Symptoms:
- severe itching;
- hyperpigmentation;
- alopecia (baldness) of the paws, muzzle, belly, tail, ears due to scratching.
Infectious
Chlamydia is an infectious disease caused by chlamydia. This disease is very common among all living things. The infection infects the blood and with its current penetrates all organs, lymph nodes, joints and even the brain and spinal cord. This can result in death if treatment is not started. It is worth noting that this infection can be transmitted to humans, so it is important to temporarily reduce contact with a sick animal to a minimum.
Read 10 symptoms of allergies in dogs and effective ways to treat the disease
Symptoms include a slight increase in body temperature and damage to the mucous membranes. The lesion is characterized by the development of otitis, rhinitis, conjunctivitis and other diseases that manifest themselves on the mucous membranes. Appetite decreases.
Infectious hepatitis. In most dogs, this disease occurs latently.
The disease manifests itself quite rarely and usually occurs simultaneously with the plague.
In acute cases, mortality in puppies is almost 100%. In adult dogs it drops by 10-50%
Leptospirosis is a common disease that is quite dangerous for humans. Infection occurs through blood or urine.
Symptoms:
- vomit;
- dehydration;
- jaundice;
- visual impairment and photophobia.
Mortality in severe cases is about 30%.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Hip dysplasia is more often diagnosed in large breed dogs. The symptom is lameness of the hind limbs.
The disease affects the dog's firmness when standing. The center of gravity shifts forward, and accordingly the front legs begin to suffer.
The disease is classified as incurable. With conservative treatment or surgical intervention, doctors achieve significant relief of symptoms.
Oncology
Oncological diseases are quite common among animals. If a lump is detected, the veterinarian prescribes cytological and histological examinations. Surgical methods of treatment are used in treatment.
Very often, owners decide not to treat their dog, considering it a hopeless endeavor and a waste of money. But modern technologies, even in advanced cases, make it possible to achieve success, and if recovery is impossible, to improve the quality and prolong the life of the pet.
Eye diseases
If the dog begins to blink quickly and often without stopping, then this is the main sign of blepharospasm. It is also characterized by the following symptoms:
- the eye and the inflamed area around it may become swollen;
- palpation causes pain;
- photophobia;
The disease itself is not dangerous, but it can become a sign of other, more complex diseases.
Prolapse of the third eyelid. With this pathology, the dog's third eyelid moves from its usual place to the corner of the eye. Mostly only one eye is affected, but pathology of both eyes also occurs. Medicine has not determined the cause, but it is assumed that the disease is caused by muscle weakness.
This is also a non-life-threatening disease, but it can cause conjunctivitis and keratitis. The latter are characterized by souring of the eyes.
Ear diseases
Otitis is an inflammatory process that affects the mucous membrane of the external auditory canal. Otitis media is characterized by purulent and foul-smelling discharge. The disease is caused by ear mites, poor hygiene or infection (i.e. otitis media can become a sign of a more serious disease).
Ear hematoma - bruising. It is caused by a bruise or irritation. It mainly affects breeds with droopy ears.
The dog often shakes its head and scratches its ear. The owner may notice redness of the skin - these are the main signs of a hematoma. Treatment is symptomatic.
Diseases of the heart, blood vessels and blood
Cardiovascular disease in dogs is almost as common as in humans.
The cause of the development of pathology can be a previous serious illness, significant physical activity, heavy blood loss and injury, as well as congenital defects and diseases transmitted by inheritance.
Symptoms:
- lethargy;
- decreased appetite;
- disturbance of heart rhythms;
- dyspnea
- wheezing when breathing.
Animals also experience blood diseases, or to be more precise, anemia.
Symptoms:
- poor appetite and weight loss;
- pale mucous membranes;
- dark colored urine;
- rapid and uneven pulse.
Read Treatment of enteritis in dogs at home
Hemophilia - manifests itself with severe bleeding due to soft tissue injuries. Genetic disease transmitted from bitches.
Liver diseases
Older dogs are more susceptible to liver disease.
The liver is susceptible to acute diseases - leptospirosis or infectious hepatitis, but there are also chronic disorders of the organ.
Symptoms:
- loss of appetite
- unquenchable thirst
- vomit
- drowsiness
- diarrhea
- lethargy and apathy
REFERENCE! By the time the symptoms become obvious, half of the liver will have failed, so the prognosis for such diseases is disappointing.
Respiratory tract
The respiratory system is the nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. Respiratory diseases are the most common.
