Piroplasmosis in dogs is a deadly disease caused by Babesia, which is transmitted by Ixodid ticks. Microbes enter the blood and destroy red blood cells, causing a deficiency of oxygen in the blood, which is actively involved in oxidative processes. Their waste products poison the body, causing vomiting and diarrhea. If the owner does not treat babesiosis in the dog, there is a high probability that the pet will die.
What is piroplasmosis in dogs
Babesia are the simplest of the genus of protists. They are able to mutate and adapt well, so in nature there are more than 100 forms of these parasites, each of which is dangerous only for a certain type of mammal.
A negative reaction in dogs is caused by protozoa, which belong to the species Babesia canis:
- Babesia canis canis is the largest variety, causes an acute reaction, and is severe.
- Babesia canis vogeli – the disease has a favorable prognosis.
- Babesia canis rossi – causes the most deaths.
- Babesia gibsoni is one of the smallest forms of Babesia.
The mechanism of development of the disease piroplasmosis in dogs
When a tick attaches itself to a pet, Babesia is activated. They migrate to the salivary glands of the tick and enter the bloodstream as part of the saliva. Babesia penetrate red blood cells and begin to reproduce asexually. When there are too many of them, they destroy red blood cells to become uninfected red cells.
The immune system reacts to this with an acute reaction:
- The amount of fibrinogen and C-reactive protein increases.
- The level of platelets and leukocytes decreases.
- Blood pressure decreases.
- Antibodies are formed that can destroy not only Babesia, but also healthy red blood cells.
Despite the active reaction, the immune system cannot completely eliminate piroplasmosis after a tick bite in a dog. Red blood cells are a reservoir of parasites, and when destroyed, they constantly splash a new portion into the blood.
How the disease spreads
A dog can catch the disease wherever there are ticks: in parks, on tall grass, in squares, in forests. Outbreaks of the disease may depend on the region, usually in spring - autumn, but in the southern regions cases of infection can occur even in winter. Animals of all ages are susceptible to piroplasmosis: small puppies, adults. At a young age, the risk is increased. According to veterinarian statistics, the disease affects purebred dogs and is much more severe. Animals over 4 years of age tolerate the disease more easily, but older animals often experience serious complications.
The duration of the incubation period may depend on several factors:
- age of the dog: young individuals are most susceptible to the problem;
- general health. Weak pets who have previously undergone surgery or other serious illnesses are at risk;
- duration of blood sucking. If the tick has been on the surface of the dog’s body for a long time, then the dosage of the infection increases;
- the actual number of parasites and piroplasms (infected) that entered the dog’s blood;
- state of immunity. If your dog has previously suffered from piroplasmosis, then he already has immunity.
It is important whether the animal has been vaccinated. Of course, vaccination does not provide a 100% guarantee, but it will help develop immunity, which will make it much easier to cure the disease.
How does babesiosis become infected?
Ticks can be called both the main and intermediate hosts of protozoa. They become infected from rats and other small rodents that are not susceptible to Babesia.
In the body of ticks, Babesia reproduce both sexually and asexually. They pass through the stage from larvae to imago, and are transmitted through eggs to the next generation of arthropods. Ticks, to which the infection is inherited, become completely infected. In particular, Babesia enter the salivary glands.
When a tick bites through an animal's skin, the protozoa enter the bloodstream with saliva. They immediately invade red blood cells and begin to multiply, destroying red cells. When red blood cells rupture, new parasites emerge and infect other blood cells. Therefore, ticks are not the only route of infection.
Infection can also occur:
- when receiving blood transfusion from a sick animal;
- from bitch to litter;
- with bites (for example, during a fight).
Can babesiosis be transmitted from dogs to other animals and humans?
Blood parasites are transmitted only through ticks. Another form of transmission is possible through blood transfusion of a sick animal. Babesia is not dangerous for humans, so pets are cared for without special protection.
If there are other dogs living at home, it is worth isolating the infected pet - but rather for its own good, to protect it from unnecessary fuss. It does not act as a source of disease for its relatives.
Acute form of piroplasmosis in dogs: symptoms and signs
The incubation period of piroplasmosis in dogs usually lasts from 5 to 7 days, less often it extends to 3 weeks. If you miss the signs of babesiosis in dogs after a tick bite, the pet will die in a few days due to breathing problems, anemia, and kidney failure.
