Another common type of ectoparasite (external) is ticks in dogs. When people talk about ticks and how dangerous it is in the warm season, they mean one of the types of skin parasites – ixodid ticks (Ixodidae). In fact, several species of these arthropods parasitize dogs. Some of them gnaw the skin of animals, others suck blood, and for others, the lymph and skin secretions of your pet are a source of food. As a result of the activity of ticks, the animal may develop a severe allergic reaction, viral and bacterial diseases, as well as abscesses and dermatitis.
Where can a dog catch a tick?
The danger of infection with ixodid ticks appears in the warm season. Ticks become active in early spring and go into hibernation only in late autumn, when the first frosts occur. The most dangerous time is the end of May and the beginning of June. These carnivorous arthropods have special thermal sensors with which hungry parasites find prey.
Ticks sit on tall grass or bushes, waiting for prey. As soon as a dog passes by, the little parasite makes a jump, grabs the animal’s fur with its tenacious tentacles and begins to look for a place free of hair. When such a place is found, and this could be the groin area, parotid area, legs, stomach or neck, the tick pierces the skin and begins to suck blood.
Infection with other types of ticks occurs mainly through care items contaminated with parasite eggs: beds, bedding, dog toys. The second method of infection is contact.
When to take your dog or cat to the vet
If you did not do this immediately after the bite, then carefully monitor the animal’s well-being for at least three weeks. Signs of infection do not always appear immediately. Sometimes this happens after 7–21 days.
The first symptom of Preventing ticks on your pets is loss of appetite.
Here are a few more common signs of Tick-Borne Diseases in Dogs, in which you need to urgently rush to the clinic:
- weight loss;
- change in gum color;
- discharge from the eyes or nose;
- vomit;
- back or neck very sensitive to touch;
- convulsions;
- diarrhea;
- uncontrolled urination;
- brick-colored urine;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- swelling of the limbs or joints;
- weakness.
Types of ticks
So, there are three types of ticks that parasitize dogs:
- Ixodes. The largest tick that feeds on the blood of animals.
- Subcutaneous mite (demodectic mite). It feeds on epithelial cells and blood.
- Scabies (internal, ear). Feeds on epidermal tissues.
Ixodid ticks
Parasites wait for their victims on the street: in the forest, on a dog-walking area, in the country, in public gardens and parks. Despite the painful symptom, ixodid tick bites themselves do not pose any particular danger. Much more dangerous than the diseases that a tick can infect a dog with.
Attached ixodid ticks are revealed by visual inspection of the animal's body - these are small brown bubbles with legs. If your dog's fur is very thick, you may not notice parasites right away. The situation is complicated by the fact that the tick can suck blood and fall off unnoticed.
Symptoms of a tick bite in a dog:
- weakness, the animal is lethargic, constantly lying down;
- thready pulse;
- loss of appetite;
- the whites of the eyes acquire a jaundiced tint;
- urine darkens: brown, brown;
- vomiting with bloody mucus;
- hyperthermia (40°-42°C);
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath;
- swelling;
- lameness.
Dangerous diseases caused by tick bites
- Piroplasmosis (canine encephalitis). The encephalitis tick poses the greatest danger to young purebred animals. Without timely, properly selected treatment, the mortality rate from this disease can reach 100%.
- Lyme disease (borreliosis). A widespread disease with a long incubation period - up to 2 months. Detected by a laboratory blood test. Treatable if detected early.
- Ehrlichiosis. The incubation period is 7-20 days. The disease is common in tropical and subtropical regions. In progressive cases, death is possible.
Sometimes, after removing the tick, a reddened lump remains on the dog’s body. This is not a symptom of a dangerous disease, it is the result of an allergic reaction to chemicals in the bloodsucker's saliva. All you need to do is lubricate the seal with brilliant green and prevent the dog from scratching this area.
Dog lovers should know what to do if their dog is bitten by a tick. First, you need to properly remove the attached parasite at home or in a veterinary clinic. Secondly, submit the removed insect for analysis. Third, take the dog to a veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment.
Subcutaneous mites
The peculiarity of this type of parasite is that they live in the internal organs, hair follicles and sebaceous glands of any dog. If an animal has excellent health and strong immunity, its body independently controls the number of uninvited guests. But as soon as the animal’s body weakens and the immune system fails, the tick begins to multiply uncontrollably - this leads to the development of a disease such as demodicosis. Popularly, this pathology is often called red scabies or scabies.
