Prostate diseases
In male dogs, an enlarged prostate gland causes constipation rather than difficulty urinating. Compression of the intestines makes the stool thin or ribbon-like. Due to abdominal pain, movements are constrained, the dog constantly presses his hind legs. But some prostate diseases can cause obstructed urine flow:
- hyperplasia (BPH) - a benign formation, a growing nodule or nodules;
- neoplasia – precancerous degeneration of gland cells;
- metaplasia – benign changes in tissue at the cellular level;
- abscess - a limited accumulation of pus;
- cysts - a pathological cavity, usually filled with fluid;
- prostatitis – inflammation of the prostate gland.
At risk are older, sedentary males who are overweight. In most cases, drug therapy involves hormones and provides temporary relief, so it is best not to delay surgery. Castration is indicated as a prevention of complications and relapses.
Obstruction of the urethra or bladder neck
An emergency condition in which urine cannot pass naturally. The causes of obstruction are stones, protein fractions, parasites, injuries, tumors. Rotting of the accumulated fluid leads to general intoxication, sepsis, kidney damage, and shock. Signs of urinary tract obstruction:
- the stomach is painful, full;
- frequent attempts to defecate;
- outflow in small portions drop by drop;
- impurities, turbidity, rotten smell of discharge;
- apathy, dehydration, intoxication.
A catheter is used to perform forced emptying and rinsing with an antibacterial solution. When this is not possible, the obstruction is removed surgically. A course of broad-spectrum antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs is required. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of obstruction and preventing recurrence.
Bladder rupture
Occurs due to excessive stretching of the walls due to prolonged stagnation of urine or trauma to the abdominal cavity - a fall from a height, an accident, a blow to the abdominal area.
Symptoms:
- there is an urge, but no urination;
- instead of urine, blood is released;
- the stomach is painful, tense;
- the dog walks on half-bent legs;
- due to bleeding, the mucous membranes are pale, temperature and pressure drop.
Even if we are talking about an incomplete rupture, this is a life-threatening condition. Possible sepsis, peritonitis, shock. Urgent surgical treatment is required - it is necessary to eliminate the consequences of the rupture and restore the integrity of the organ. A long-term gentle regime is required.
Bladder atony
Atony is a condition in which the walls of the bladder or skeletal muscles lose the ability to contract. This occurs due to diseases of the spine, spinal cord injuries, pathologies of the nervous system, and infections. The cause may be aging, inactivity, excessive stretching due to infrequent walking, adenoma or obstruction.
Symptoms:
- discharge is very scanty or absent at all;
- long pause before starting to urinate;
- weak stream or emptying drop by drop;
- protruding large belly;
- apathy, immobility;
With atony, incontinence also occurs, especially in large dogs. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of dysfunction and preventing relapses. In addition to drug therapy, it is imperative to increase the frequency of walks, diet and exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles - swimming helps a lot.
Anuria
A condition in which urine does not enter the bladder. Occurs with decreased cardiac function and severe kidney disease. The free flow may be obstructed by stones or compression of the urinary tract by a nearby tumor.
Symptoms:
- there are no urges or they are too rare;
- swelling throughout the body, often on the paws;
- depression, weakness, loss of appetite;
- thirst, nausea, vomiting after drinking;
- ascites - the abdomen is full of fluid.
Anuria is a life-threatening emergency condition. Products of protein metabolism accumulate in the blood, which can lead to uremic coma. It is important to quickly relieve intoxication, eliminate the cause of the disease or take control of it. The prognosis is cautious even with timely access to the clinic and a correct diagnosis.
Neoplasms
In most cases, we are talking about papillomas, polyps or a malignant tumor. If the neoplasm is localized in the organ cavity, there are no symptoms for a long time. But if the tumor prevents the outflow of urine, general signs of stagnation increase - abdominal pain, constrained movements, apathy, intoxication.