Signs of piroplasmosis in dogs after a tick bite
With babesiosis, urine becomes the color of beer. A sick pet refuses to eat, apathy and increased fatigue appear. The temperature during dog piroplasmosis first rises to 40-41°C. Then it can drop to 37°C, before dying it can drop to 36-35°C.
Other symptoms of babesiosis in dogs at the acute stage:
- increased heart rate and breathing;
- vomiting blood;
- yellowing of the mucous membranes, sclera of the eyes;
- greenish or yellow stool.
Symptoms of liver and spleen damage
2-3 days after infection, anemia develops due to the breakdown of red blood cells. The urine becomes dark because it contains bilirubin, a toxic pigment produced by the breakdown of red blood cells in the spleen. Usually it is processed by the liver and sent into bile, in which it helps digest food. It then ends up in the stool and comes out, giving it a dark color.
With babesiosis, the liver cannot cope with the task, so bilirubin goes into the blood and poisons the body. The kidneys partially filter it out and remove it from the body in urine, which is colored by bilirubin the color of beer.
Thus, the liver and spleen are greatly affected by piroplasmosis. Ascites may develop - fluid retention in the abdominal cavity, which leads to the appearance of a belly.
Babesiosis in dogs: symptoms of platelet damage
Due to a deficiency of platelets, the blood vessels of the mucous membranes burst, and blood clotting is impaired. This leads to stomatitis, gastritis, and muscle inflammation.
Babesiosis in a dog: signs of brain damage
The disease often causes complications on the central nervous system. The following symptoms are possible:
- epileptic seizures;
- movement disorders;
- complete or partial paralysis – the dog has difficulty moving and cannot stand on its hind legs.
Symptoms
Between the bite of the parasite and the development of the dog’s disease, 2 to 20 days pass. The parasite is located in red blood cells, instantly destroying them. There are acute and chronic forms of piroplasmosis, each of which has different symptoms. In the acute form, the following symptoms are observed:
- pet's refusal to eat or drink water;
- the shade of the mucous membranes changes - jaundice appears;
- apathy;
- dyspnea;
- body temperature rises;
- there is no reaction to others;
- itching on the affected area of the body;
- urine changes color.
Sometimes after these symptoms a pseudo-recovery may occur, but then the temperature may drop to subnormal levels. This form most often ends in death. It is the acute form that manifests itself most clearly in animals that have become ill for the first time. Vomiting and diarrhea appear - sure signs of general intoxication of the body. It is important to prevent complete dehydration after vomiting. These signs can haunt the pet for a maximum of 2 days, then the condition will sharply worsen.
The chronic form occurs in those who have previously suffered from piroplasmosis. This also includes dogs with a high level of immunity. The symptoms are mild, Babesia are found inside the blood, but they are practically inactive. But if the dog was under severe stress, he underwent surgery, the parasites are activated - the acute phase will begin again. In this case, the symptoms are as follows:
- weakness;
- lethargy;
- diarrhea;
- exhaustion;
- temperature increase;
- lack of appetite.
The disease lasts from 3 to 6 weeks; after an effective course of treatment, recovery may not occur immediately, but after 2 to 3 months.
One of the early signs of piroplasmosis is rapid breathing. The fact is that blood cells are responsible for the delivery of oxygen to all internal organs and the removal of carbon dioxide. Since red blood cells die in unrealistic quantities, oxygen metabolism is disrupted. Thus, oxygen starvation and anemia develop, and in order to slightly increase the volume of oxygen in the lungs, the dog begins to breathe frequently. His pulse quickens, as a result - the load on the heart and blood vessels. The pet's behavior changes: the dog becomes lethargic, it is difficult for him to walk and he does not want to play at all.
Diagnosis of piroplasmosis (babesiosis) in dogs
The clinical symptoms of babesiosis can be confused with other dangerous diseases. Babesiosis often occurs simultaneously with leptospirosis and is combined with other dangerous diseases. A blood test for piroplasmosis in dogs will help to understand the nature of the disease. Based on this, the veterinarian will be able to prescribe the correct treatment regimen for babesiosis.