The first signs of the disease:
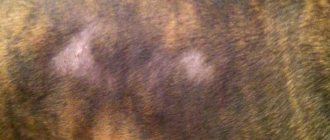
- bald patches appear on the animal’s body;
- the skin in areas of bald patches becomes rough, peels, becomes covered with scales and thickens;
- pink or red rashes appear in areas without fur, sometimes with purulent contents;
- the dog experiences severe itching, constantly scratches, injuring itself;
- the hair changes its structure, becomes dull, brittle, and shaggy;
- in long-haired breeds, shortening of the guard hairs is possible;
- Dandruff may appear.
The main forms of demodicosis:
- Focal (localized). Dogs up to one year of age are susceptible. It is characterized by the appearance of several bald patches with rough, flaky skin. In the vast majority it goes away on its own. Only 10% of cases become generalized.
- Generalized. Bald patches gradually spread throughout the dog's body. Inflammation develops and the skin develops an unpleasant odor. Older individuals have a less favorable prognosis for full recovery.
- Juvenile. Hereditary disease. Puppies up to one year of age are susceptible. Favorable prognosis for cure.
- Pododemodicosis. A disease with a lesion on the paws. The weak point of cocker spaniels. Bald patches, boils, purulent inflammation, and erythema appear on all limbs.
- Otodemodecosis. Inflammation of the outer ear. Bald patches appear around the ear. Black crusts form in the ears. The dog is experiencing severe itching.
Regardless of its form, ironworm is considered a non-contagious disease. The main reason for the appearance of bald patches, itching and painful areas of the skin is weak immunity. To reduce the risk of this pathology, the dog owner must take care of improving the health of his pet.
Scabies mites
This group of parasites includes two types of mites: scabies (internal) and ear mites (cutaneous). These are microscopic arthropods that resemble crabs in appearance. Once on the dog's skin, the parasites begin to multiply very quickly. Tick colonies in advanced cases can number up to several thousand individuals.
Signs of scabies mite infestation:
- the dog experiences severe itching, because of this it constantly itches, shakes its head, scratches itself;
- Scabs appear in places where scratching occurs;
- Foci of redness and blisters with cloudy liquid appear on the ears, eyebrows, bridge of the nose, at the root of the tail, on the stomach, in the chest area and on the head;
- the skin in places of irritation becomes rough;
- the dog's hair changes its structure: it becomes dull, coarser, and a shaggy effect appears;
- in places of pathological foci, hair falls out intensively;
- dermatitis develops;
- the skin becomes rough, cracks, and an “elephantiasis” effect appears;
- large dandruff appears - particles of dead epidermis;
- the animal is worried, sleeps poorly;
- The dog loses its appetite and becomes exhausted.
The main question that worries dog owners is whether a dog can die from infection with scabies mites. The answer is disappointing - maybe, if treatment is not started in time. The death of the animal occurs from general exhaustion of the body.
Diseases caused by the scabies mite:
- Sarcoptic mange. Caused by itching of the genus Sarcoptes. Locations affected: head, abdominal area, root of the tail, sternum area.
- Notoedrosis. Invasive disease. The causative agent is the Notoedres mite. Location: dog’s head: forehead, brow ridges, nose. In advanced cases, it can spread to the limbs.
- Otodectosis. Ear scabies is a contagious disease. The causative agent is the small white tick Otodectes cynotis. Parasites are localized in the ear. The skin of the shells turns red, ulcerates, and becomes covered with dark crusts. It is characterized by severe itching. Without treatment, it can spread to the head and entire body. The danger of the disease is that inflammation can spread to the inner and middle ear, meninges. This provokes nervous attacks and can cause the death of the dog.
The clinical picture of scabies resembles other diseases: dermatitis, demodicosis, eczema of the auricle. Therefore, a final diagnosis can only be made within a veterinary clinic based on the results of laboratory tests.