Neoplasms are more often diagnosed in older animals; their location is the cervix, ureter, urethra. Delay leads to atony, renal failure, wall rupture, and peritonitis. As a rule, surgical intervention is used to eliminate obstruction. The therapy is complex, aimed at eliminating the consequences of obstruction - antibiotics, antispasmodics, painkillers.
Diagnostics
When you arrive at the clinic or hospital, be prepared to tell the veterinarian any symptoms and behavioral changes you have seen in your dog who cannot pee. In most cases, the veterinarian will want to begin a full physical examination followed by a urine test, which may show infection or signs of inflammation. Blood tests including CBC and chemistry profile may be included.
© shutterstock
If the veterinarian has not diagnosed a simple infection or believes further investigation is necessary, a urethral catheter may be placed to rule out the possibility of a blockage. It is interesting to note that urethral obstruction is more common in male dogs due to the narrowing of the urethra on the penis.
Additional testing may include:
- Palpation of the abdomen - if the kidneys are full and the bladder is empty (anuria), this indicates a lack of urine output, which is the disease itself;
- CT to evaluate the caudal spine for tumors;
- Myelography (x-ray examination for damage to the spinal cord);
- Epidurography (X-ray test to check for spinal cysts);
- Abdominal ultrasound to check for kidney or bladder problems;
- Cystoscopy (insertion of a hose to examine inside the lower urinary tract).
Therapeutic techniques
Treatment depends on the identified cause of difficulty urinating. If your dog is experiencing unbearable pain (bladder or prostate stones), painkillers are used as first aid . The following methods can be used in treatment:
- For urinary tract antibiotics . They give only those drugs that are 90% or more excreted by the kidneys.
- In some (but not all!) cases, it is recommended to increase the amount of fluid your dog receives.
- Alkalinizing or acidifying drugs and nutritional supplements may be prescribed
- Bladder catheterization . It is done up to three times a day.
- If the inability to urinate is associated with damage to the spinal cord, the veterinarian or the owner himself will need to regularly massage the area where the bladder is located, stimulating the natural process of urination.
- In cases where urine does not pass due to urethral obstruction (adhesions, scars, etc.), surgical intervention will have to be resorted to.
- The same applies to any other congenital or acquired anatomical defects.
- If the cause is inflammation of the male dog's prostate and if the inflammation does not respond to treatment, castration is recommended.
Take your sick pet to the veterinarian as often as possible. The more regularly he conducts urine tests and examinations (ultrasound, x-ray, etc.), the greater the chance that the specialist will be able to notice the deterioration of the process in time and adjust the prescribed treatment. Do not forget that difficulty urinating in a dog often leads to the development of uremia and death of the pet.
What causes constipation?
Constipation can be caused by many reasons. Some of them can be easily eliminated, for example, by changing the dog's diet - adding more fiber to it. However, constipation can also be a sign of a more serious problem, such as a tumor in the colon or rectum or an intestinal obstruction. Veterinarians can usually identify the problem based on where in the digestive tract it occurs.
Along with nutrition, the AKC identifies other common problems related to constipation in dogs:
- Aging.
- Activity level.
- Tumors in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Other tumors.
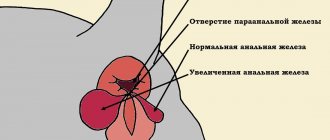
- Anal gland diseases.
- Prostate enlargement.
- Dehydration or electrolyte imbalance.
- Medications.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Diseases and injuries of the spine.
- Central nervous system disorders.
- Stress and psychological problems.
- Orthopedic diseases.
- Postoperative problems.
- Other disorders of the digestive tract, for example as a result of ingestion of foreign objects.
If your dog is constipated and it hasn't been long since his last bowel movement, there are some solutions you can try at home. For example, add wet dog food to your pet's diet. The high moisture content of this food can help move the intestinal contents forward. Exercising your dog more frequently can help, and you should also make sure he drinks enough water.