In the early stages of infection, pathogens may not be detected unless the infection has spread throughout the body. Traces of it appear in a capillary blood smear a week later. A more expensive test for babesiosis in dogs, PCR, detects traces of DNA 3-5 days after infection.
Testing for antibodies in the acute course of the disease does not make sense, since they have not yet formed in animals by this time. They can be used to determine the chronic course of the disease.
Since Babesia is not easy to detect in the blood at the initial stage, the doctor makes a diagnosis by analyzing the number of leukocytes, platelets, and young red blood cells. Before treating piroplasmosis in dogs, the doctor must exclude:
- anaplasmosis is another disease caused by ticks;
- immune hemolytic anemia;
- immune thrombocytopenia;
- urinary tract infection;
- poisoning.
Diagnostics
A veterinarian can only make a comprehensive diagnosis of piroplasmosis. The following factors are taken into account:
- the presence of all of the above symptoms: fever, jaundice, brown urine;
- a tick on the dog’s body or the owner’s assumptions about a bite;
- preventive measures: if before this there was a trip to a park, forest area, walk in public gardens;
- based on blood results and identified parasites in red blood cells.
To detect the presence of the parasite using laboratory methods, microscopy of a stained blood smear is used. To understand whether a dog is sick, a comprehensive examination is necessary.
Treatment of piroplasmosis in dogs
If a dog becomes ill with babesiosis, it should be taken to the doctor immediately. Babesiosis must be treated in a clinic - the pet may need IVs or blood transfusions at any time. Treatment of piroplasmosis at home is allowed if it is not possible to leave the pet in the hospital or if it is recovering. In this case, the doctor must personally monitor the animal and always be in touch.
To treat babesiosis in dogs, the doctor prescribes the following medications:
- Antiprotozoal drugs – Forticarb, Imochem-120. These drugs for piroplasmosis for dogs can be used not only for treatment, but also for prevention (only after consulting a doctor).
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (dexamethasone) - when treating babesiosis in dogs, drugs are prescribed to relieve swelling and reduce abnormal immune responses.
- Antibiotics (azithromycin, tetracycline).
- Giskan-5 - to normalize the functioning of the immune system, improve its resistance to disease. This drug can also be used if there is a suspicion that the pet has been in contact with an infected animal.
- Hepatoprotectors – strengthen the liver during illness and prevent complications.
- Heart medications – protect the heart.
- Blood transfusion - in severe cases.
Consequences of the disease
Consequences of treatment occur even with a successful course. This may be heart or kidney failure, damage to brain tissue, inflammatory processes in the liver. Very often complications arise during the illness. For example, a dog suffers from convulsive syndromes, which in 99% result in the death of the dog. In case of kidney failure, urine is not produced at all, so it is not possible to save the animal. To protect the kidneys as much as possible, blood purification (hemosorption) or plasmapheresis is used. In addition, dysfunction of the liver and pancreas occurs, and anemia develops. To prevent such consequences, it is important to start a course of therapy in a timely manner.
Possible consequences and complications of piroplasmosis in dogs
Babesiosis severely damages the liver, so the most common complication after treatment is chronic hepatitis. Provide your pet with high-quality nutrition that will not overload the liver.
Other complications after piroplasmosis in dogs:
- anemia;
- renal failure;
- problems with the heart, blood vessels (heart failure);
- cerebral ischemia;
- spleen diseases;
- pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas;
- partial paralysis of the hind limbs;
- nervousness, seizures and other problems related to the nervous system.
Treatment regimen
The treatment regimen for piroplasmosis in dogs is aimed at destroying the pathogen, relieving symptoms and normalizing the condition. In severe cases of the disease, accompanied by excessive loss of red blood cells, the dog is filtered or given a blood transfusion.
Destruction of the pathogen
To destroy piroplasms, special medications are used, for which it is very difficult to calculate the dosage. Many of them are highly toxic, so self-treatment is excluded.
All antiprotozoal drugs are available in the form of injection solutions. To give a dog an injection, it is taken to a veterinary clinic or a veterinary nurse is called to your home.