Diseases and symptoms
As already noted, a tick bite can cause serious diseases, the most dangerous of which are:
Piroplasmosis or babesiosis
The most common disease, dangerous for dogs of all breeds and ages. The incubation period is up to two weeks. Symptoms:
- lethargy;
- temperature increase ;
- refusal to eat;
- thirst;
- mild jaundice - the mucous membranes become pale, with a yellowish tint;
- at the peak of the disease, the urine becomes dark, sometimes with a red tint;
- diarrhea, yellowish or greenish stool color;
- vomit .
Borreliosis or Lyme Disease
An infectious disease that can affect all systems of the body, because of this, the symptoms in each individual case are very different. The appearance of any symptoms may begin several months after infection!
Ehrlichiosis
An infection that affects several body systems at the same time. The incubation period ranges from several weeks to several years. This disease knows how to wait. First warning signs:
- poor appetite;
- elevated temperature;
- depressed state;
- reluctance to play;
- sudden weight loss;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- bruising on the mucous membranes and skin.
None of these diseases can be waited out or cured at home; at the first suspicion, immediately contact a veterinarian!
How to remove a tick from a dog
A tick removed in a timely manner is a chance that the animal did not have time to become infected with anything. All parasites found on the dog's body must be removed. This must be done by adhering to the following rules:
- If a tick has attached itself to your pet, forget about the common advice - do not use vegetable oil or gasoline to pre-treat the insect. This will kill the bloodsucker, but at the moment of death he will release the contents of his stomach into the dog’s blood - dangerous infections will occur.
- All you need to remove is tweezers and rubbing alcohol. The body of the parasite and the place where it has attached itself to the skin are moistened with alcohol or its analogue.
- When the alcohol takes effect and the dog’s tick slightly relaxes its proboscis, begin to remove it.
- The parasite is grabbed with tweezers and slowly and carefully twisted counterclockwise. The tweezers should be held parallel to the skin or at a slight angle so as not to damage the bloodsucker's body.
- If the head of the tick remains inside the dog's skin, it is necessary to immediately show the animal to a veterinarian.
After removing the insect, it is submitted for analysis, and the pet is closely monitored in order to notice in time changes in the dog’s behavior after the bite and a possible deterioration in its condition.
Important! Remember that many dangerous diseases transmitted through parasite saliva have a long incubation period.
Read also
Subcutaneous mites in dogs: treating demodicosis
What disease can lead to serious consequences for a dog’s body or even death? The most common and dangerous disease is demodicosis.
Ear mites in dogs: Symptoms and treatment of otodectosis
Otodectosis or ear scabies is a chronic invasive disease caused by microscopic itch mites.
Dog castration: 5 reasons for and against
Castration is one of the most responsible ways to care for a dog. With the help of the procedure you will reduce aggression and anxiety associated with testosterone
What diseases are most common in dogs? Symptoms and signs
A dog cannot complain; it is necessary to determine that it is sick by the appearance and behavior of the pet
Fleas on a dog. How to withdraw?
Fleas can cause a lot of discomfort and suffering to your animals, but they must be removed very carefully
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures begin with collecting anamnesis and differ depending on the type of ectoparasite. Ixodid ticks can be identified by visually inspecting the animal's body after each trip outside. The found parasite is carefully removed and sent for analysis to a veterinary clinic. Blood is taken from the dog to make a diagnosis.
If the bloodsucker is not found, monitoring the condition and behavior of the dog helps in making a diagnosis. When the first symptoms of the suspected disease appear, an urgent visit to the veterinarian is necessary for laboratory tests.
The clinical manifestations of infection with subcutaneous and scabies mites are very similar, so the diagnosis is made only after laboratory tests of superficial and deep skin scrapings. Scrapings are made in a medical facility using sterile sharp cutting objects in places where the pathology is localized. After this, microscopic examinations are carried out to identify parasites, their larvae and eggs. Depending on the type of mites detected, further treatment is prescribed.
Why are they dangerous?
Ixodid ticks carry diseases such as:
- tularemia;
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- borreliosis (Lyme disease);
- anaplasmosis;
- babesiosis (pyroplasmosis);
- typhus;
- relapsing fever and others;
From this entire list, dogs can become infected through a tick bite with babesiosis (pyroplasmosis), anaplasmosis and borreliosis (Lyme disease). Tick-borne encephalitis in dogs is a myth; dogs do not get sick from this dangerous disease for humans.