If constipation continues for more than a few days, consult your veterinarian to make sure it is not the result of a medical condition. Be sure to tell your veterinarian the last time your dog pooped, what the consistency of his stool was, what his diet was like, and any other signs of a problem. If you have an intestinal obstruction, a special procedure may be needed to clear the blockage.
Urination
What if the dog doesn't urinate?
The average healthy adult dog should urinate three to five times a day. A puppy or older dog may need to urinate more often.
A dog that doesn't pee is just as serious a problem as a dog that doesn't poop. This could be a sign of a health problem. If your dog truly cannot urinate, the inability of the bladder to remove toxins from the body can quickly become fatal.
The AKC notes typical causes of urinary problems:
- Infection.
- Bladder stones.
- Tumors.
- Kidney disease.
- Spinal damage.
It should also be noted that environmental stressors can also cause an animal to be unable to urinate. A dog that is uncomfortable in its surroundings—for example, due to the recent addition of another dog—may not urinate for a long time. This in itself is not a cause for concern. Just give her enough time and opportunity to go to the toilet, and she will eventually feel more comfortable.
Your dog and veterinarian are counting on you to spot the first signs of a health problem. That's why it's important to pay attention to any changes in your pet's typical behavior and toilet routine. While it may not always be convenient to watch your pet doing his business, it is often one of the most noticeable signs of a dog's overall health. So if you see changes in her behavior when she relieves herself or defecates, or changes in the consistency of her stool, take the time to contact your veterinarian to see if you need to come in for an evaluation.
How do huskies handle the heat?
Husky is considered one of the oldest dog breeds. The owners of the first huskies were the Chukchi and Eskimos. Today there are many legends and myths about these dogs, which do not always correspond to reality. And they are not always positive. Having heard another “rumor” about a husky, some even decide not to adopt this dog. But she has so many positive aspects.
Here are some of the main advantages of dogs of this breed:
- Husky loves all people, so will love all family members;
- Huskies never bite people; cases when these dogs attacked people are an exception (this happened when they tried to re-educate the dog or damaged its psyche);
- for lovers of active recreation and an active lifestyle, the husky will become the best friend and inquisitive partner;
- Huskies don't bark at all (but sometimes they howl);
- Huskies are very original and beautiful dogs, they combine wolfish grace and the famous blue eyes.
How do huskies cope with hot climates?
Many people are interested in the question of how huskies tolerate hot climates. After all, this is a northern breed of dog. So, another undoubted advantage is that huskies adapt perfectly to any climate.
If you live in a hot climate, you should purchase a husky puppy from a kennel located in a city with the same climate. These dogs have lived in kennels for more than one day, which means they have already adapted to the local climate.
If you do not have a nursery nearby, then it is necessary to create favorable acclimatization conditions for your pet. Evening walks, plenty of cool water and, if possible, a cool place are perfect for this. Within a week, your husky will adapt to the local climate.
By and large, you don’t have to worry about how huskies handle the heat, because these dogs are known to live in many hot regions, including African countries.
The husky's thick, two-layer coat protects it from direct sunlight. And thanks to it, the dog’s body temperature remains constant, both in cold and hot weather.
In the summer heat or in a too warm room, a dog may suddenly increase the amount of fluid it consumes to quench its thirst. Naturally, she will begin to ask to go outside more often to urinate. There is nothing surprising or dangerous about this.
It is equally normal for thirst to appear after eating specific salty foods, for example, if a dog ate a piece of salted fish or smoked sausage, as well as after increased physical exertion. Thirst also increases after castration, as well as during breastfeeding, especially with large numbers of puppies.
It's a completely different matter if the animal suddenly starts drinking too much water for no apparent reason. This may be one of the first signs of a developing disease, which is important not to miss. In this case, treating the dog will be much easier and faster, and cheaper too.