Before using antiprotozoal drugs, it is necessary to suppress the autoimmune reaction and relieve allergic symptoms. Glucocorticosteroids, which are also prescribed by the doctor, cope with this task.
Adjuvant therapy
In case of severe intoxication and dehydration, the four-legged patient is given drips with Ringer's solution, glucose and sodium chloride. They normalize urinary function, facilitating the outflow of urine and the removal of toxic substances.
To restore damaged organs, the following is prescribed:
- hepatoprotectors (Karsil, Silibor), which improve the condition of liver cells;
- immunomodulators (Gamavit, Ribotan), stimulating the functioning of immune cells;
- vitamins B and C, which restore the natural number of red blood cells;
- injection solutions (Cordiamine, Lauritin) that normalize the nutrition of the heart muscle and lungs.
Patients with liver and kidney failure undergo plasmapheresis - blood purification through a filter. This procedure allows you to remove settled toxins and prevent the development of complications.
Patient care
During treatment, the dog is limited in physical activity and prescribed a gentle diet. The duration of walks is reduced to 10 minutes, but their frequency is increased to 4-6 times a day.
Soon after taking the medication, the dog returns to normal activity. This improvement is deceptive. Therapy takes up to six months, so do not stop using the medications until you receive permission from your veterinarian.
Features of feeding
The recommended diet is aimed at reducing the load on affected organs and regenerating damaged tissues. Its principles include:
- Fractional meals
. Reduce the usual portions and increase the frequency of feedings to 5-6 times.
- Increasing the number of meat products
. The main task is to increase hemoglobin.
- Use of medicinal feed
. Animals that are not fed “naturally” are fed dry pellets soaked in water. A separate series of veterinary lines contains many nutrients and is lower in calories.
- Warming food to room temperature
. Do not serve food from the refrigerator or immediately after cooking.
- Grinding food
. Offer your pet liquid porridge and meat, ground with vegetables. Eliminate cabbage from your diet, which causes increased gas formation.
To restore the intestinal microflora, the doctor may recommend a course of antibiotics or stop using fermented milk products. If kidney damage is severe, protein foods are reduced or completely eliminated from the diet. To track the results and possible adjustments to the diet, you need to take tests monthly.
What to feed your pet with piroplasmosis
If your pet doesn't want to eat, don't force food in. To maintain strength, give your pet food often - take liquid (you can use lean broth) into a large syringe without a needle and squeeze it into the mouth. Don't give me milk!
The diet should be aimed at increasing hemoglobin, immunity, and vitality. If you still have an appetite, give pureed lean meat (turkey, beef, lamb), add a little vegetable oil. Check with your veterinarian whether you can give porridge (rice, buckwheat, wheat) with meat. If yes, cook the cereal and make a puree. If the dog refuses porridge, do not give it.
As an option, you can buy ready-made dietary food intended for animals with diseased kidneys and liver. The dry must be soaked until it becomes a paste, the canned food must be mixed with warm water. The food should not be cold.
Proper nutrition for a sick dog
The consequences of the disease can be incredibly dangerous, so it is important not only to treat the animal with medication, but also to choose the right menu for it. As a result of an incorrect diet, the dog may die: the kidneys, liver will fail, or an acute form of pancreatitis will develop. If the dog’s condition is very serious, the veterinarian will prescribe special drips, but force-feeding the pet is prohibited. Each portion, even a small one, will become a huge burden for the animal’s stomach.
If the dog has an appetite, it is allowed to feed it twice a day, in small portions. It is important to consult with an experienced doctor. The diet includes: buckwheat, lean meats, meat puree, butter. Dry food is mixed into porridge with boiled water.
What to feed a dog after piroplasmosis
After an illness, the dog is exhausted and weakened, so food should be given little by little. The diet should be developed by a veterinarian taking into account the pet’s condition. The basic feeding rules are:
- Portions should be small.
- Feeding is fractional - if before you fed your pet 2 times a day, now you need 4-5 times.
- Food should be warm, liquid, pureed. Cereals and boiled vegetables can be given in the form of puree.
- Grind lean meat (beef, lamb, turkey).
- Liver – contains iron (in limited quantities).
- Fish can be given only boiled, low-fat. If the disease causes complications on the kidneys, it is better to refuse it.