Anti-tick medications for dogs
Since dogs are susceptible to infection by three types of ticks, veterinary medicine uses targeted drugs that are active against one type of parasite. In addition, the pet industry produces products to prevent infection.
Medications are available in several forms:
- ointments;
- aqueous emulsions;
- liniments;
- pills;
- oil solutions;
- drops;
- injections;
- shampoos;
- aerosols and aerosol foams.
Preventive measures:
- tick collar;
- drops on the withers;
- anti-tick spray.
Effective treatments for ticks
In modern veterinary medicine, to get rid of tick-borne infestations, the following are used:
- Sulfur-tar ointment (AVZ). An effective domestic cure for scabies.
- Dectomax (USA). Injection for the treatment of demodicosis (subcutaneous mite).
- Delcid (AVZ). Therapeutic and prophylactic emulsion against tick infestation.
- Bravecto (MSD Animal Health). Anti-tick tablets.
- Vio (Beaphar). Drops on the withers against fleas and ticks.
- Lawyer (Bayer). Drops against scabies mites.
- Tropiclean "Maximum protection". Anti-tick shampoo.
- Stronghold. The best drops against ear and scabies mites.
- Yam BK (AVZ). Ointment against scabies and dermatitis.
- Ivermek. Injectable drug against sarcoptic mites.
- Frontline (Merial). Tablets for killing ticks.
The following are used as protective and preventive agents:
- Bars (AVZ). Spray with insectoacaricidal effect.
- Foresto (Bayer). Anti-tick and flea collar.
- Mr Bruno. Spray against ixodid ticks.
- Rolf Club. Anti-parasite spray.
- Inspector. Therapeutic and prophylactic drops.
- Anti-mite. Ultrasonic repeller.
How to use medications correctly
We described how to properly remove ixodid ticks just above in this article. Let's talk about how to properly organize treatment for a dog in cases of infection with subcutaneous and scabies mites.
The first thing a dog owner should do after an accurate diagnosis has been established is to isolate the animal from other pets. After this, the sick animal must be thoroughly washed with tar soap. This is necessary in order to cleanse the dog's skin of scabs, dandruff, oil and dirt.
At the end of bathing, to enhance the effect and reduce itching, the animal is rinsed with decoctions of medicinal herbs: chamomile, string or celandine. After water procedures, the dog is thoroughly dried with a dry cloth and kept in a heated room until the fur is completely dry.
The fur in areas affected by ticks is shaved. Wounds and scratches on the skin are treated with antimicrobial ointments. To do this, you can use drugs from the owner's first aid kit: Vishnevsky ointment or Konkov suspension.
After this, the mite-infested areas of the skin are treated with medications prescribed by the veterinarian. The doctor selects an individual treatment regimen for each dog, taking into account its age, breed, health status and existing chronic diseases. It is unacceptable to treat a dog without an accurate diagnosis, selecting medications yourself. Rehabilitation of an animal after an ixodid tick bite should also be carried out under the supervision of a veterinarian .
What to do after deletion
Destroy small insects, preferably with open fire. Parasites in a tightly closed bottle can remain viable for months. Place a large, blood-fed parasite in a bottle so that, if necessary, you can send it to the laboratory to identify pathogens. Small settlements are deprived of equipment, specialists, and reagents for analysis. The cost of a comprehensive study using the PCR method is 1500-2000 rubles. Within 1-3 days you will receive the result.
Outbred dogs may be immune to piroplasms; the disease occurs in a chronic or asymptomatic form. Pedigree animals have a hard time withstanding the invasion. When the dog’s temperature rises to 41-42 degrees, loss of appetite, dark urine, seek veterinary help.
If a hunting dog is sick and has been cured, it cannot be used this season. The dog is prescribed medications according to the diagnosis. Piroplasmosis (babesiosis) is considered the most dangerous disease in dogs. To make a correct diagnosis, you need not a tick, but a drop of blood from the pet’s ear, more than 14 days after the bite. To monitor the effectiveness of treatment, the analysis is repeated after 2 months.
Folk remedies for ticks
Folk remedies have no proven effectiveness; they are used for mild forms of the disease and in the initial stages to alleviate the pet’s condition.
- Garlic. Garlic cloves are crushed and poured with almond oil (1:2). After this, they are placed in a dark place for 3-4 days. The resulting tincture is applied to the affected areas.