Water treatments
Since we've touched on the topic of dousing, let's talk about how to cool a dog in extreme heat. She doesn't have sweat glands, which is why she can't smell in the heat because she's sweating. The only place they are located is at the tip of the tongue. This is no coincidence, because the skin of our pets is covered with a special film that protects it from dermatitis. Frequently washing your dog with soap destroys this membrane and opens the way for infections. Therefore, you can wash your dog with various products very rarely. On the contrary, it is recommended to rinse with water as often as possible. In addition, you need to stock up on special products that are used when it is necessary to wash away heavy stains. Pet pharmacies have herbal shampoos that clean much more gently than those sold in household chemicals departments.
Urinary incontinence
Common symptoms are sudden uncontrollable urges, involuntary urination, and constant leakage of urine in small portions. There are small wet spots on the bedding after sleep, urine is released from sudden movements. If we are not talking about a congenital pathology, older, larger dogs are more likely to suffer from incontinence. Provoking factors are excess weight, low mobility, frequent childbirth. In chronic cases, the risk of urinary tract infections increases.
| CAUSE | SYMPTOMS | TREATMENT |
| Ectopia is a structural anomaly in which the ureter protrudes into the vagina (females) or urethra (males). | Leaks in the first days after birth. The puppy smells bad. The genitals are inflamed, licked by the bitch. | The ureter is surgically removed into the bladder. |
| Sphincteric insufficiency after sterilization. Large females that are spayed after puberty are susceptible. | Involuntary bowel movements, usually in the morning and at night. Sometimes the dog constantly leaks drop by drop. | Long-term hormonal therapy aimed at maintaining sphincter function. Surgical correction is possible. |
| Complicated course of infectious diseases of the genitourinary tract. | Due to decreased receptor sensitivity, it is impossible to control urges. Urine flows randomly, first drop by drop, then in larger portions. | Elimination of infection and the cause of the disease, strengthening the immune system. |
| Injury - blow to the stomach, fall from a height. The injury initially causes delay, but the long-term consequence may be incontinence. | Due to decreased innervation of the bladder and/or sphincter, the dog ceases to feel the urge and control the process. Partial or complete incontinence may occur. | Treatment is surgical coupled with long-term therapy. The forecast is cautious. |
| Problems with urethral closure - decreased sphincter function due to congenital pathology, infection, obesity, and age-related changes. | Urine flows out even at rest, in small portions. The dog constantly licks himself, smells unpleasant, and his genitals are inflamed. | Long-term therapy, often including hormonal drugs. |
Incontinence is usually not as dangerous as urinary retention, but it does cause a lot of inconvenience for owners. It is important to remember that you should not scold your pet - stress will only make the situation worse. To minimize the consequences, you need to use diapers, remove carpets during treatment and walk longer.
You should not try to reduce the amount of drinking water in your diet - concentrated urine more irritates the walls of the organ, which leads to increased urination. It is important to follow the prescribed diet, avoid hypothermia, and exclude sweets and dairy products.
Air conditioning – friend or foe?
Of course, the behavior of a dog in the heat evokes sympathy; I want to help my furry friend, who, desperately sticking out his tongue, is trying to hide in any secluded place. And many people think of turning on the air conditioner. Dogs, like children, who are often on the floor, are prone to pneumonia if a stream of cool air is directed at them. Therefore, adjust your split system so that the air flows in a diffuse flow, which is directed towards the curtains. In addition, do not set the temperature below +22 degrees. It is quite comfortable and your pet will not get sick.
Diagnosis of urinary problems in dogs
The dog does not urinate for two days, what should I do? To identify diseases in which a dog pees a little, you need to:
- Visit a veterinary clinic or call a doctor at home.
- Describe in detail the symptoms and changes in the animal's behavior.
- Take the necessary tests (blood, urine).
- It is possible to prescribe computed tomography, myelography, epidurography, cystoscopy or ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity.
Only a veterinarian can make an accurate and correct diagnosis. After undergoing tests and diagnostic procedures, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment strategy.
Important! The sooner the owner notices that the dog cannot pee normally and brings the animal for examination, the faster the pet will recover. Also, timely treatment reduces the risk of complications.
At the vet