- If the dog is accustomed to industrial food, give the product for a diseased liver and kidneys.
- When your pet eats natural food, exclude fatty, carbohydrate foods, and chicken.
- Iron supplements, vitamins, and minerals should be added to food (the doctor will tell you the name).
Recovery after illness
Even after complete recovery from piroplasmosis, babesia can remain in the pet’s blood . It is necessary to do repeated blood tests (biochemical and general). This will help determine the subsequent recovery plan, depending on the area of organ damage, the presence of side symptoms of complications (heart failure, anemia, etc.). The further condition of the pet and the possibility of relapses will depend on the quality of the recovery program.
In addition to prescribing immunomodulatory drugs, cleansing the blood, restoring water balance, and normalizing organ function, it is important to follow a diet and exercise plan . The pet should not be too active, run and walk often. His diet should consist of easily digestible food, rice and buckwheat cereals, rabbit and lamb meat, low-fat kefir, and whey.
It is recommended to add boiled beef liver (to combat anemia), fresh beef (to increase the level of red blood cells).
Dioretic drugs prescribed to cleanse the blood of decay products and Babesia activity can lead to blockage of the renal tubules. Therefore, it is important to monitor your pet’s condition in the first few hours after the start of recovery.
Treatment can be completed after 6-8 months, but for each dog the duration of therapy and recovery complex will be different.
Prevention of piroplasmosis in dogs
Regularly treat your pet with anti-tick medications. If you live outside the city and often go into the forest, give preference to tablets. Even if a tick grabs a dog, it will die before it can drool into the blood.
Ticks attack pets in the warm season, especially in early spring, but there are cases when parasites were found in winter, at -12°C. Therefore, after every walk, inspect your dog for ticks.
If you find a tick on your pet, carefully remove it. For prevention, give an injection against piroplasmosis for dogs with the following drugs:
- Forticarb - the effect lasts for a month, it is recommended to inject if the possibility of infection is suspected. You can use the medicine in the treatment of piroplasmosis for dogs.
- “Nobivak-Piro” - vaccination is done in winter, when the risk of infection is minimal. Vaccination against piroplasmosis for dogs does not completely protect against the disease, but significantly alleviates its course. Nobivak-Piro is a prophylactic agent and cannot be used for treatment.
Remember that the infection is transmitted during fights. Keep an eye on your pet, do not allow it to fight or play with other people's dogs.
At the first symptoms of piroplasmosis (lethargy, apathy, vomiting, dark urine), take your pet to the veterinarian. Remember - timely treatment will save the life of your four-legged friend.
Prevention of babesiosis
Prevention of the disease consists of vaccination and antiparasitic treatment. After each walk during periods of increased tick activity, carefully examine your pet. Pay attention to hard-to-reach places: tail, ears, armpits, groin area and paws.
Vaccinations
Vaccination is carried out only on healthy animals. During pregnancy, lactation or recent illness, vaccinations are contraindicated.
The vaccine does not provide 100% protection, but it can weaken the course of the disease and prevent the development of complications. The immune response is formed after the second vaccination and lasts from six months to a year.
The disadvantage of this type of prevention is represented by its advantage. Weak symptoms in a vaccinated animal after infection interfere with the timely determination of the pathology. Anti-tick medications are used as additional protective measures.
Question answer:
Piroplasmosis in dogs: what to do?
At the first symptoms, consult a doctor and donate blood to be tested for piroplasmosis in your dog. If the dog is sick, adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen.
Can a pet cure babesiosis on its own?
No, if the pet is not provided with qualified medical care, the dog may die.
How does an animal become infected with babesiosis?
A dog becomes infected with piroplasmosis after a tick bite. The infection is also transmitted through blood transfusion, after a fight with infected dogs, from mother to puppies.
How long does it take for piroplasmosis to appear in dogs?
Signs of piroplasmosis in dogs after a tick bite may appear the very next day, but on average the incubation period lasts 5-7 days. Sometimes it lasts up to 3 weeks.
Will vaccination prevent piroplasmosis?
Vaccination against piroplasmosis protects the dog in 75% of cases. But vaccination is necessary: if the pet gets sick, the disease will be easier.