- Sulfuric ointment. Helps with scabies.
- Black sulfur. Used as part of kefir tincture (1:3).
- Lavender oil. Apply to the skin. When the oil is absorbed, rub the affected areas with chalk powder.
- Vanillin. Vanillin is infused in water or vodka, and the dog’s fur is treated with this solution before going outside.
You should not abuse any of these products - they act very aggressively on the dog’s skin: they cause burning, dry it out, provoke allergic reactions and other negative consequences.
As a preventive measure against ixodid tick bites, the following are used in folk medicine:
- Essential oils. The pet's fur is rubbed with oils: lavender or tea tree.
- Tar soap. Use it while bathing - it is an excellent therapeutic and prophylactic remedy.
- Sagebrush. Spray your dog with a water tincture of wormwood.
You can prepare a remedy for ticks at home from an aqueous solution of tar soap, myrrh, tea and rose tree, juniper and grapefruit oils. Fill a bottle with a spray bottle with the resulting mixture and spray your pet before a walk in the country or in the park.
Treatment
Treatment for bites is carried out in two directions:
Destruction of the causative agent of piroplasmosis
To destroy the causative agent of the disease, drugs from the group of organic dyes, diamidine derivatives, are used: Berenil, Azidine, Veriben, Batrizin . The active ingredient of these drugs is diminazene aceturate.
Imidocarb derivatives are also used: Piro-Stop, Forticarb, Imidosan.
The drugs are administered intramuscularly; a common property of the active substances is their high toxicity not only to the pathogen, but also to the patient. Since these drugs do not have a preventive effect, they are used only after a diagnosis has been established, under the supervision of a veterinarian!
Removing intoxication and maintaining the general condition of the animal’s body
To relieve intoxication and maintain the body, a large number of medications are used:
- Saline solutions (Ringer's solution, Sodium chloride, Glucose 5%)
- Vitamin complexes (Gamavit, Vitam, Ribotan, Butastim, Azoxyvet, Catozal, Vetozal)
- Heart medications (Sulphocamphocaine, Riboxin, Cordiamin, Camphor, Lauritin S)
- Inflammation-reducing agents (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone)
- Maintaining liver function (Essentiale forte, Legalon, Silibor, Karsil, Coverta
The volume and duration of treatment depends on the patient's condition. In any case, the recovery period lasts at least one month and requires follow-up tests.
Preventive actions
To protect your pet from tick infestation, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Do not allow sick animals to come into contact with healthy ones.
- Avoid walking your dog in areas where there are stray animals.
- Try to keep your pet away from other dogs when visiting the veterinarian.
- Use special collars, repellers and other means of protection against ticks.
- As prescribed by your veterinarian, carry out preventive treatment against parasites.
- Disinfect and boil care items for sick animals.
- Never use other people's collars, combs or muzzles.
- Strengthen your dog's immunity with balanced nutrition and vitamin supplementation.
Prevention against ixodid ticks consists of treating the animal with anti-tick compounds before a walk, wearing special collars and ultrasonic repellers, as well as a thorough examination of the animal returning from the street. Visual inspection is the most important component of prevention. It doesn’t matter at all how long a tick can sit on a dog, the important thing is that infection with dangerous diseases occurs within 30-60 minutes of sucking on this little bloodsucker. The sooner you remove the tick, the greater your pet's chance of survival.
Ways to protect your animal from parasites
The easiest way to protect your dog from ticks is to inspect his coat and skin after every walk. The peculiarity of insects is that for the first few hours they may not bite the animal, looking for a convenient place, so the chance of getting rid of it without loss is high. To detect a tick, run your hand against the dog's fur, carefully examine it, and feel it. If it has already “sucked in”, you will feel a small, convex ball to the touch. Examine the scalp, neck, ears, and abdomen especially carefully.
Anti-tick drops and sprays
There is no way to constantly examine the dog if the owner goes with it to nature or to the country. To prevent bites, veterinarians have created special preparations that repel arthropods and prevent the risk of infection from a bite. A few days before departure, it is recommended to treat the dog’s neck with Advantix drops - the product lasts for about a month, so it does not require frequent application.