These include the following diseases:
- rhinitis - difficulty breathing, mucus from the nose, swelling and redness;
- laryngitis - cough, shortness of breath, wheezing in the chest;
- bronchitis - cough, hoarse breathing, nasal discharge, rapid pulse, fever;
- pleurisy - lethargy, weakness, weak cough, fever;
- emphysema - difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, cough, cloudy nasal discharge.
Some diseases pose a serious threat to life, others are less dangerous. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis.
Invasive
This group of diseases is also very common. They are transmitted through contact with an infected animal.
Helminthiasis is a lesion caused by parasitic worms (nematodes or cestodes) that settle in the gastrointestinal tract, affecting the liver and heart. The disease can be fatal to the animal if not treated.
Symptoms:
- lethargy and decreased activity;
- aggression; vomiting and diarrhea, followed by constipation;
- Worms may be visible in the feces.
Endocrine
Diabetes. This disease most often affects dogs over 5 years of age who are obese. This is an incurable disease that can be controlled.
It is difficult to determine the disease only by symptoms. They are of a general nature:
- apathy;
- refusal of food;
- diarrhea;
- vomit;
- weakness;
- emaciation.
Only a veterinarian can make a diagnosis based on the research performed.
Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases are a group of diseases characterized by disruption of the immune system.
This condition can be caused by a previous tumor disease, a virus, a bacteria, taking certain medications, or a genetic predisposition.
This group of diseases includes:
- autoimmune hemolytic anemia (fever, shortness of breath, gums become pale pink, urine is dark, sometimes you can see blood in the stool);
- Systemic lupus erythematosus. The main characteristic for determining the disease is nosebleeds;
- Pemphigus vulgaris is characterized by rashes in the form of blisters and the formation of extensive erosions;
- Rheumatoid polyarthritis (limited movement, swelling, tension, pain when moving).
Genetic diseases in dogs
This is the largest group of diseases. Most often, dogs with genetic diseases are not allowed to breed,
This group includes maxillofacial defects, brain abnormalities, sensory organ disorders, diseases of the cardiovascular system, diseases of the spine and musculoskeletal system, genitourinary organs and gastrointestinal tract, diseases of the hematopoietic organs.
What to do first
If you notice the first signs of illness in your pet, do not panic and try to provide him with peace. To do this you will need:
- Isolate a potentially sick animal in a separate room or special pen. Children and overly active pets can accidentally hurt the dog, so their interaction will have to be temporarily excluded. This measure will also help prevent the spread of infection.
- Curtain the windows and remove noise sources. During illness, bright lights and loud noises are very irritating and can lead to serious sleep disturbances.
- Provide a comfortable temperature. Banal hypothermia and mild food poisoning cannot be ruled out. In both cases, chills may occur, so make sure there are no drafts.
- Arrange a fasting day. If there is no appetite at all, do not insist on feeding, but watch the amount of fluid you drink. Dehydration can worsen the patient's condition.
- Reduce your usual walking time. Physical activity takes a lot of energy, so leave going outside only to relieve yourself. Small dogs that are litter trained can simply be left at home.
ADVICE:
Use a regular blanket to keep your pet warm. Heating pads and heating devices are contraindicated for internal bleeding and inflammation.
If all of the above does not help, contact your veterinarian. Do not try to relieve existing symptoms on your own. This will blur the clinical picture and complicate the diagnosis.
Taking medications before an examination is only possible if the chronic disease is exacerbating, when you already have a list of effective and safe medications approved by your doctor.
Prevention of diseases in dogs
Vaccination is the main preventive measure. This method can protect the pet and owner from most contagious and deadly diseases.
Veterinarians also recommend periodic deworming and treatment for parasites, namely fleas and ticks.
ATTENTION! The dog must follow a strict but balanced diet.
Any dog illness is difficult to bear not only for the pet, but also for the owner. Anxiety and excitement accompany the owner until recovery. If any suspicious condition is detected in a dog, it is better to contact a veterinarian to prescribe timely and correct treatment. Modern medicine makes it possible, if not to cure, then to alleviate even the most complex diseases.
Canine flu
In 2005, canine influenza was detected on our territory. Doctors say that even a vaccine cannot completely protect a dog from the disease. Therefore, during an epidemic, it is not recommended to walk with pets in places where stray animals accumulate.
You need to take care of your four-legged friends, and in cold, dank weather you can even put a blanket on them. Signs of the flu include a severe cough and nasal discharge. Among the complications after influenza, pneumonia should be especially noted.
All infectious diseases of dogs must be diagnosed promptly and treated promptly. Only then will there be no unpleasant consequences for the pet’s health.