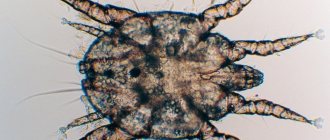
What ticks carry
Not all ticks are carriers of blood parasites.
Ticks can be roughly divided into scabies and ixodids. Scabies are dangerous by other diseases; they have nothing to do with piroplasmosis. “Our option,” in this case, is ixodid ticks.
Whether the ixodid tick is a carrier of this disease can only be determined by examining it in the laboratory. Therefore, it is better to consider all ticks as conditionally dangerous.
A few facts you need to know about ticks:
- Infected individuals pass Babesia to their offspring for many generations.
- Ticks do not jump on their victims and do not fall from trees. They climb up the grass, stretch their legs forward and, at the right moment, cling to a potential owner.
- The longer a tick feeds, the higher the risk of infection. But do not forget that in some cases, Babesia can penetrate the pet immediately from the moment of the bite.
- A hungry tick is brown in color, and when it drinks blood, it becomes light gray and acquires a steel tint.
Rehabilitation
Recovery from an infection takes a long time. When the sign of illness disappears, the animal will begin to feel well. The owner must remain attentive.
Measures to be taken:
- Reduce physical stress on your pet;
- Consider the dog's diet;
- Give vitamins and medications.
The goal of recovery is to eliminate the effects of the disease.
The duration of taking vitamins and medications is determined by the degree of infection.
Do not try to treat your dog yourself. Follow the directions given by your veterinarian.
Can be assigned:
- Antibiotics;
- Choleretic and diuretic drugs;
- Multivitamins;
- Medicines for the liver;
- Therapeutic diet.
During the rehabilitation process, the dog should be in a calm state and not get tired. Food during the recovery period should be healthy. Pet stores have therapeutic foods.
The duration of rehabilitation varies. Depends on:
- How dangerous the infection was;
- The age of the animal, its immunity;
- Breed;
- Treatment provided.
A case of relapse of the disease is possible. This happens when not all Babesia are eliminated by treatment. After recovery time, a visit to the veterinarian is necessary. The specialist will examine you and take another blood test to rule out a hidden symptom.
How to find out the truth
Another possible way for veterinarians to make dishonest money is to conceal the diagnosis. Let's say a veterinarian discovers a malignant tumor in a cat. But if he says that the tumor is benign and treatable. A housewife who dotes on her pet will give money for already useless procedures, medications and surgical interventions.
The veterinarian may deliberately “downplay” the diagnosis in order to earn more money. If something doesn't add up, insist on clarification. There is no need to be intimidated by unfamiliar terms - take a short break and try to find information on the Internet.
You are free to leave (or threaten to do so) to another clinic at any time.
Make sure that the veterinary clinic is honest - get tested in an independent laboratory.
Justice
What to do if an animal was injured as a result of unprofessional actions of a veterinarian:
- Write an official complaint addressed to the head of the clinic.
- File a complaint with the city veterinary department.
- You can contact Rospotrebnadzor.
- Contact a lawyer for help
The Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” and Article 245 of the Criminal Code “Cruelty to Animals” are the grounds for considering claims regarding the work of veterinary clinics.
Duration of the recovery period
The recovery period for a dog can last a varying number of days. It is influenced by the following factors:
- how seriously the vital organs of the animal were damaged;
- the age of the animal and general health (old dogs and puppies are in the 1st risk group);
- breed characteristics and genetic predispositions;
- timeliness and correctness of treatment.
At the end of the rehabilitation period, you should conduct a general examination of the dog by a doctor and pass the necessary tests. This is necessary in order to find out what condition your pet is in and whether there is a threat of exacerbation of the disease (in any of its manifestations).
Caring for a sick dog at home
Responsibility for the dog's recovery lies with the pet owner.
During treatment, you must strictly follow the medication schedule prescribed by your veterinarian.
Be sure to provide constant access to cool, purified drinking water. The more your pet drinks, the faster it will cleanse itself of toxins.
When feeding, you must adhere to the recommended diet. The prescribed medications have side effects on the liver and kidneys, so the diet during treatment should be low-fat, mostly carbohydrates.
Responsibility for the dog's recovery lies with the owner