There is no way to constantly examine the dog if the owner goes with it to nature or to the country. To prevent bites, veterinarians have created special preparations that repel arthropods and prevent the risk of infection from a bite. A few days before departure, it is recommended to treat the dog’s neck with Advantix drops - the product lasts for about a month, so it does not require frequent application.
Folk remedies
Experience shows that there are no effective folk remedies against ticks, because insects sense blood well, although there is a method that slightly reduces the risk of a bite. To do this, you need to wash the mammal with tar soap, and then rinse it with a decoction of wormwood. Another way to avoid bites is to sew a light summer jumpsuit and wear it for walks in parks, where there is tall grass and there is a high risk of catching a tick. In addition, your pet should not be allowed to interact with yard dogs.
Prices for anti-tick medications
Russia
- Sulfur-tar ointment (AVZ), 15 g., from 55 to 60 rubles;
- Dectomax, 50 ml, from 7500 to 7750 rubles;
- Deltsid, 5 ampoules of 2 ml, from 146 to 170 rubles;
- Bravecto, 250 mg, from 1410 to 1480 rubles;
- Vio (Beaphar), 3 pipettes of 1 ml, from 730 to 750 rubles;
- Advocate (Bayer), 3 pipettes of 2.5 ml, from 1390 to 1450 rubles;
- Tropiclean “Maximum Protection”, 592 ml, from 1000 to 1050 rubles;
- Stronghold, from 1200 to 1280 rubles;
- Foresto (Bayer), collar, from 1700 to 1800 rubles;
- Anti-mite, ultrasonic keychain, from 1400 to 1600 rubles;
- Mr.Bruno, 200 ml, from 350 to 400 rub.
Ukraine
- Dectomax, 50 ml, from 590 to 800 UAH;
- Deltsid, 5 ampoules of 2 ml, from 65 to 70 UAH;
- Bravecto, 250 mg, from 590 to 750 UAH;
- Advocate (Bayer), 3 pipettes of 2.5 ml, from 340 to 360 UAH;
- Stronghold, 3 pipettes of 0.25 ml, from 520 to 540 UAH;
- Foresto (Bayer), collar, from 600 to 800 UAH;
- Bars (AVZ), 4 pipettes, from 100 to 110 UAH;
- Rolf Club, 1 pipette 0.5 ml, from 80 to 85 UAH;
- Inspector. 1 ampoule, from 280 to 290 UAH.
What to do if the head remains in the dog
It is necessary to remove the tick from the dog's body entirely; leaving its head under the skin is unacceptable. Otherwise, the process of inflammation and suppuration will begin.
The tick's head looks like a small black dot, similar to a splinter. To extract it, use a thin needle. Before carrying out the procedure, the needle must be calcined and disinfected. To prevent the dog from resisting, it is better to numb the area of skin and calmly carry out the extraction. Then the wound site is wiped with a disinfectant solution.
If the parasite's head is deep in the wound, you should seek help from a veterinarian. He can pull it out by making a small cut.
Are ticks on dogs dangerous for humans?
We found out whether ticks are dangerous for dogs a little higher, now we will tell you about the danger dog ticks pose to humans and how to protect yourself from this danger. First, we need to clarify that dog scabies mites are not able to live on human skin, so it is impossible to get scabies from a dog. Secondly, demodicosis is a non-contagious disease; it is also not transmitted from dogs to humans.
Only ixodid ticks pose a real danger. A dog can bring them into the house on its fur, and they can attach themselves to a person. If it is an encephalitis tick, a person can become infected with a dangerous disease when removing the tick from a dog with bare hands. In addition to encephalitis, a person can become infected with the following diseases from dog ticks: borreliosis, tularemia, Marseilles fever.
To protect yourself, you need to carefully examine not only the dog, but also yourself after a walk in the fresh air, remove attached parasites from the dog’s body using rubber gloves, and use ultrasonic repellers and repellents.
Video: how to get a tick at home
In order to remove the tick accurately and not harm the dog, you should have a good understanding of the removal technique. The video below shows manual removal. The dog breeder does not recommend using oils, vodka or other liquids to block his access to oxygen. The owner of the dog, who uses a means at hand to remove the insect, notes that it is not worth pulling or pressing on the tick, otherwise it will stick even stronger. After removing the arthropod, the wound is treated with disinfectant iodine, and the ixodid tick is destroyed.
How to get a tick using improvised means